- How to use TENS machines to relieve meniscus tear pain?
- Best TENS units to treat meniscus tears
- How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent torn meniscus?
- Best EMS machines to avoid meniscus injuries
- Video: How to place electrodes pads on the knee?
- More types of EMS stimulators and TENS machines you should know about
- What is a meniscus tear and what are the causes?
- What are the most common types of meniscus injury?
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating meniscus injury?
- Contraindications in the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
The knees play a vital role in the motor processes of the human body, since the legs have a wide range of motion and a cushioning system when performing more demanding activities such as walking and running. This cushioning is originated by a system of cartilages located in the knees, which are called menisci.
Due to the constant stress to which they are exposed, the menisci have the possibility of suffering tears that can generate considerable ailments. In these cases, it is necessary to use electrotherapy methods to treat the symptoms of this injury. Below, we will teach you everything you need to know about the consequences of meniscus tears and how to use TENS and EMS electrotherapy to deal with their symptoms.
How to use TENS machines to relieve meniscus tear pain?
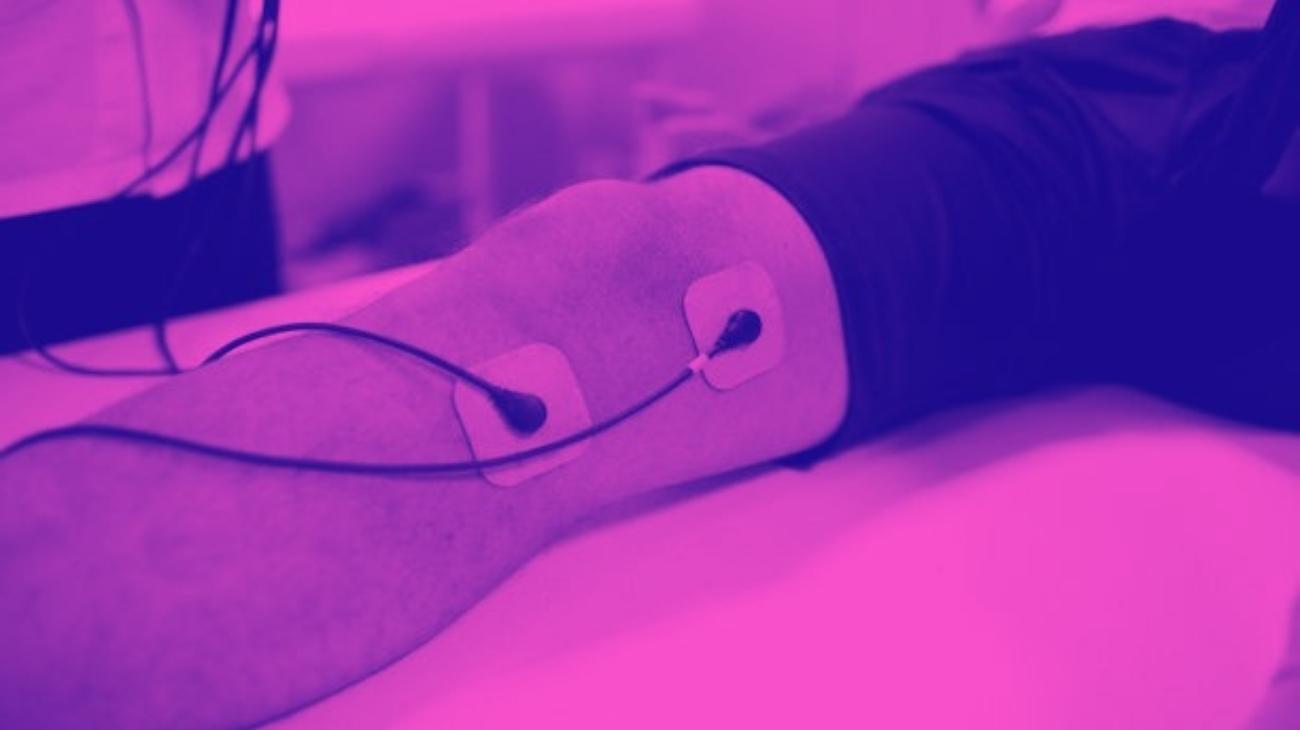
The optimal use of TENS units for the treatment of knee pain responds to specific criteria to ensure their effectiveness in reducing pain on a long-term basis. These criteria are the location of the electrodes and the intensity of the electric current applied.
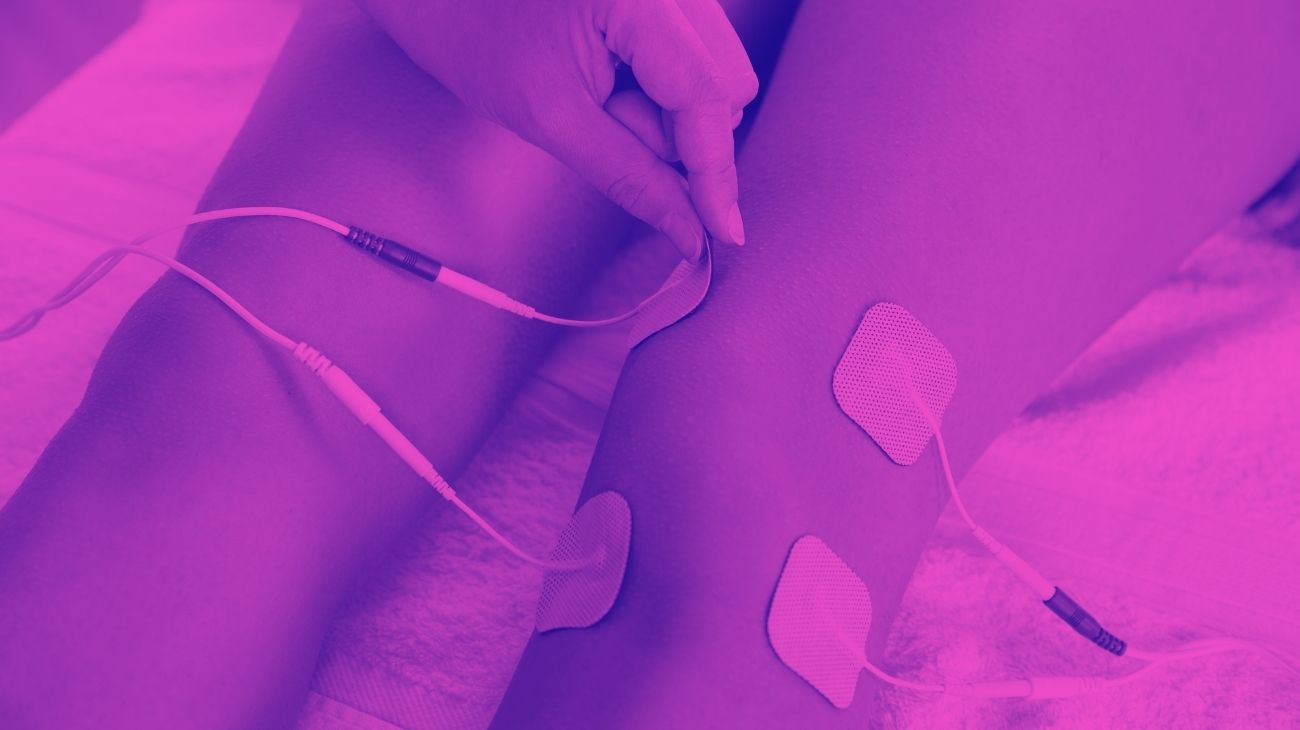
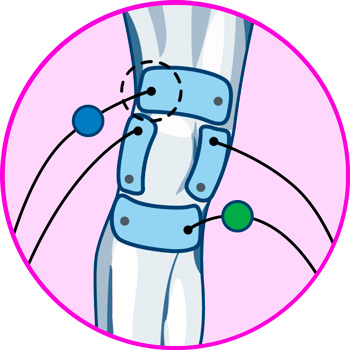
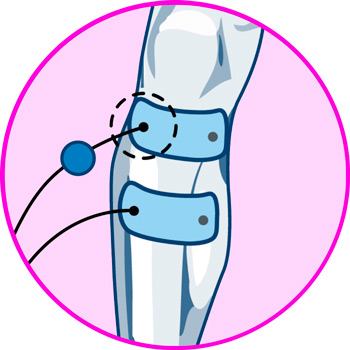
Where to place the electrodes?
In general, TENS treatment for knee injuries requires avoiding positioning the electrodes over the patella, so that the electrical discharges interact with the nerves as effectively as possible.
In the case of meniscal tear pain, this rule holds true, indicating that the optimal positions are as follows:
- Over the vastus medialis muscle, to interact with the sensory branches of the femoral nerve.
- Over the lateral portion of the thigh, aligned with the lateral femorocutaneous nerve.
- Below the knee joint, just above the tibia, to interact with the tibial nerve branches.
- Inner lateral aspect of the knee, over the anterior branch of the obturator nerve.
Which current to use?
For the purposes of numbing the nerve endings in the area and encouraging the production of endorphins to combat pain, it is necessary to select a frequency in the middle spectrum of the possible range of TENS devices.
This frequency is usually 100 Hz, although it can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the level of pain presented by the patient.
Best TENS units to treat meniscus tears
In order to be able to apply TENS therapy effectively for pain caused by meniscal tears, it is necessary to select devices that have the appropriate settings. Among these we can mention the following:
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Touch
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Portable and small size
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Does not specify intensity levels
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Does not include carrying bag
It includes 24 massage programs in total, which are designed to treat a wide variety of ailments. Each of the modes has 4 different options to choose from, and comes with all the accessories you may need, from electrodes and guide wires to a user guide and an electrode positioning guide.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 20 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: Yes
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 4.12" x 2.24" x 0.43" - 1.54 lbs
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Rechargeable battery
- Includes user manual
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Not for muscle hypertrophy
- No heat therapy
- No touch screen included
It has 20 modes of use that apply different types of massages oriented to treat a wide variety of ailments, and with its independent channel control mode you will have the possibility of configuring different programs for each of the channels individually, to apply different types of massages in various areas of the body.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (10 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 24 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- 4 outputs with 2 separate channel configurations
- Includes 24 different pads
- Rechargeable battery
- Large display
- 24 massage modes with 20 intensity levels
- No adapter for non-US plugs
- No size specified
It has an incredibly portable size that will allow you to take it anywhere, and a high-powered rechargeable battery that will give you up to 20 hours of continuous use. It can be connected to AC power through its AC adapter, or to an external battery or laptop through its USB charging port.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- 4 independent channels
- Provides cramp relief
- Portable Device
- Promotes tissue healing
- 24 programs
- Few electrodes
- Does not specify battery life
- Does not specify intensity and size
It has 24 clinically proven massage programs, which are divided into 12 TENS therapy programs and 12 muscle stimulation training modes. It has a long-life rechargeable lithium battery that will give you a great autonomy of several hours of continuous use, eliminating the extra cost of buying replacement cylindrical batteries.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 8 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 3 AAA Batteries
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 2.14" x 5.5" x 7.08" - 0.33 lbs
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves joint mobility
- Portable and small size
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Good quality
- Few types of programs
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
- Battery operated
It has an interesting session timer function that allows you to adjust the duration of each therapy up to a maximum of 60 minutes. Its compact size allows it to be carried in your pocket, so you can take it with you from home to work, or on the road, and use it whenever you need it.
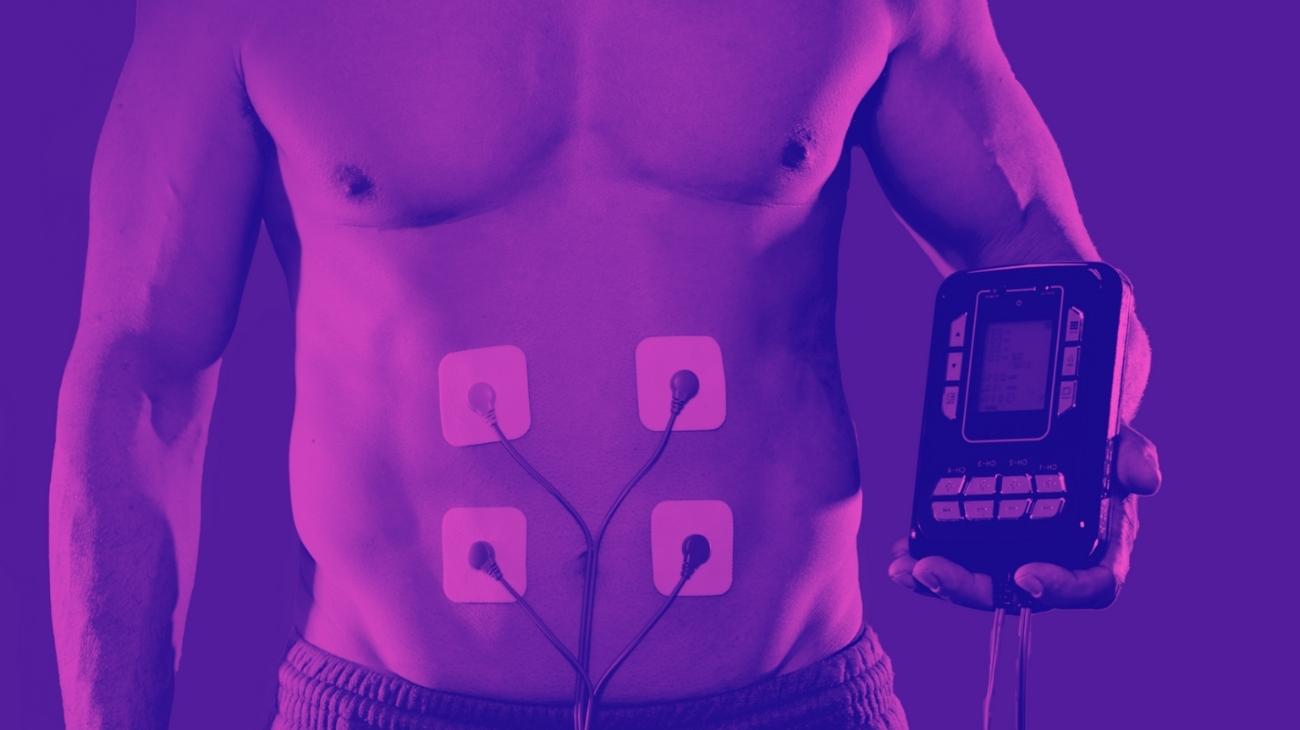
How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent torn meniscus?
Its effect is best highlighted when applied on the knee muscles in late stages of the recovery process, in order to minimize the risk of the impulses generating a painful sensation in the patient. Below, we will teach you what you need to know to apply optimal EMS therapy.
Where to place the electrodes?
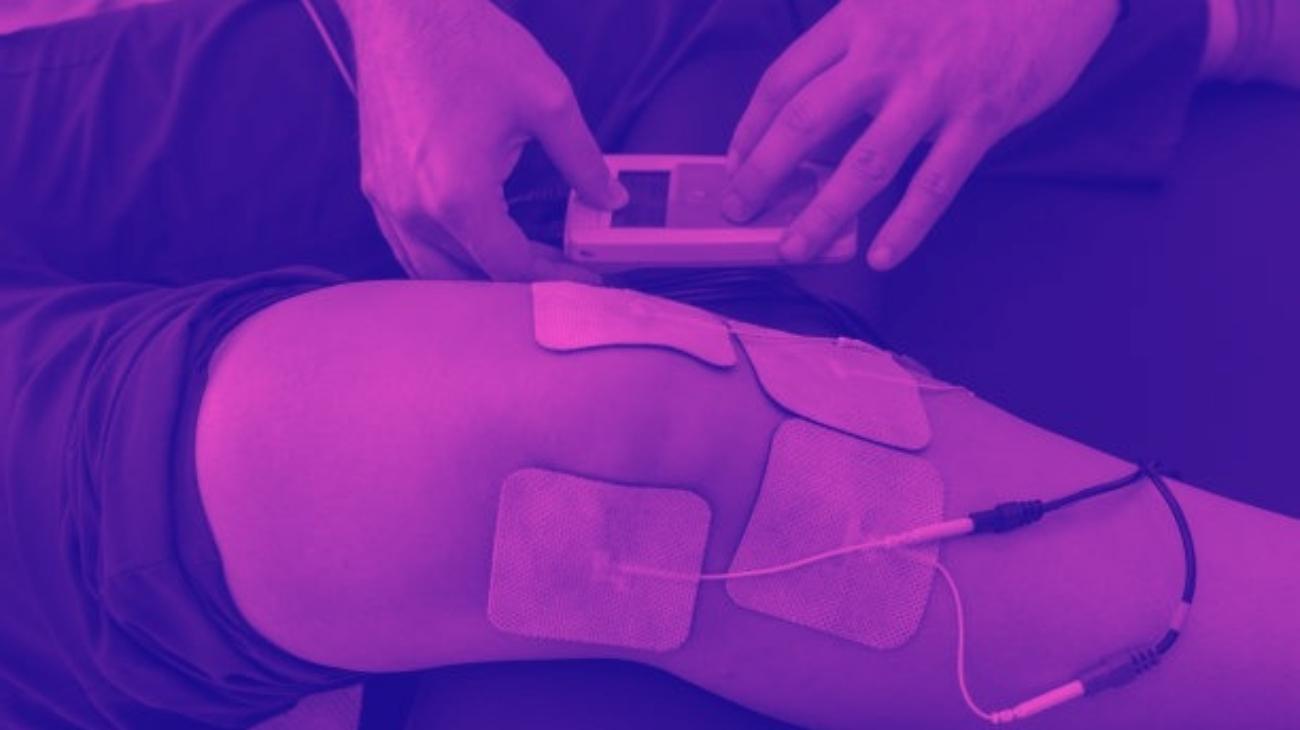
The positioning of the electrodes for meniscus training should surround the knee joint to properly stimulate the muscle groups that mobilize and stabilize the joint, so the correct positions are:
- Vastus medialis muscle
- Rectus femoris muscle, on the border with vastus lateralis
- Along the tibialis anterior muscle
What intensity to use?
Muscle strengthening of the groups surrounding the knee requires a medium intensity for optimal tissue development, generating a better contraction on the joint and thus improving its stability.
For this, the intensity varies between 70 and 90 Hz with periods of 200 microseconds, thus promoting activity in the muscle and the creation of muscle fibers that increase its density, strength and endurance.
Best EMS machines to avoid meniscus injuries
Most muscle EMS machines have the necessary settings to strengthen knee muscles and improve their function, as well as endurance. However, it is always useful to know the most commonly used devices for strengthening this muscle group. Among these we can highlight:
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 6 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (8 hours)
- Electrodes: Not specified
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- Improves joint mobility
- Improves blood circulation
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Long battery life (up to 8 hours)
- Does not specify intensity levels
- Measurements and weight not specified
- 6 programs
It has a powerful rechargeable lithium battery that gives it an autonomy of up to 8 continuous hours, and 6 programs of use that are divided into 1 warm-up program, 3 programs for increasing output, 1 recovery program and 1 TENS program. It is one of the most complete options to improve physical performance and recovery.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 32 Modes
- Intensity: 100 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 4 AA Batteries
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 5.4" x 3.1" x 1.1" - 0.6 lbs
- TENS+EMS combo
- Includes carrying bag
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes user manual
- No heat therapy
- No battery life specified
- No touch screen included
It has 8 customizable modes of use, of which 5 apply TENS current and 3 apply EMS current. It also has different levels of intensity, frequency and pulse radius, making it one of the most versatile electrostimulation machines on the market.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 14 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 6 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Rechargeable battery
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Battery life not specified
- Does not include touch screen
The compact size of the device makes it incredibly practical and easy to carry, so you can use it anywhere you like quickly and discreetly. It is FDA approved, so it is completely safe to use, and its LCD screen gives you a full display of all settings so you can easily adjust your requirements.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 12 Modes
- Intensity: 30 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Batteries
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves blood circulation
- Portable and small size
- Improves joint mobility
- TENS+EMS Combo
- No battery type specified
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify size and weight
It offers a professional solution through its 12 massage modalities with 30 intensity levels, which you can easily adjust to adapt the therapy to your needs. Additionally, its dual channel function allows you to apply different modalities on the A and B channels of the stimulator, allowing you to treat two different areas of the body, or even two different people, simultaneously.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 20 Programs
- Intensity: 40 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 12 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes 40 intensity levels
- Portable device
- 12 pads with different sizes
- Rechargeable battery
- Features 20 modes
- Somewhat slow charging
- No size specified
It has a function of 4 individual channels that will allow you to apply different massage programs in various areas of the body, in addition to 3 programs that together give you more than 20 options between TENS, EMS and recovery massages, 40 levels of intensity and time control function that will allow you to define the duration of each session.
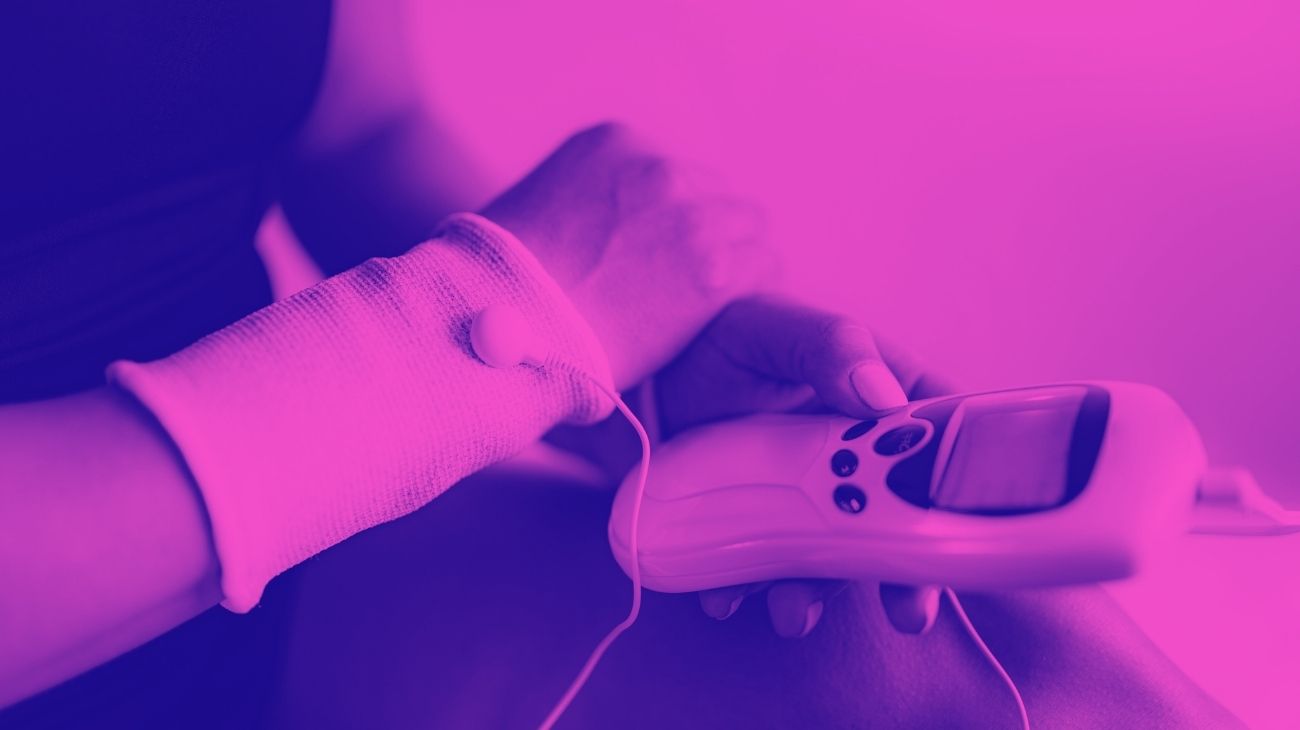
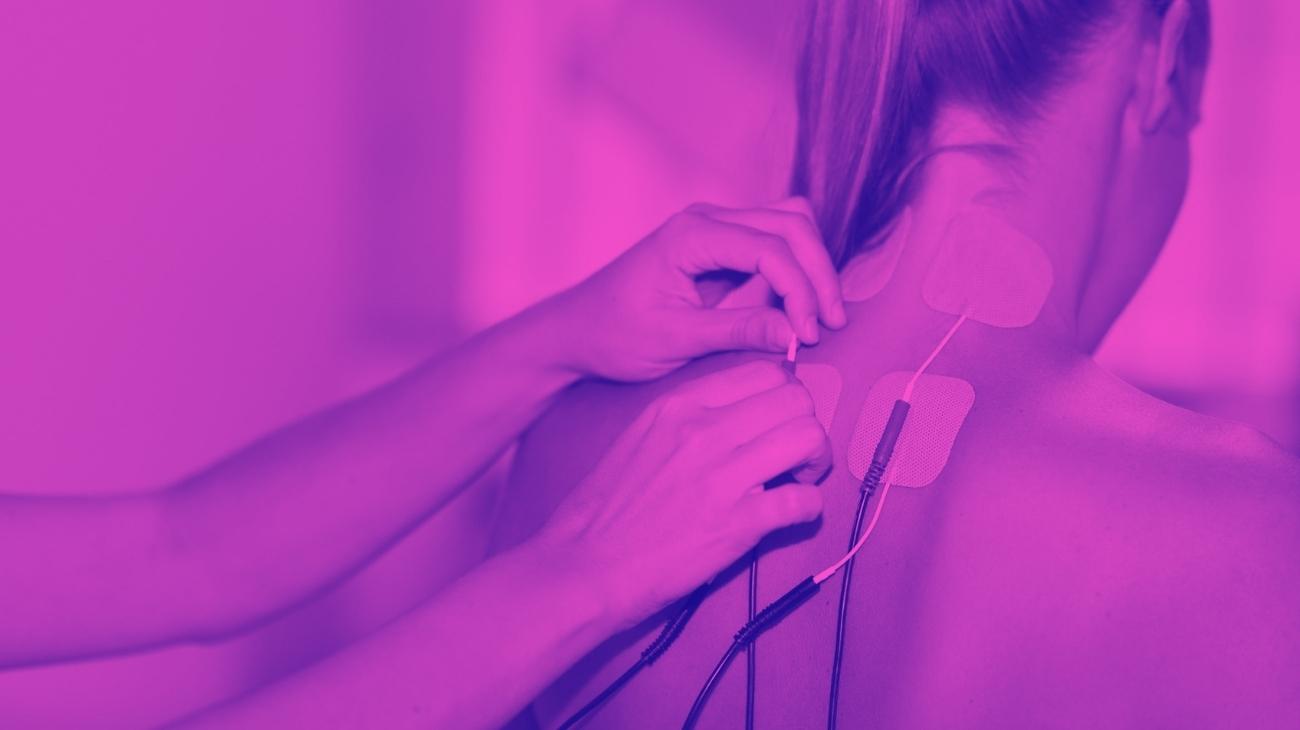
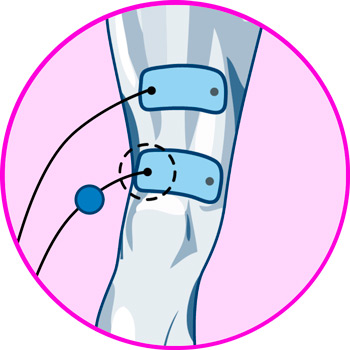
Video: How to place electrodes pads on the knee?
Electrodes for knee
More types of EMS stimulators and TENS machines you should know about
What is a meniscus tear and what are the causes?
A meniscus tear is an injury that affects the cartilage in the knee that functions as a shock absorption system in the knee. This cartilage forms a cushion between the bones that serves to absorb shock and aid in lubricating the knee.
Its main causes can be listed as follows:
- Aggressive pivoting
- Sudden turns
- Excessive pressure
- Overload
- Trauma
- Cartilage degeneration
Meniscal tears are very common injuries in sports involving running and jumping, such as soccer or basketball, as well as in the elderly. Among the main risk factors that increase the likelihood of meniscal tears we can highlight:
- High-intensity physical activity: contact sports such as soccer or sports that involve a lot of pivoting of the knees, such as basketball, can cause meniscal tears.
- Aging: over time, knee cartilage naturally wears down, increasing the risk of injury.
- Obesity: the extra weight increases the pressure applied to the knees, eroding the cartilage and increasing its rate of wear.
What are the most common types of meniscus injury?
Meniscal tears or tears are very common injuries in people who play contact sports and in older people. They can occur in many ways and this variety dictates to some extent the procedure by which the injury should be treated.
The most common forms of meniscal tears are:
- Longitudinal tears: these are tears aligned with the circumferential fibers of the meniscus, parallel to its outer surface.
- Horizontal tear: very frequent form of rupture in older people, it consists of a tear that extends from the internal face of the meniscus to the intrameniscal substance.
- Radial tear: it is a vertical fracture that covers the entire junction between the posterior and middle thirds of the meniscus, sometimes extending to the periphery and completely severing the cartilage. It is caused by trauma and is very common in physically active patients.
- Oblique tear: it is a vertical tear that occurs between the posterior and medial portions of the cartilage.
- Pedicle tear: these are fragments of meniscus that can move to other positions within the joint, generating a particularly intense sensation of pain for the patient.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating meniscus injury?
Forms of electrotherapy are widely used within the field of physical therapy and fitness, especially Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) and Electro Muscle Stimulation (EMS) modalities. However, it is necessary to be able to distinguish the uses and effects of each of these forms of therapy in order to apply them optimally.
TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) is a form of physical therapy aimed at the treatment of symptoms caused by disorders and trauma such as those that can lead to meniscal tears, being identified with the following properties:
- It applies low intensity electric currents, variable between 1 and 250 Hz.
- Its effect is applied to the articular branches of the femoral nerve, as well as to the branches of the tibial and peroneal nerves, reducing the effect of the lesion on them.
- It works as a method to relieve the pain caused by the meniscus tear, however it is not a method to cure the injury.
- It works by numbing the nerve endings in the affected area, causing the release of endorphins and preventing electrical pain signals from reaching the brain from the affected area.
Unlike TENS, EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) has effects more focused on increasing muscle strength, endurance and elasticity through contractions caused by electrical impulses.
We can recognize EMS therapy by the following characteristics:
- The minimum frequency of its electrical impulses is 70 Hz, and can reach a maximum of 150 Hz.
- Its effect is applied mainly on muscle tissue, creating contractions to increase fiber production.
- It can be applied to certain injuries in its lower frequencies, informing muscle management.
- It is designed as a method to condition and rehabilitate muscles, it is not intended to eliminate the sensation of pain.
Thus, we can conclude that both methods have merit in the treatment of meniscal tears, although the field of action of each therapy must be taken into account in order to apply it correctly and obtain the best results.
The functionality of TENS units is based on its ability to numb the articular sensory branches of the femoral, tibial and peroneal nerves, greatly minimizing the effect of pain caused by the joint and favoring the production of endorphins.
It should be emphasized that in an injury of this type, the effect of TENS therapy is limited to treating the pain caused by the cartilage tear, so the treatment of the injury itself should be carried out by a specialist.
For its part, the effectiveness of EMS therapy can be noted in more advanced stages of the meniscus tear healing process, thanks to the fact that its electrical impulses create a muscle massage that reduces inflammation, promotes optimal contraction of the muscles in the knee and reduces pain to a certain extent. It is necessary to emphasize the fact that it should only be applied in advanced stages of the rehabilitation process and at low frequencies, in order not to overstimulate the nerves and generate more pain in the patient.