- How to use TENS machines to relieve tendonitis pain?
- Best TENS units to treat nerve damage
- How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and avoid tendon damage?
- Best EMS machines to prevent tendon inflammation
- Video: How to place electrodes pads for tendonitis pain?
- More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
- What is tendonitis and what are the causes?
- What are the most common types of tendonitis?
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating tendon inflammation?
- Contraindications to the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
Tendonitis is one of the most common ailments that you can suffer, it is mainly associated with sports injuries. Although, in principle, it is not a serious injury, it is necessary to take certain measures both for the treatment and rehabilitation of the injury and for the symptoms it may cause, among which a feeling of acute pain in the affected area stands out.
One of the most popular treatments for tendonitis symptoms is electrotherapy, which uses electrical impulses to reduce the sensation of pain. In the following paragraphs, you will learn all you need to know about tendonitis, and how to use TENS and EMS electrotherapy devices to treat its symptoms.
How to use TENS machines to relieve tendonitis pain?
Tendonitis pain can be sudden or progressive, depending on the type of injury and the area in which it occurs, so it is necessary to have a thorough knowledge of the location of the vulnerable tendons in the joints, in addition to knowing how the devices work.
Fortunately, right now we will teach you everything you need to know in order to apply effective TENS therapy and treat the symptoms of tendonitis in any of its presentations.
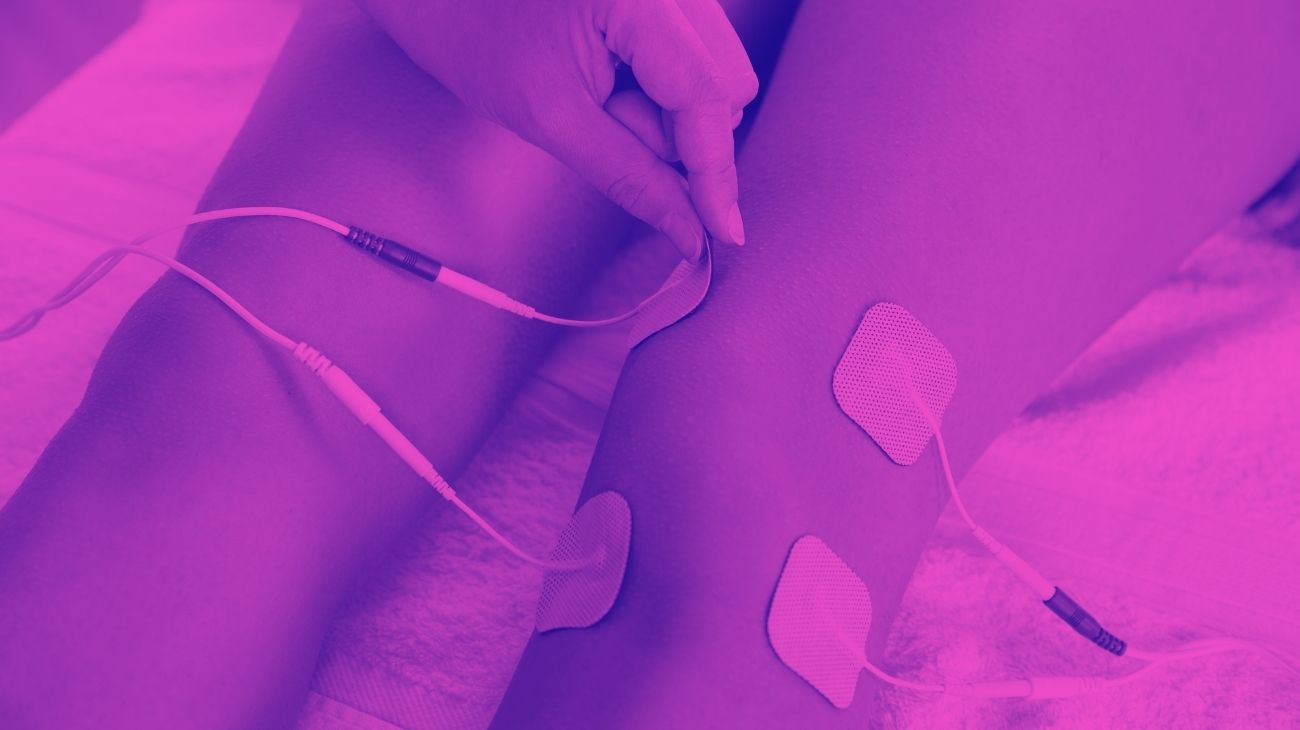
Where to place the electrodes?
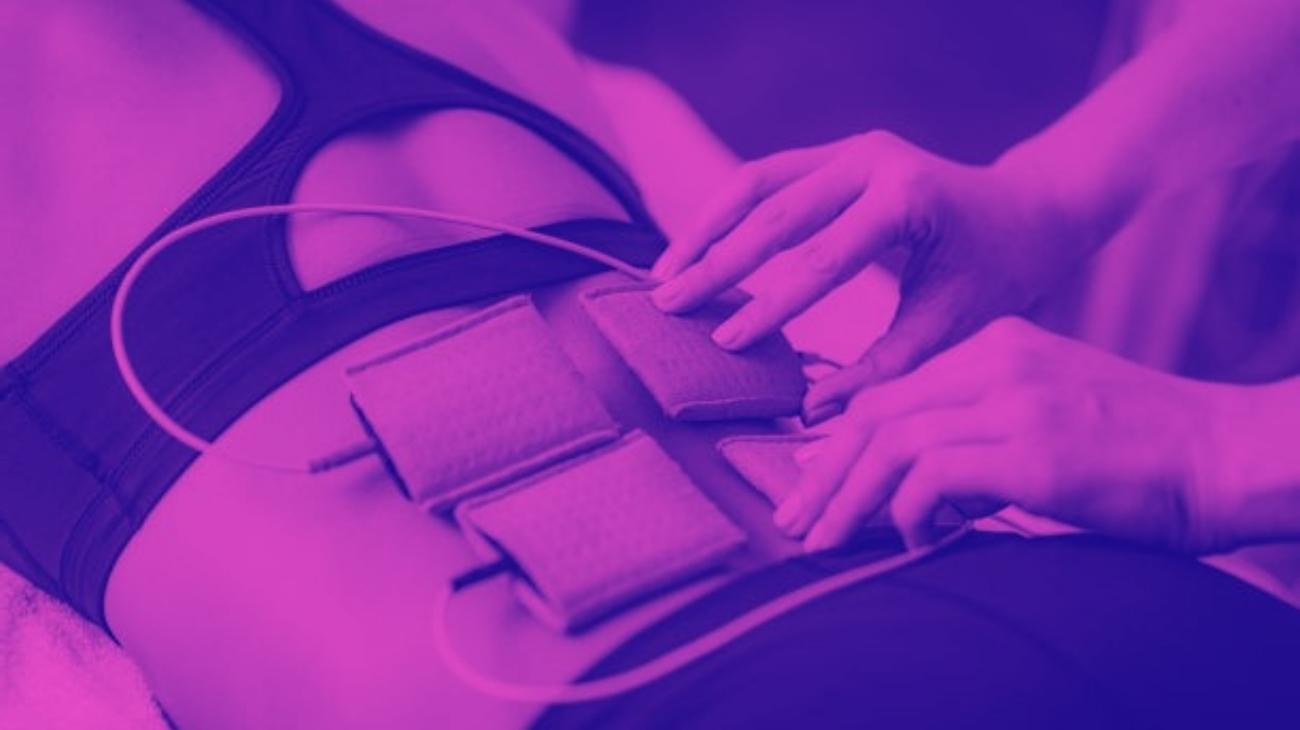
One of the main characteristics of tendonitis is that it can affect almost any joint. However, there are certain joints that are more prone to suffer this injury. These are the shoulder, elbow, wrist, knee and heels.
Below, we will teach you the positions to treat tendonitis pain in all of these locations:
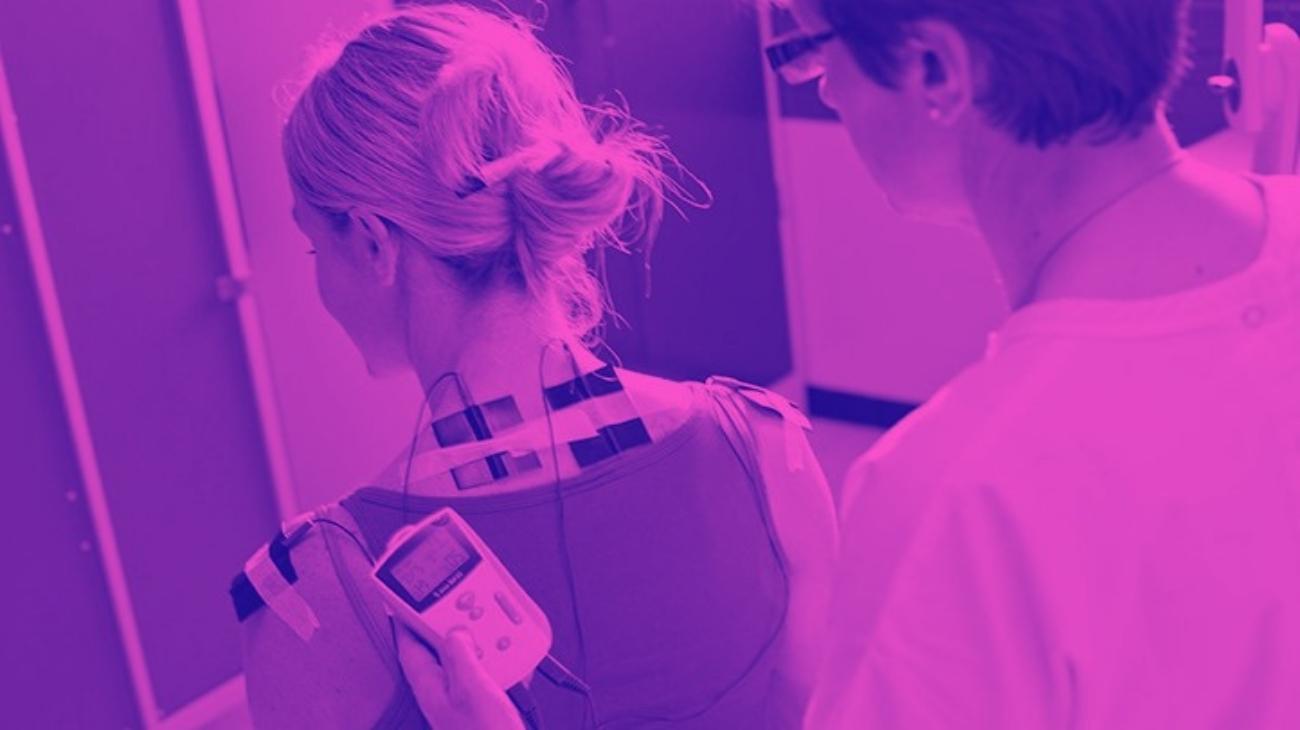
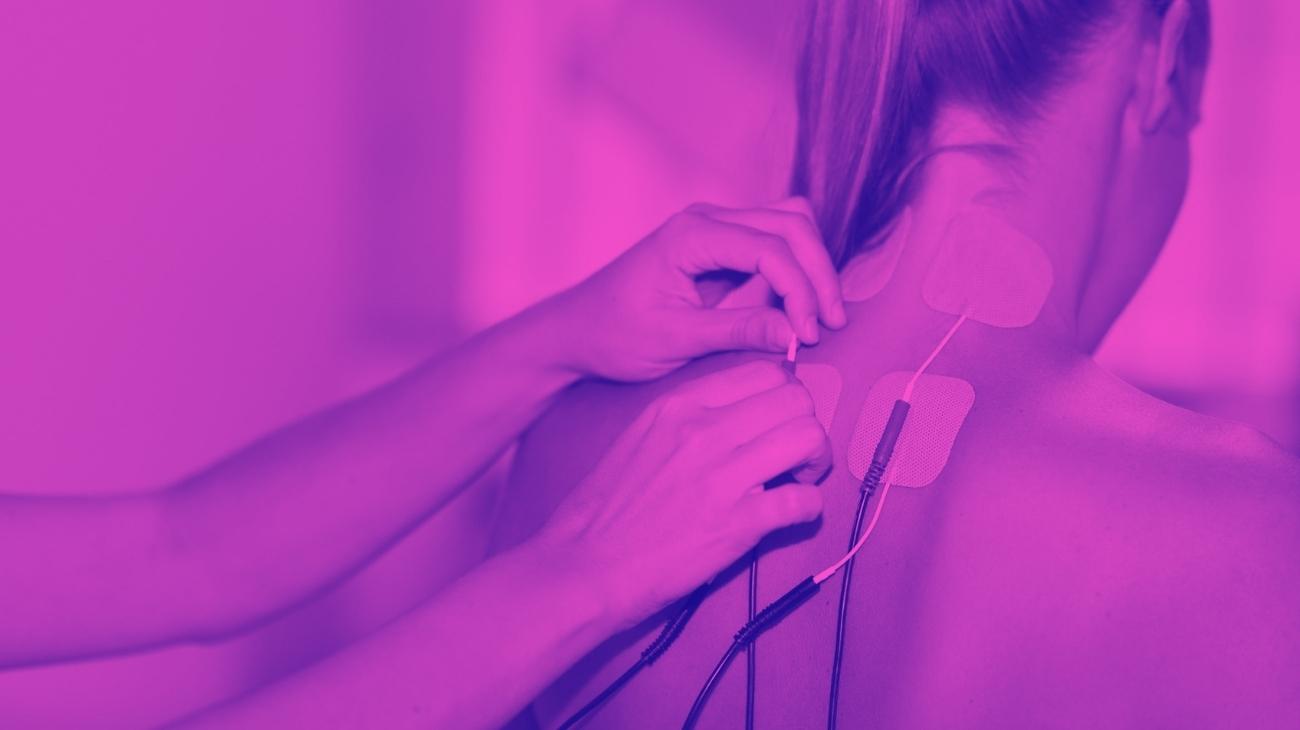
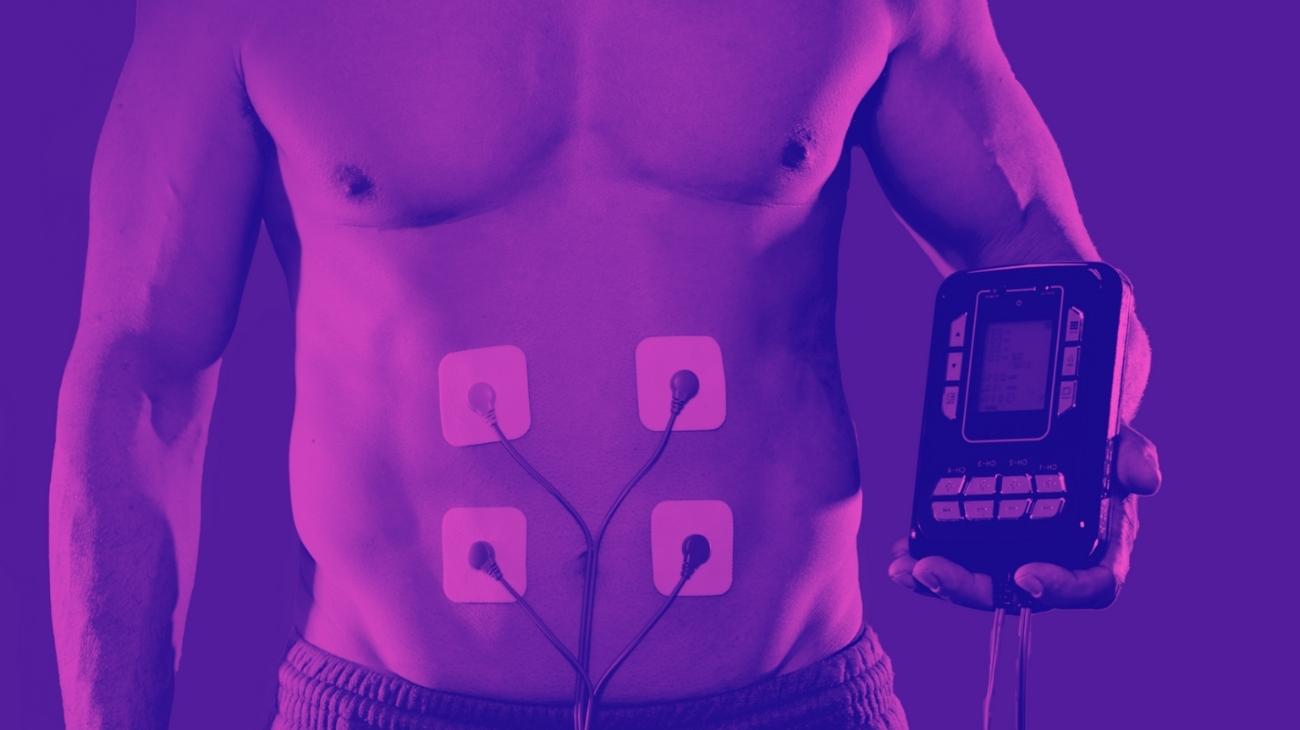
- Shoulders: one of the most common is rotator cuff tendonitis, for which you should position one electrode on the border of the trapezius muscle and the deltoid, while the other three will be positioned on the posterior deltoid, lateral anterior, thus interacting with the supraclavicular and circumflex grooms.
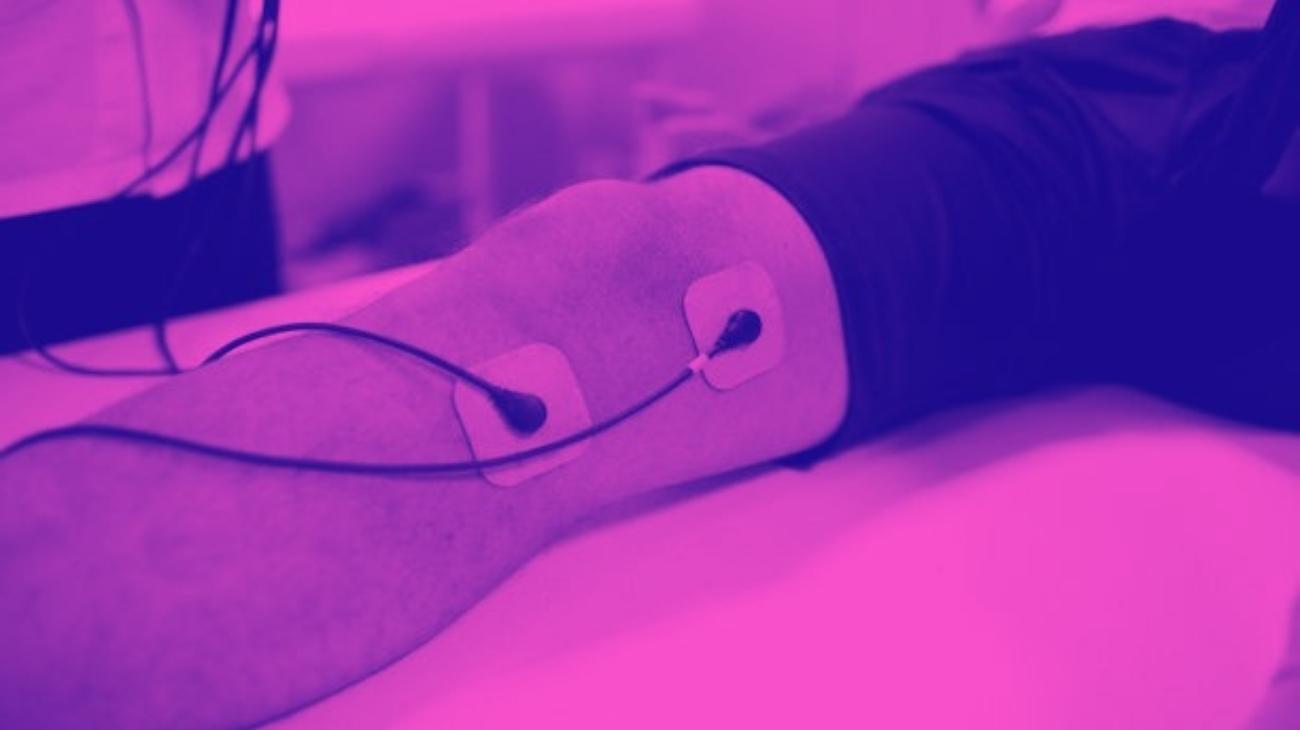
- Elbows: the most common conditions of tendonitis in the elbow are epicondylitis and epitrochleitis, for which the ideal positions for the electrodes are the vastus externus of the triceps brachii, the pronator teres muscle, the medial head of the triceps brachii, and the brachioradialis muscle.
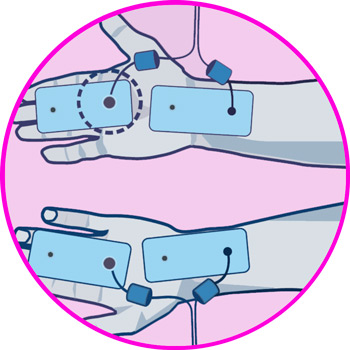
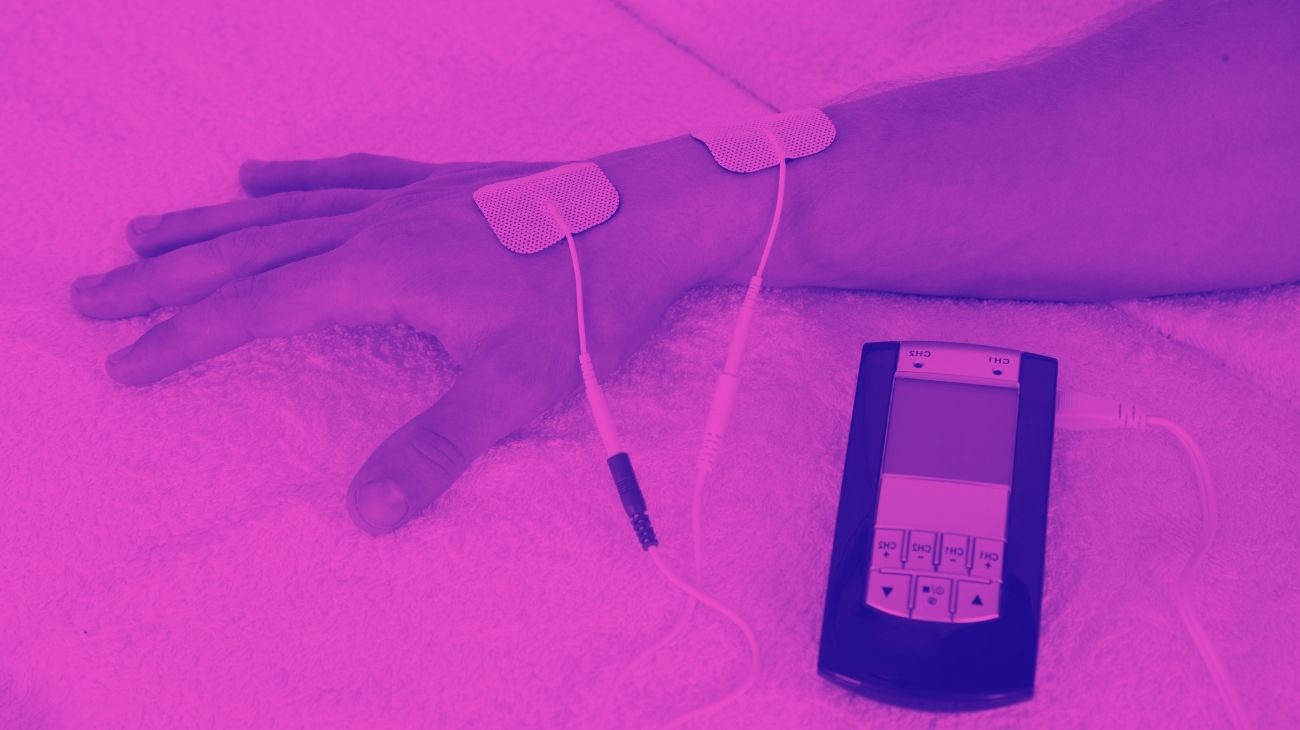
- Wrists: tendonitis in the wrist can be treated by placing the electrodes on the wrist joint, and on the forearm just below the ulnar fossa, in order to cover the full extent of the wrist tendon.
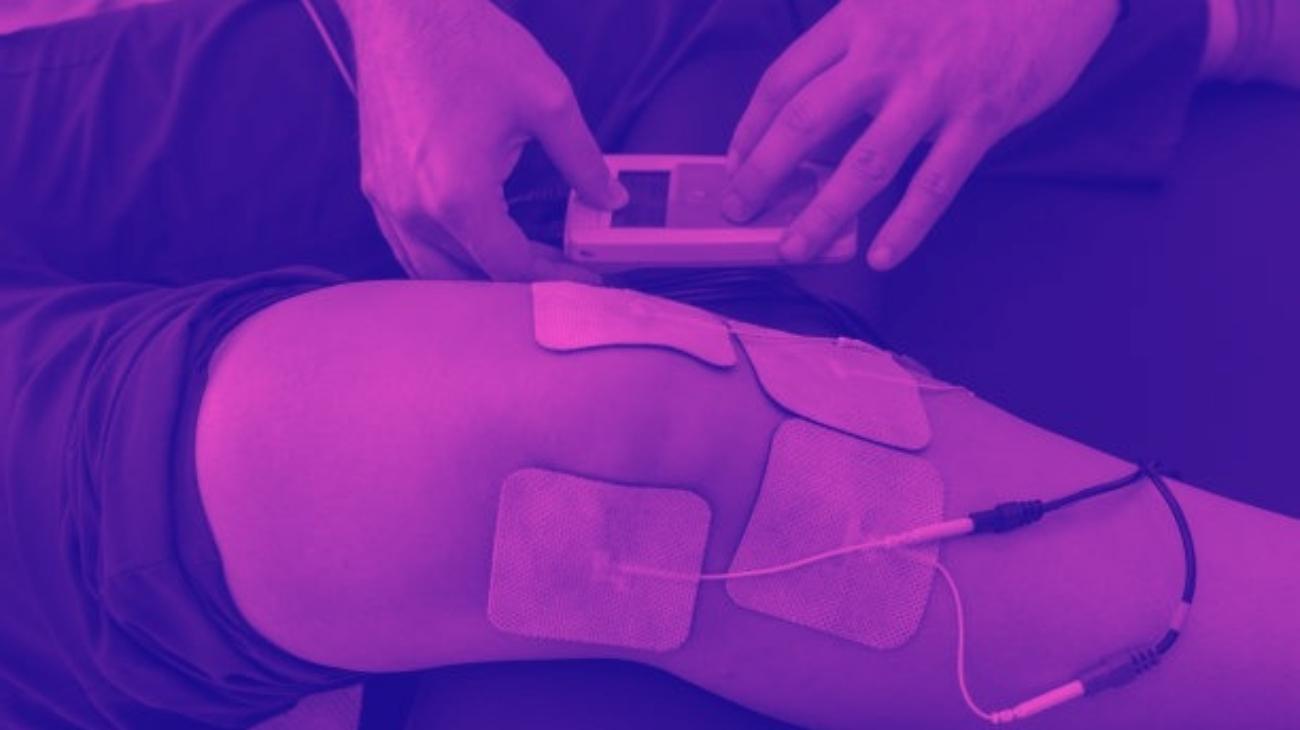
- Knees: the treatment of pain caused by patellar tendonitis can be treated by positioning the electrodes on the vastus medialis, rectus femoris and tibialis anterior muscle, interacting with the vastus medialis and lateral femorocutaneous nerve, reducing the sensation of pain.
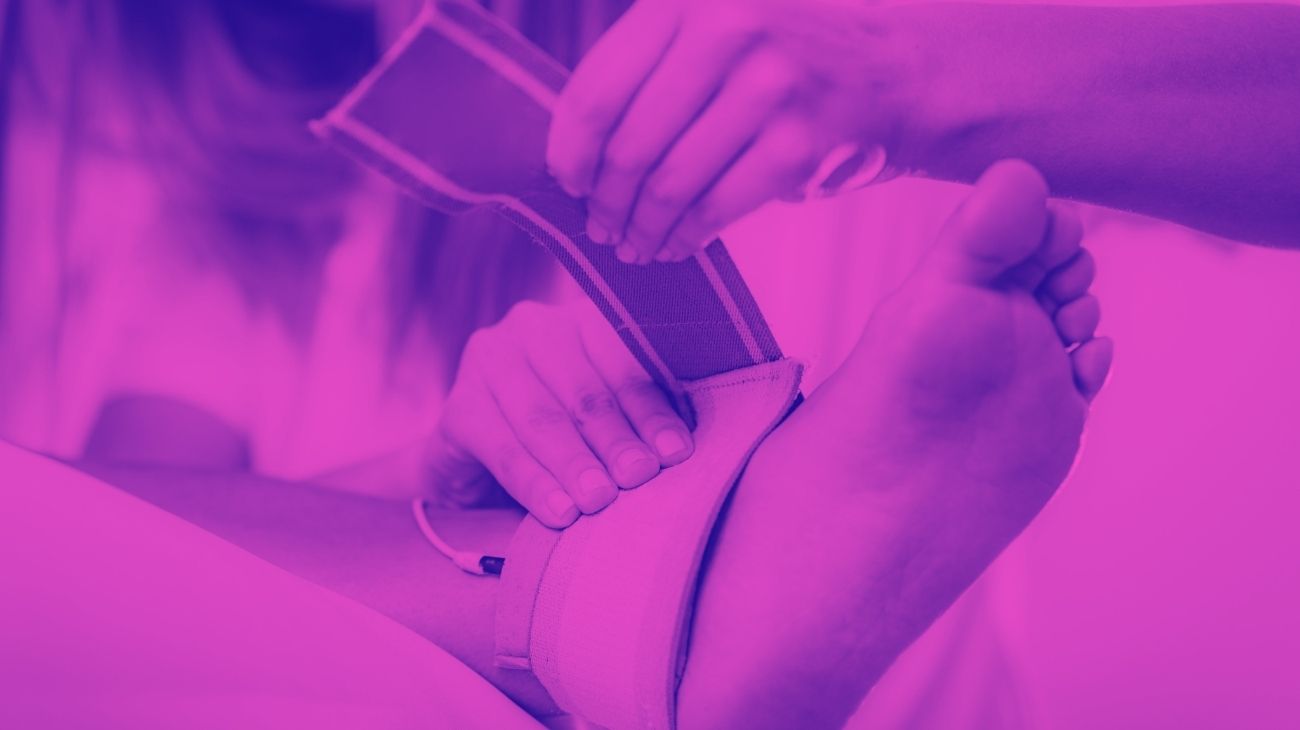
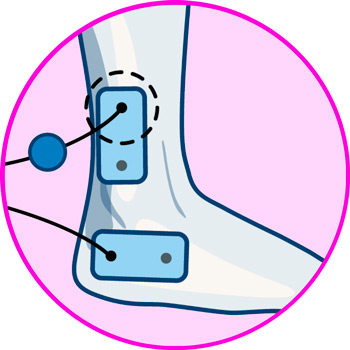
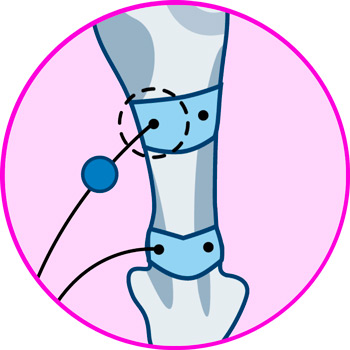
- Ankles: Achilles tendonitis is the most common cause of heel pain, and to treat this injury, it is necessary to position the first electrode on the portion of the tendon just below the calf, while the second is positioned on the calcaneal tendon, above the heel.
Which current to use?
The pain caused by tendonitis can have a variable intensity, however, as it is an ailment caused by inflammation of a tendon, it is necessary to use low frequencies to achieve a more lasting pain relief effect.
The ideal frequency to treat tendonitis in most of its presentations ranges from 2 to 10 Hz, a burst frequency that promotes the release of endorphins and treats the ailments caused by tendonitis.
Best TENS units to treat nerve damage
Treatment of tendonitis damage should be carried out by a specialist, as TENS machines are only designed to treat the pain caused by these injuries. However, their use makes the rehabilitation process much more bearable, and it is possible to focus TENS units suitable for this treatment, among which we can mention the following:
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 14 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 6 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Rechargeable battery
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Battery life not specified
- Does not include touch screen
The compact size of the device makes it incredibly practical and easy to carry, so you can use it anywhere you like quickly and discreetly. It is FDA approved, so it is completely safe to use, and its LCD screen gives you a full display of all settings so you can easily adjust your requirements.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 10 Pads
- Display: Touch
- Size: 5.12" x 2.56" x 0.39" - 0.35 lbs
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Not for muscle hypertrophy
- Does not include user manual
- No heat therapy
It has 24 modes of use and 20 intensity levels that can be applied in isolation to each of the device's channels thanks to its dual channel function, allowing different therapies to be applied to separate areas of the body. In addition, it has a session timer mode and automatic shut-off that will allow you to give greater efficiency to your sessions and make better use of the energy of its high-capacity lithium battery.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- 4 independent channels
- Provides cramp relief
- Portable Device
- Promotes tissue healing
- 24 programs
- Few electrodes
- Does not specify battery life
- Does not specify intensity and size
It has 24 clinically proven massage programs, which are divided into 12 TENS therapy programs and 12 muscle stimulation training modes. It has a long-life rechargeable lithium battery that will give you a great autonomy of several hours of continuous use, eliminating the extra cost of buying replacement cylindrical batteries.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (10 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 24 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- 4 outputs with 2 separate channel configurations
- Includes 24 different pads
- Rechargeable battery
- Large display
- 24 massage modes with 20 intensity levels
- No adapter for non-US plugs
- No size specified
It has an incredibly portable size that will allow you to take it anywhere, and a high-powered rechargeable battery that will give you up to 20 hours of continuous use. It can be connected to AC power through its AC adapter, or to an external battery or laptop through its USB charging port.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 6 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Portable and small size
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Includes carrying bag
- No intensity levels specified
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
It has 6 modes of use that emulate different types of massages to achieve different objectives, along with 10 levels of intensity that provides greater effectiveness. The package includes 1 control, 2 large electrodes, 2 small electrodes, 2 guide cables, 1 user's manual, 1 cable case and 1 treatment guide.
How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and avoid tendon damage?
Although muscle electrostimulation is not recommended for the treatment of tendonitis in any of its forms, using it as a training method is an excellent way to prevent these injuries thanks to the strengthening of the muscles that can be achieved.
Where to place the electrodes?
The positions to improve joint resistance are classified as follows:
- Shoulders: the electrodes will be positioned on the trapezius muscle, the anterior, lateral and posterior deltoids, and the infraspinatus muscle.
- Elbows: the ideal position for the electrodes are the biceps brachii, the anterior brachialis muscle and the biceps brachii muscle.
- Wrist: in this area, the location is more complicated due to the low muscle mass. However, the ideal positions are the brachioradialis muscle and the deep flexor.
- Knee: training of the muscles adjacent to the knee is achieved by positioning the electrodes on the vastus medialis, rectus femoris and tibialis anterior muscle.
- Ankles: electrodes should be positioned along the Achilles tendon, on the back of the calf and just above the heel.
What intensity to use?
The general treatment for physical conditioning of the muscles that give support and stability to the joints varies very little from one extremity to another, since to obtain optimal results, the frequency range to apply oscillates between 65 and 85 Hz, which generate contractions that increase muscle capacity, strengthening the joints and helping to prevent injuries such as tendonitis.
Best EMS machines to prevent tendon inflammation
Physical training is vital to avoid most injuries, yet paradoxically, the repetitive movements of most workouts can cause tendonitis. In contrast, EMS devices provide a way to strengthen muscles safely, without risk of injury, allowing you to decrease the likelihood of tendonitis. Among the best EMS machines for this we can highlight the following:
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Touch
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Portable and small size
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Does not specify intensity levels
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Does not include carrying bag
It includes 24 massage programs in total, which are designed to treat a wide variety of ailments. Each of the modes has 4 different options to choose from, and comes with all the accessories you may need, from electrodes and guide wires to a user guide and an electrode positioning guide.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 12 Modes
- Intensity: 30 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Batteries
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves blood circulation
- Portable and small size
- Improves joint mobility
- TENS+EMS Combo
- No battery type specified
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify size and weight
It offers a professional solution through its 12 massage modalities with 30 intensity levels, which you can easily adjust to adapt the therapy to your needs. Additionally, its dual channel function allows you to apply different modalities on the A and B channels of the stimulator, allowing you to treat two different areas of the body, or even two different people, simultaneously.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 4 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: 3 AA
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: 6.25 x 2.25 x 0.80 inches
- Offers relief from cramps
- TENS + EMS
- Portable Device
- Easy to use
- Includes carrying bag
- Few modes/programs
- No rechargeable battery
- No intensity specified
It has a versatile 4-channel function that allows you to apply individual massage programs to different areas of the body simultaneously, includes 4 modes of professional massage therapy, divided into TENS, EMS, Rehabilitation and Fitness, making it the ideal complement to maximize the results of your workouts.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 6 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 12 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: 5.38" x 3.75" x 1"
- Improves blood circulation
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Rechargeable battery
- Good quality
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Does not specify intensity levels
- No heat therapy
- No weight specified
It also has 5 programs of use focused on different branches of physical conditioning: endurance, resistance, strength, active recovery and warm-up. Proper use of this device will allow you to reach your maximum performance with very little cardiovascular fatigue, and is highly recommended for fitness enthusiasts who frequently engage in competitions.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 15 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: No display
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Control from mobile app
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes user manual
- Rechargeable battery
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
- Battery life not specified
- Does not specify intensity levels
With more than 400 modes of use and a variety of intensity levels, the PowerDot 2.0 is one of the most complete electro stimulators available, as its functions focus on muscle recovery, improved physical performance, and pain relief. All these features make it the leading choice for the immediate treatment of any pain, whether caused by injury or illness.
Video: How to place electrodes pads for tendonitis pain?
Electrodes for shoulder
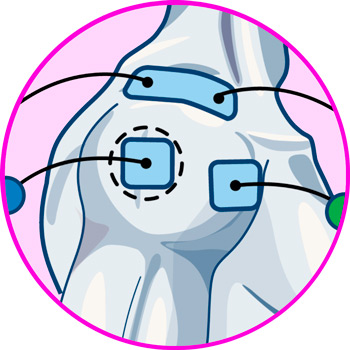
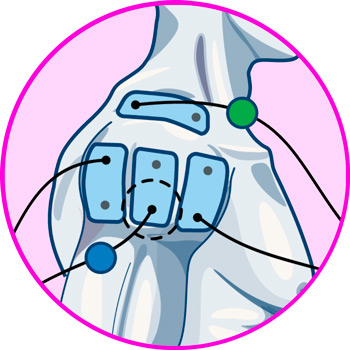
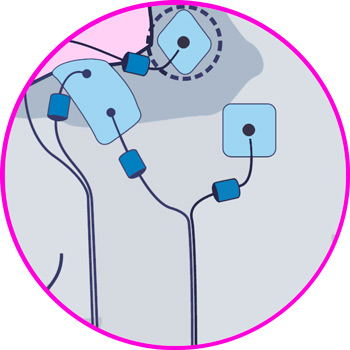
Electrodes for elbow
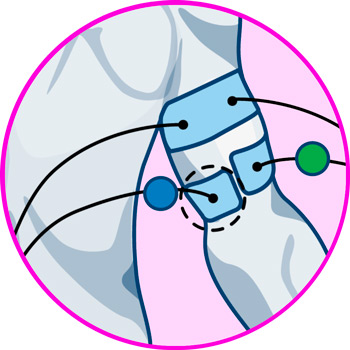
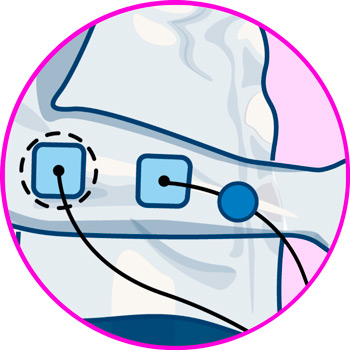
Electrodes for wrist
Electrodes for knee
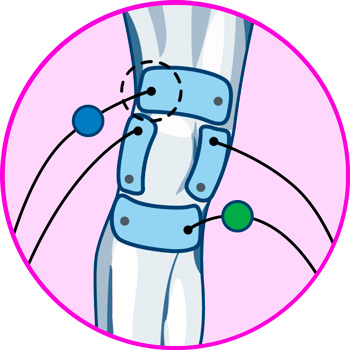
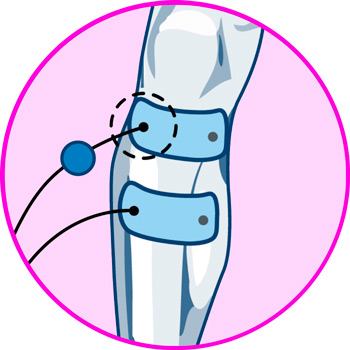
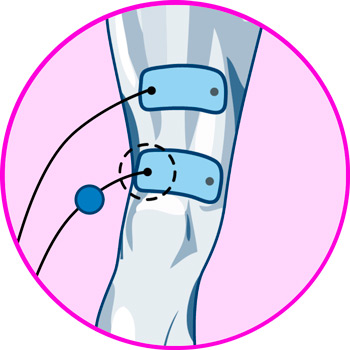
Electrodes for ankle
More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
What is tendonitis and what are the causes?
Tendonitis is defined as a severe inflammation of a tendon, and usually occurs in joints that have been exposed to excessive stress, overload or recurrent injury. It can occur in any joint, although it is most common in shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees and heels.
Among the main causes of tendonitis, we can highlight the following:
Trauma
A sudden injury to a joint can injure it enough to cause the fibrous tissue to swell and generate a stabbing pain, the sensation of stiffness and difficulty of movement characteristic of tendonitis.
The injuries that most commonly lead to tendonitis are:
- Sprains
- Fractures
- Impingement
- Excessive twisting
Overuse
Excess weight on a joint generates stress on the tendon of the joint, and while the tendon strength is almost always sufficient to resist the stress caused, damage can occur.
Repetitive movements
Sports such as swimming or tennis are very common causes of tendinitis due to the fact that these sports consist of repetitive, high-intensity movements that place great stress on the joint.
The sports that report the most cases of tendonitis are:
- Soccer
- Athletics
- Swimming
- Racquet sports
On the other hand, tendonitis is also very common in work environments that promote constant repetition of movements.
Among the jobs that most commonly produce tendinitis, we can find:
- Bricklayers
- Clerks
- Mechanics
- Athletes
Incorrect technique
At this point, regardless of whether it is in the sports field or in the workplace, the performance of repetitive movements coupled with poor technique can accelerate the rate of wear of the fibrous tissue, increasing the possibility of acquiring tendinitis. For example, applying too much tension on the elbow, lifting objects above the head, bending the wrist incorrectly and repetitively.
What are the most common types of tendonitis?
The human body has a large number of joints in which tendons are key parts in their movement, so they are all vulnerable to some extent to tendonitis.
Having said this, it is necessary to highlight that there are joints that are more vulnerable than others, which can suffer from different types of tendonitis depending on the area they affect. Among the most common types of tendinitis we can find:
- Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury to the Achilles tendon that frequently occurs in runners who make sudden changes in intensity or sudden turns. It can cause a painful sensation above the ankle and stiffness.
- Epicondylitis: Epicondylitis is the inflammation of the epicondyle tendon, located in the elbow. It is very common in athletes who play racquet sports (hence the name tennis elbow), and is characterized by pain on the outside of the elbow.
- Epitrochleitis: inflammation of the epitrochlea tendon, which causes pain, stiffness and swelling on the inner aspect of the elbow and forearm. Similar to epicondylitis, epitrochleitis, or golfer's elbow, is common in those who practice racquet sports, throwing sports or weight training.
- Patellar tendonitis: is an injury that causes inflammation in the tendon that connects the patella and tibia. It is very common in athletes whose disciplines involve jumping, such as volleyball, athletics or basketball. Hence the name "jumper's knee"
- Rotator cuff tendonitis: refers to inflammation of the tendons of this muscle, which can cause pain, visible swelling and limited movement. Its most common cause is repetitive motion overload, which causes wear and tear and subsequent weakness in the tendon area.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating tendon inflammation?
Tendonitis is an injury that can cause considerable pain depending on its severity, so it is necessary to apply treatments to minimize the pain in case it is too intense, in order to facilitate the recovery process.
For this purpose, electrotherapy machines are used, since they have proven to be effective in the treatment of pain in various types of injuries. However, it is important to note that TENS and EMS therapies have very different effects since they are designed for different treatments.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a physical therapy modality that uses electrical impulses to treat pain, and is characterized by the following properties:
- It uses low-frequency and low-intensity electrical impulses (between 1 and 250 Hz).
- It interacts directly with the nerve endings of the affected area, blocking the pain receptors of the branches that innervate the area, considerably reducing the sensation of pain.
- It is a method to treat the symptoms, but it cannot directly deal with the injury or disorder that causes them.
- There are a variety of devices of different shapes and intensities focused on treating different areas.
In contrast to this, Electrical Muscle Stimulation (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) or EMS, is a training technique aimed at improving physical condition through electrical impulses that improve muscle resistance and elasticity.
EMS can be identified by the following characteristics:
- Its effect is focused on muscle stimulation by means of electrical impulses.
- It applies discharges with a medium-high intensity that varies between 70 and 150 Hz.
- It can generate indirect stimuli in the nerves due to the muscle contractions generated.
- It is widely used by sports medical teams and high level teams.
These characteristics of each type of therapy allow us to conclude that the appropriate therapy for the treatment of tendonitis pain is TENS therapy, thanks to the fact that its electrical impulses propitiate the relaxation of fibrous tissues, decreasing the sensation of pain and dealing with tendon inflammation.
EMS therapy, on the other hand, is not recommended for the treatment of tendonitis, because its electrical impulses of such intensity generate contractions in the muscles that can be counterproductive for the relief of tendonitis pain, since they can stimulate the nerves adjacent to the affected area.