- How to use TENS machines to relieve pinched nerve pain?
- Best TENS units to treat nerve damage
- How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent nerve damage?
- Best EMS machines to avoid nerve impingement
- Video: How to place the electrodes pads for nerve pain?
- More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know about
- What is nerve damage and what are the causes?
- What are the most common types of nerve damage?
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating damaged nerves?
- Contraindications in the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
Nerves are not as strong as bones nor as dense as muscles, but without them, neither of the latter two would be able to move freely. That is why when there are injuries or pathologies that involve them, the patient's quality of life is tremendously deteriorated.
Electrotherapy, especially in its TENS modality, can be an alternative to drugs to alleviate nerve damage without altering the chemical composition of the body with drugs that can be counterproductive in the long term. That is why today we will teach you how to use it.
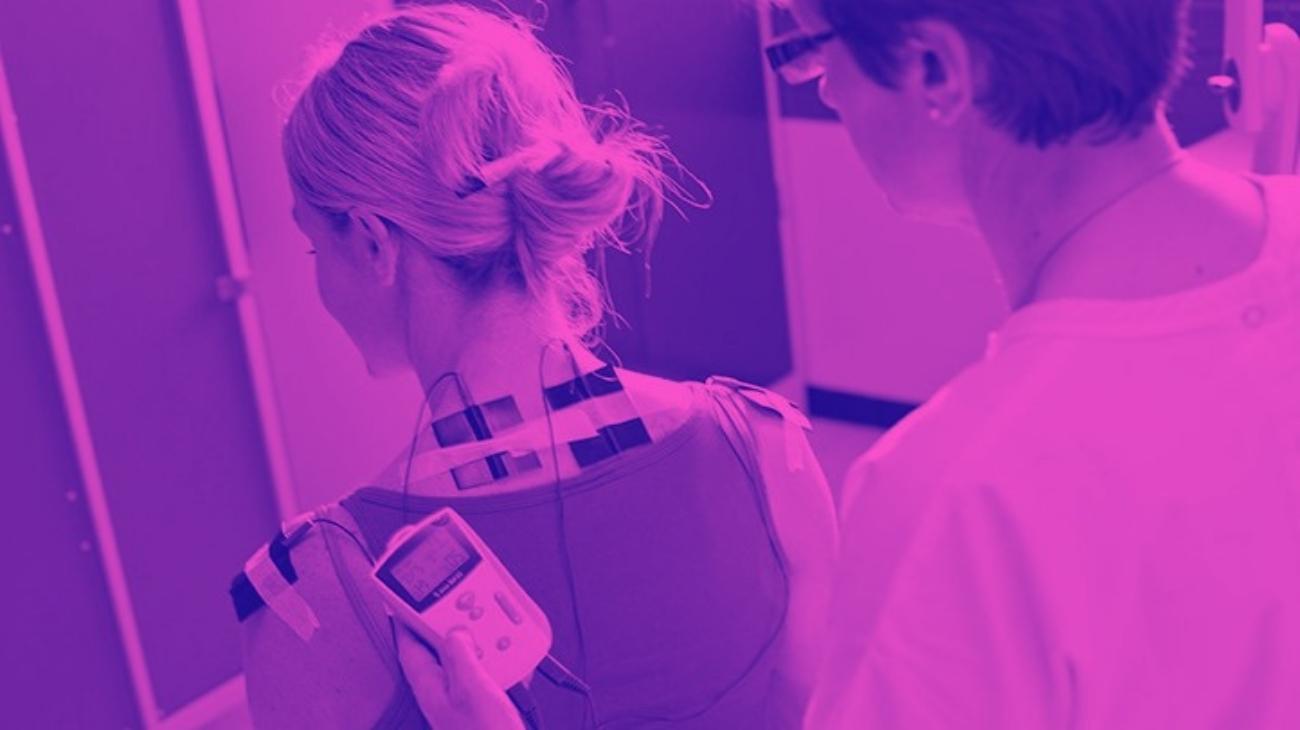
How to use TENS machines to relieve pinched nerve pain?
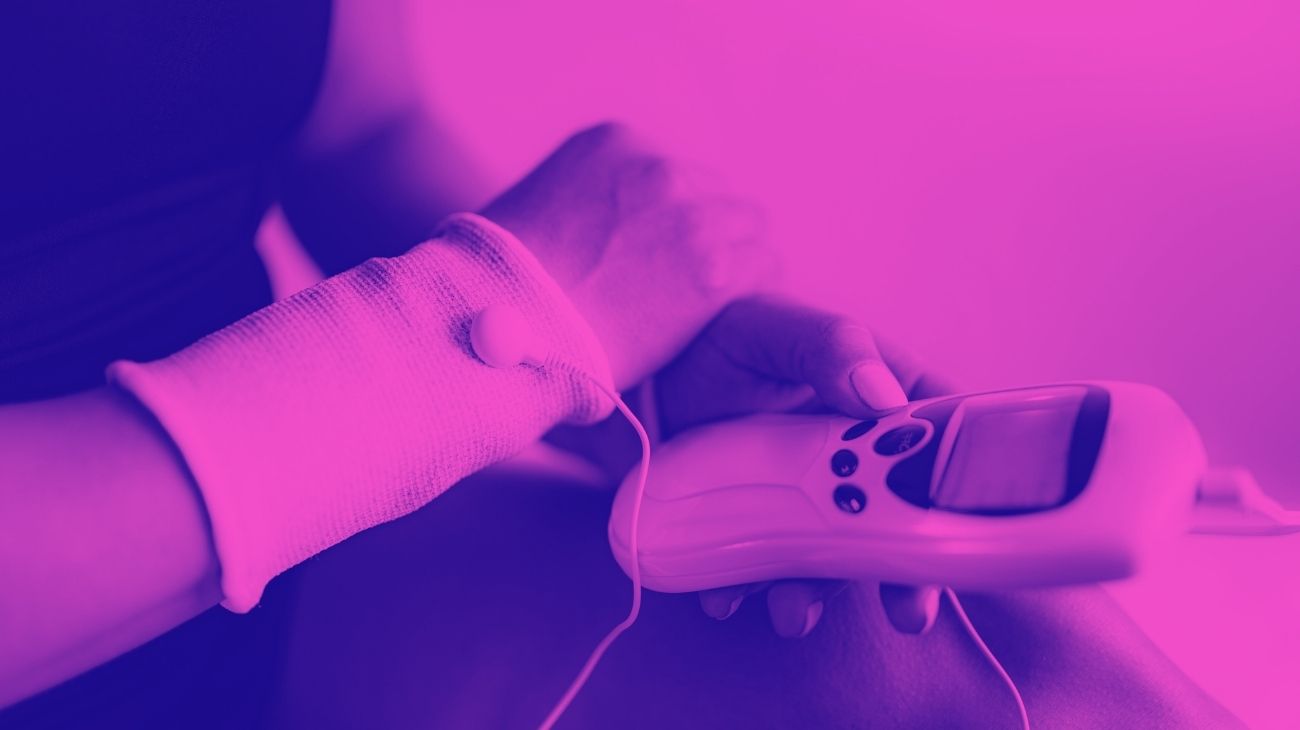
We will start by showing you how to use a TENS units to relieve pain generated by pinched nerves, or even tremors and weakness generated by degenerative nerve conditions.
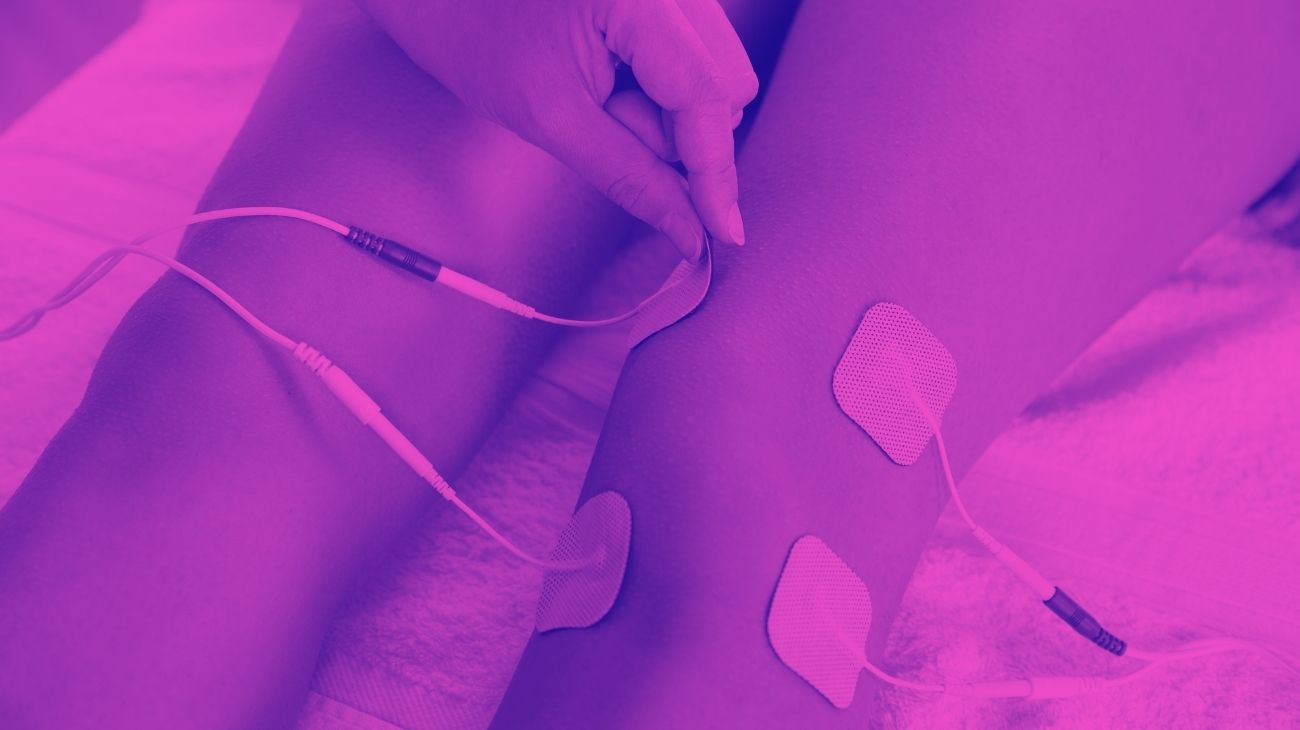
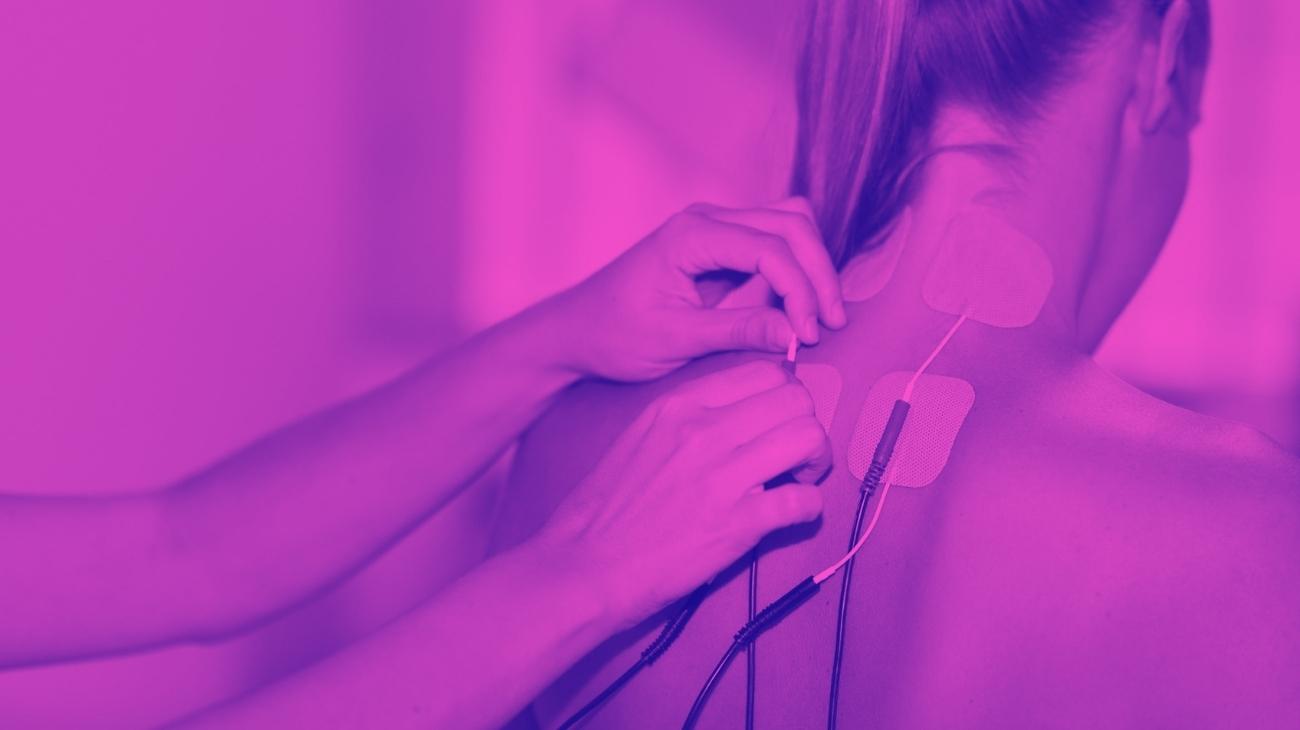
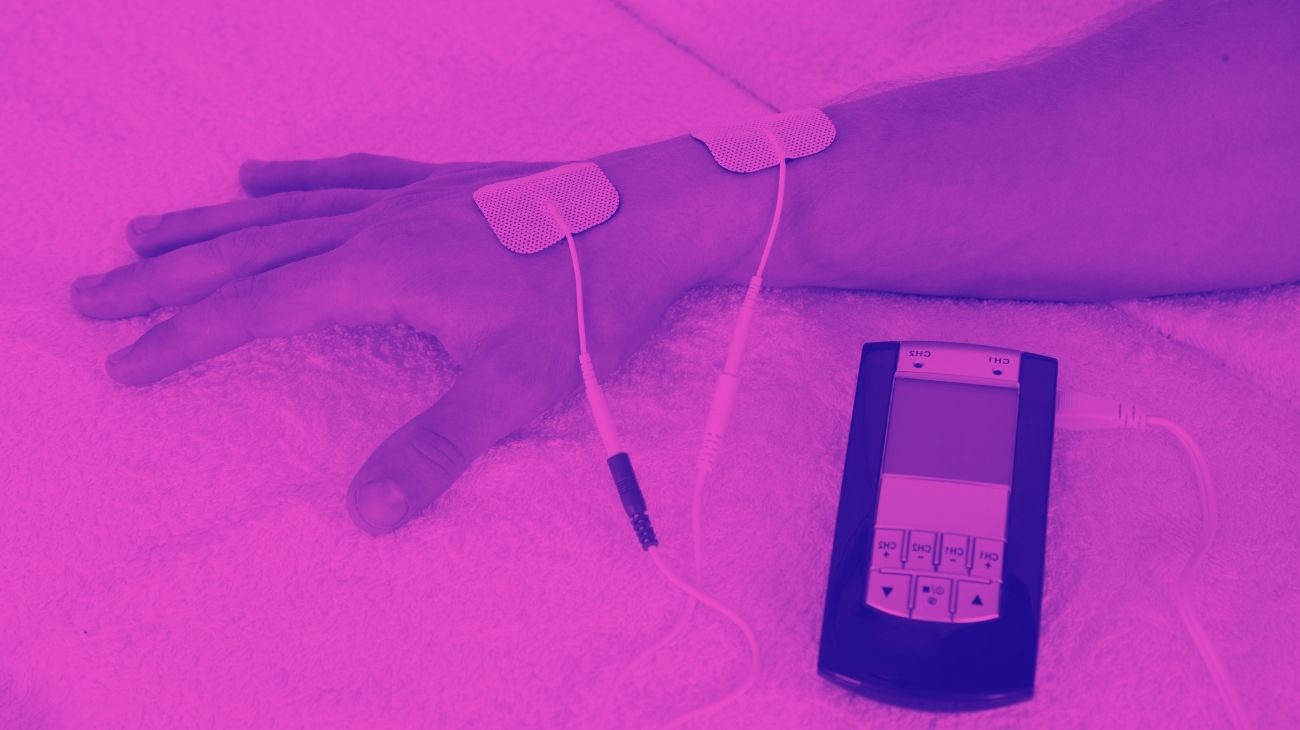
Where to place the electrodes?
To relieve nerve pain or reduce tremors, it is important to locate the area of pain precisely, and to know where it originates, since the effectiveness of the therapy will depend to a great extent on this. Once this is done, what should be done is to "enclose" this area in the middle of two pads, or even in a quadrant in case we have 4 of them in our device.
Which current to use?
In general, TENS devices have several programs that automatically adjust the frequency for each type of ailment or objective, with programs for muscle damage, arthrosis and neuropathies. However, this may not be your case and you may have to adjust the frequencies manually. In this case, take into account the following guide:
- Frequencies between 2HZ and 4Hz: endorphin release, relaxation and pain relief.
- Frequency between 20Hz and 70Hz: nerve rehabilitation, reduction of tremors and muscle weakness.
- Frequency between 80Hz and 100Hz: relief of severe pain, chronic pain in muscles and joints.
- Frequencies of 100Hz and above: as indicated by the physician.
Best TENS units to treat nerve damage
Below we share with you a list of the best TENS units you can find on the market to help you recover from your nerve damage without any problems.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 10 Pads
- Display: Touch
- Size: 5.12" x 2.56" x 0.39" - 0.35 lbs
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Not for muscle hypertrophy
- Does not include user manual
- No heat therapy
It has 24 modes of use and 20 intensity levels that can be applied in isolation to each of the device's channels thanks to its dual channel function, allowing different therapies to be applied to separate areas of the body. In addition, it has a session timer mode and automatic shut-off that will allow you to give greater efficiency to your sessions and make better use of the energy of its high-capacity lithium battery.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 8 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 3 AAA Batteries
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 2.14" x 5.5" x 7.08" - 0.33 lbs
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves joint mobility
- Portable and small size
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Good quality
- Few types of programs
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
- Battery operated
It has an interesting session timer function that allows you to adjust the duration of each therapy up to a maximum of 60 minutes. Its compact size allows it to be carried in your pocket, so you can take it with you from home to work, or on the road, and use it whenever you need it.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes carrying bag
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- No heat therapy
- No touch screen included
The use of TENS and EMS that this device provides will allow you to use them to apply relaxing massages that relieve any ailment in a natural way, stimulating the production of endorphins and blocking the body's pain signals, as well as electrical discharges that stimulate muscle movement, creating contractions that encourage the growth of muscle fibers, increasing the tone and strength of the muscles.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- 4 independent channels
- Provides cramp relief
- Portable Device
- Promotes tissue healing
- 24 programs
- Few electrodes
- Does not specify battery life
- Does not specify intensity and size
It has 24 clinically proven massage programs, which are divided into 12 TENS therapy programs and 12 muscle stimulation training modes. It has a long-life rechargeable lithium battery that will give you a great autonomy of several hours of continuous use, eliminating the extra cost of buying replacement cylindrical batteries.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 6 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Portable and small size
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Includes carrying bag
- No intensity levels specified
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
It has 6 modes of use that emulate different types of massages to achieve different objectives, along with 10 levels of intensity that provides greater effectiveness. The package includes 1 control, 2 large electrodes, 2 small electrodes, 2 guide cables, 1 user's manual, 1 cable case and 1 treatment guide.
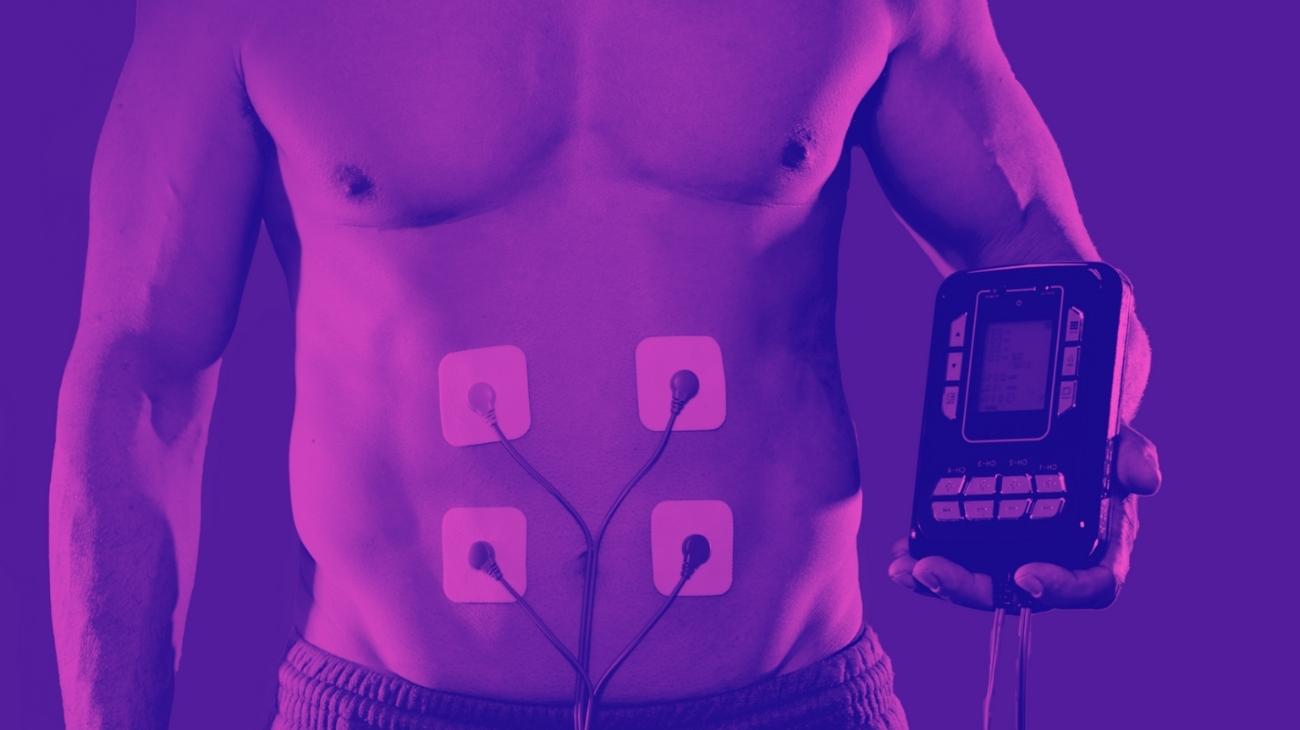
How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent nerve damage?
EMS focuses on strengthening muscles, but there is a way to use the muscle contraction it generates to provide a gentle muscle massage that releases tension from the nerves, avoiding possible pain from injuries such as nerve impingement to name a few.
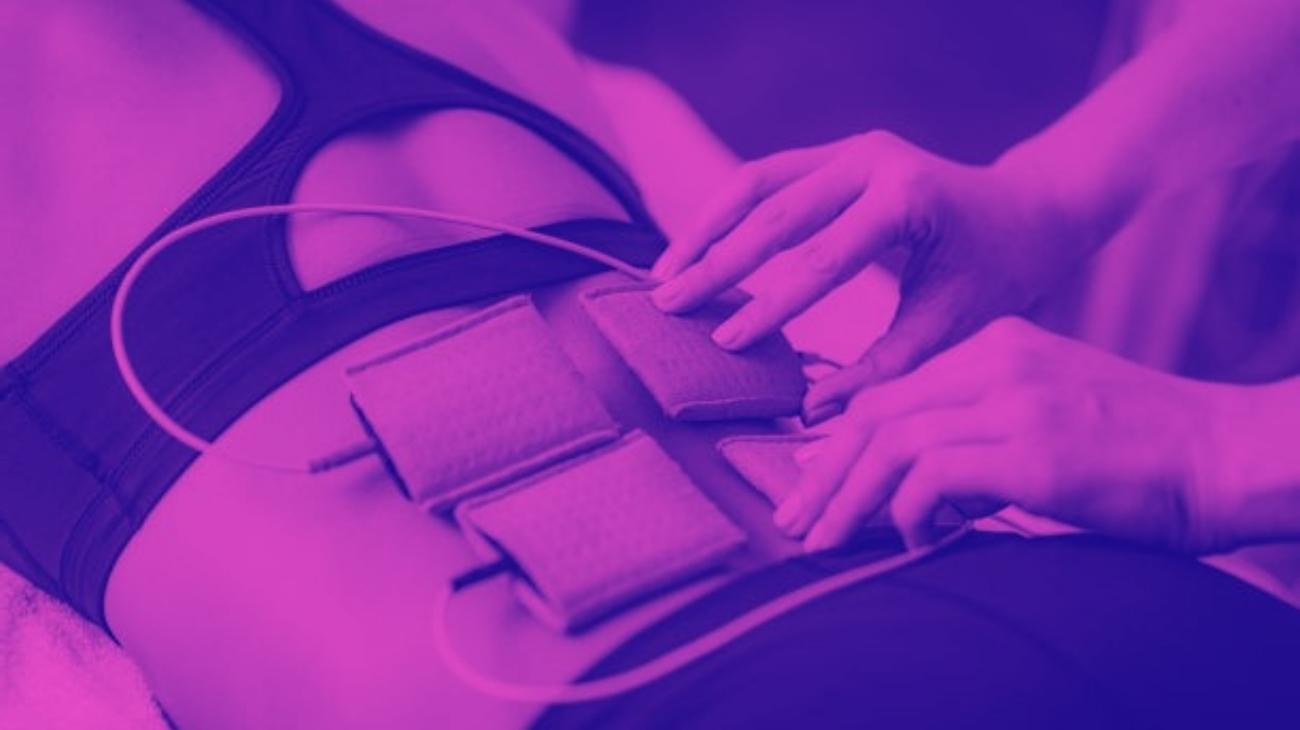
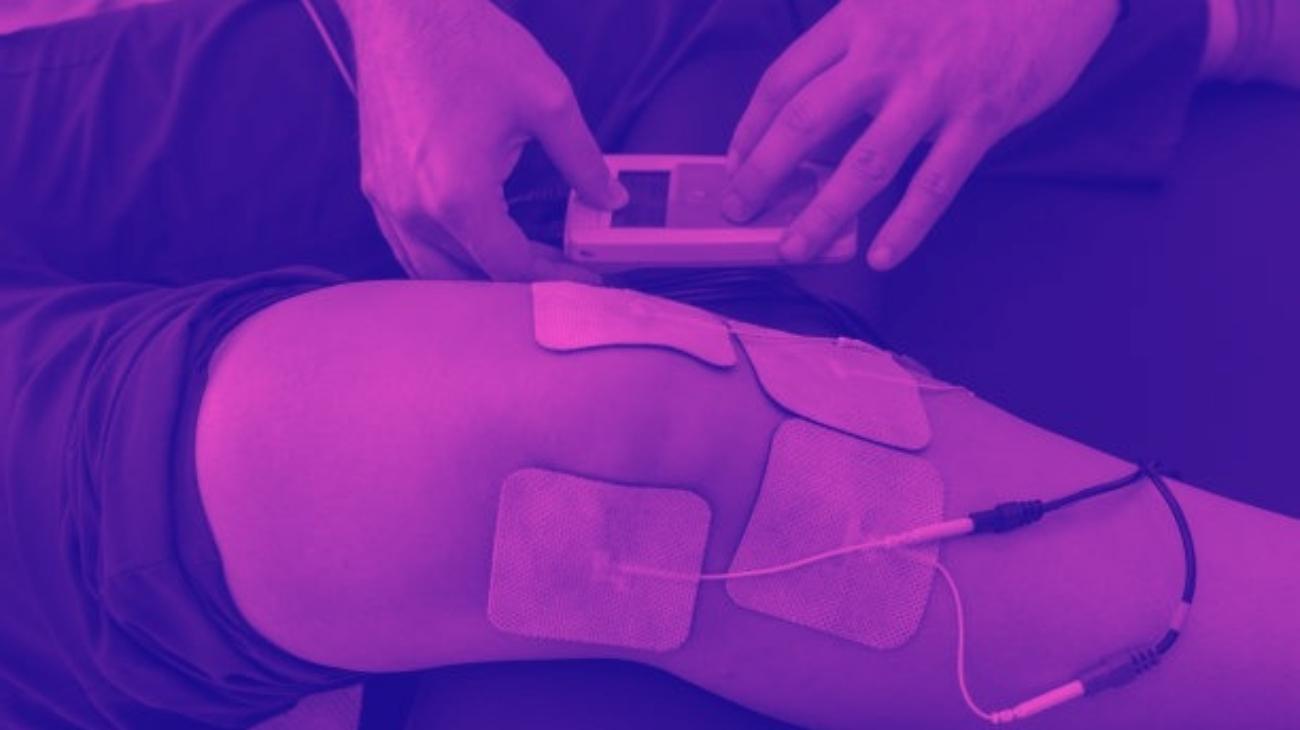
Where to place the electrodes?
The placement of the electrodes pads should be identical to what you would do when you want to train a muscle. In this case, the important thing will be the intensity of the current to be used.
What intensity to use?
The intensity is the most important thing in this case, since what we need is a high frequency current but less intense than normal, so that a slight muscular contraction is generated, not as intense as the one we would look for to achieve hypertrophy for example.
As in the case of TENS devices, EMS machines have various training programs that automatically adjust the intensity of the current, programs such as "Warm-up", "Massage", "Toning" or "Hypertrophy" can be present in your electro stimulator.
Best EMS machines to avoid nerve impingement
Here are the best EMS stimulators that you can use to get a relaxing massage that releases tension from your nervous system.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 10 Programs
- Intensity: 5 levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 12 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: 5.38" x 3.75" x 1"
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Rechargeable battery
- Good quality
- Includes carrying bag
- Few intensity levels
- No weight specified
It includes 10 electrostimulation modes divided into 3 recovery modes, 2 warm-up modes, 1 TENS massage mode and 4 strength training modes. It also has 5 levels of progressive intensity that will help you improve your strength, endurance and combat various ailments caused by exhaustion.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 32 Modes
- Intensity: 100 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 4 AA Batteries
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 5.4" x 3.1" x 1.1" - 0.6 lbs
- TENS+EMS combo
- Includes carrying bag
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes user manual
- No heat therapy
- No battery life specified
- No touch screen included
It has 8 customizable modes of use, of which 5 apply TENS current and 3 apply EMS current. It also has different levels of intensity, frequency and pulse radius, making it one of the most versatile electrostimulation machines on the market.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Programs
- Intensity: 30 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (20 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 10 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes carrying bag
- With 30 intensity levels
- 24 modes
- With 10 pads
- Timer option
- No heat therapy
- No size specified
It has 24 modes of use and 30 intensity levels that you can program individually on each of its 4 channels, so you can apply them to different parts of the body, or even different people, simultaneously. Its high-powered battery will allow you to apply electrostimulation for 20 continuous hours, and is fully rechargeable through the current or from a USB charger.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 6 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Lithium Rechargeable (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 13 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS combo
- Long battery life (up to 10 hours)
- Portable and small size
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Improves joint mobility
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify size and weight
- Some electrodes dry quickly
It has a rechargeable lithium battery that allows you to use your device for up to 20 uninterrupted hours. It can be plugged into wall outlets, or charged via USB connection. It is a perfect alternative for the treatment of ailments without side effects and avoiding the use of drugs.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 14 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 5 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS combo
- Rechargeable battery
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Includes user manual
- Includes carrying bag
- Does not specify intensity levels
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- No heat therapy
Its rechargeable battery gives you 8 to 10 hours continuous run time per full charge, and each of the pods provides 3 to 5 hours of continuous operation. With 8 TENS and 6 EMS preset programmes, along with 25 intensity levels, its 4-channel system allows you to perform isolated treatment on various muscle groups. Undoubtedly the most complete option you can find for the treatment of ailments.
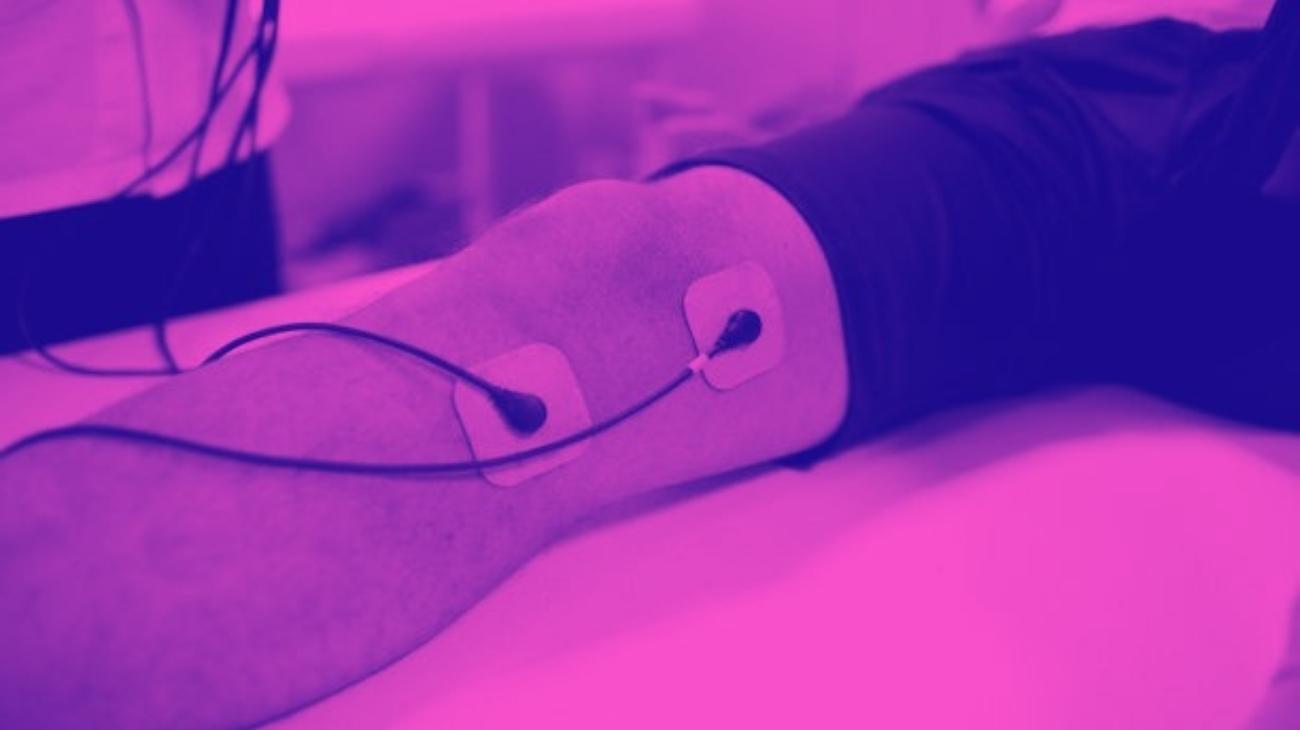
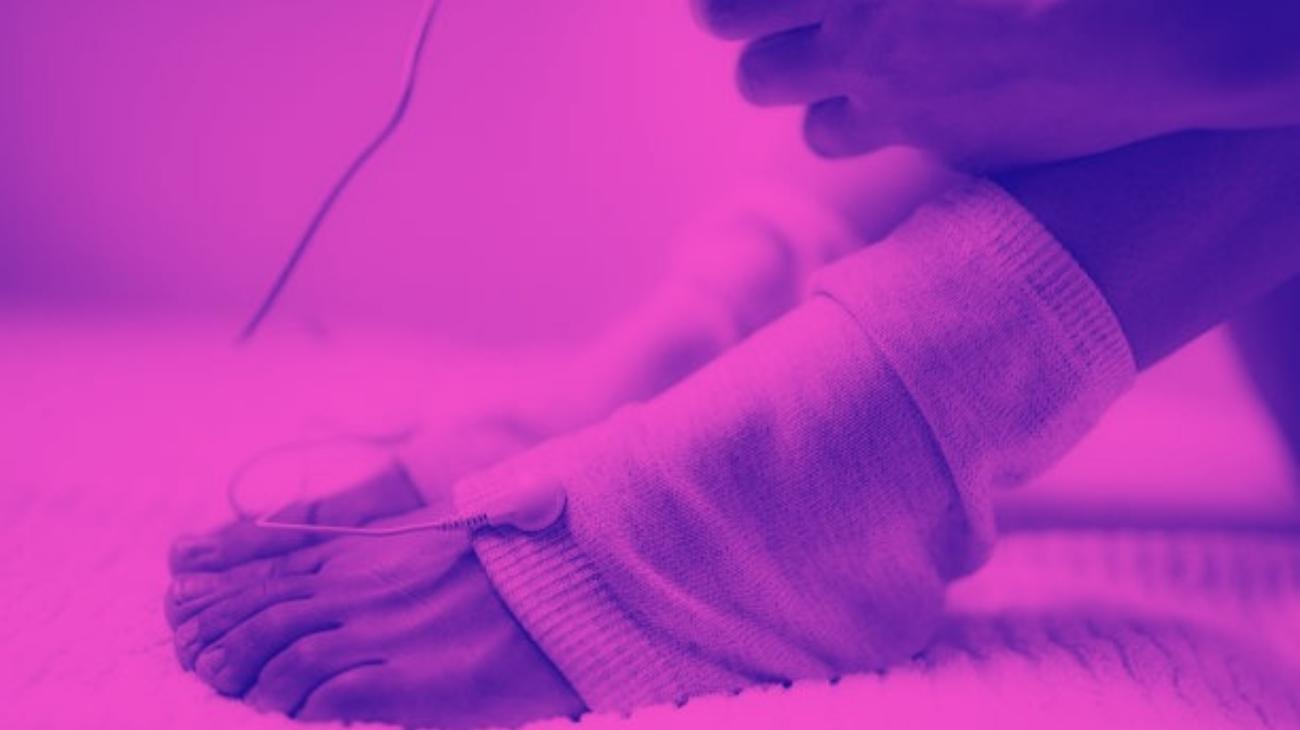
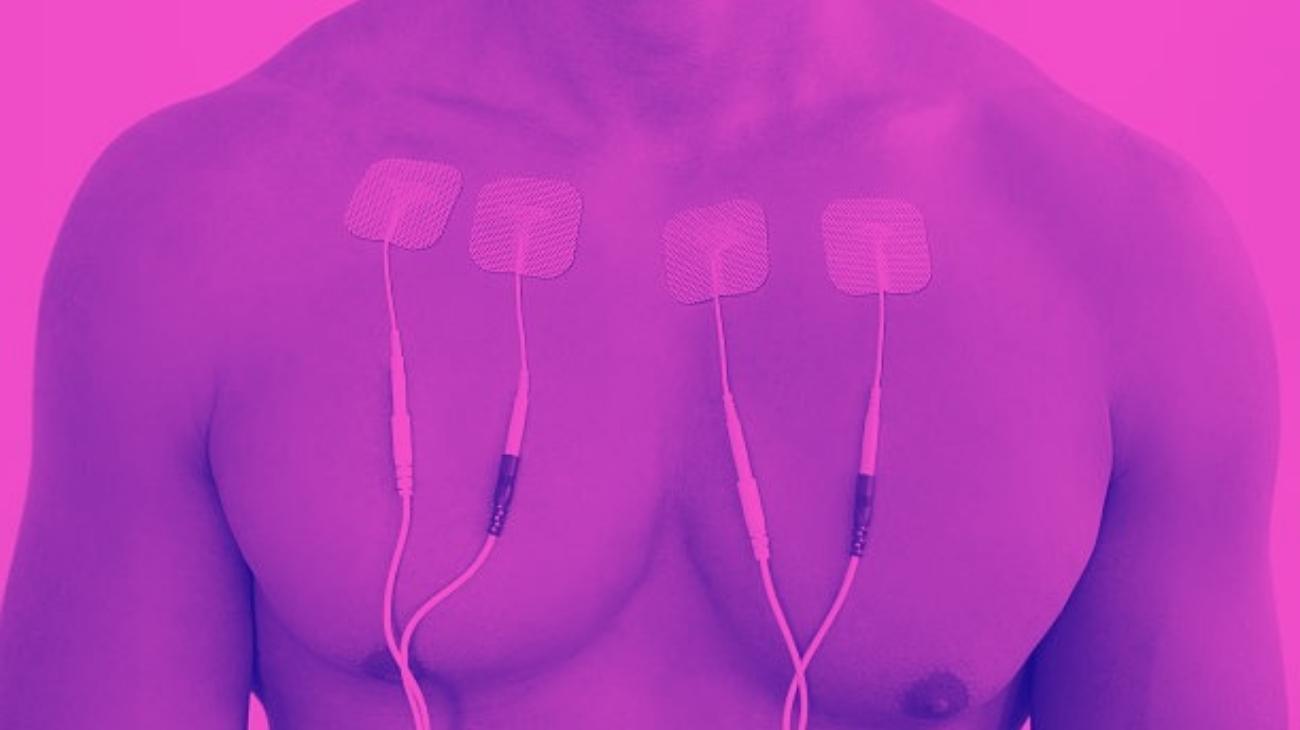
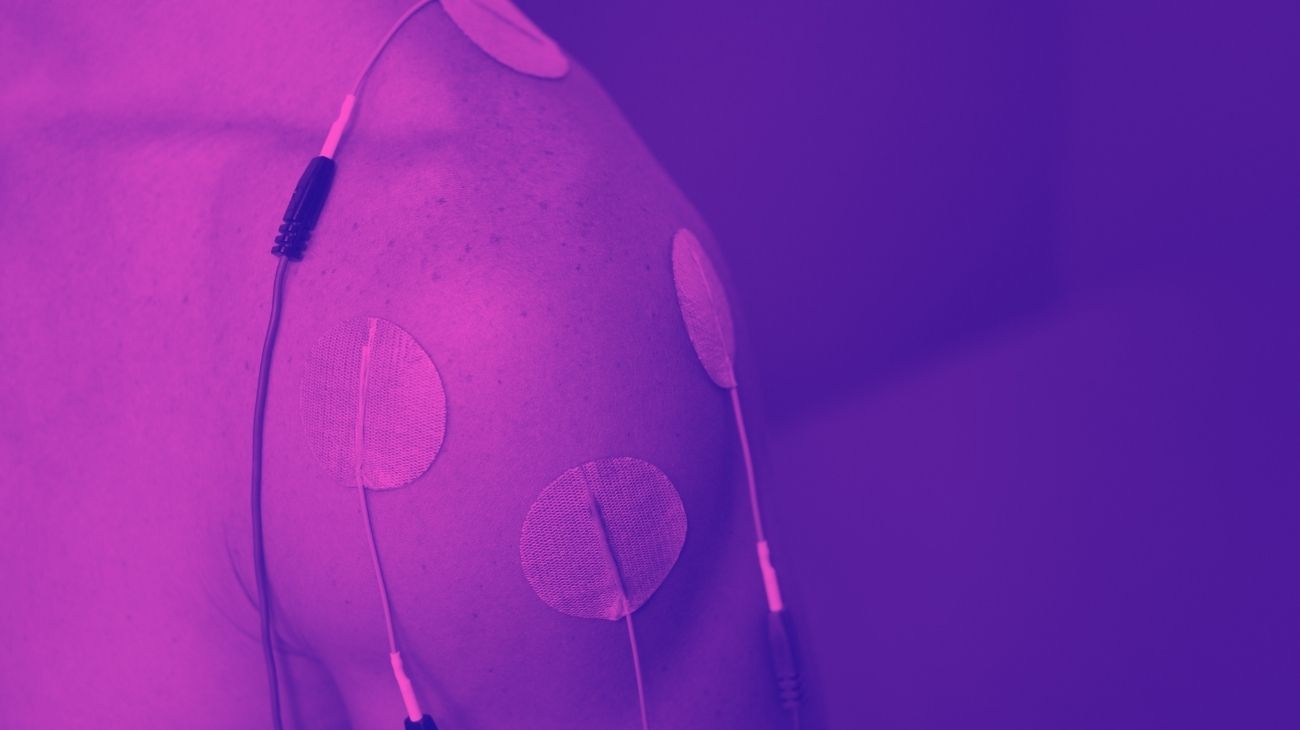
Video: How to place the electrodes pads for nerve pain?
Electrodes for arms
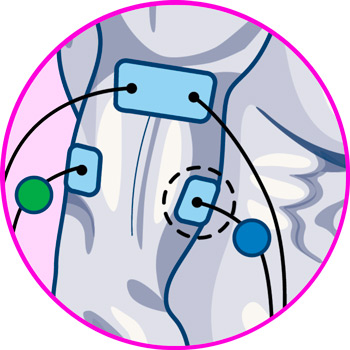

Electrodes for forearms
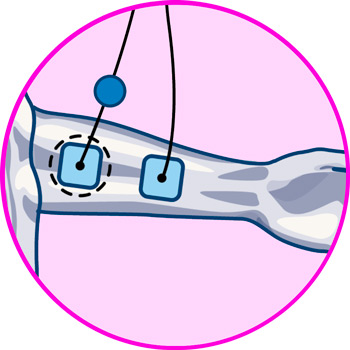
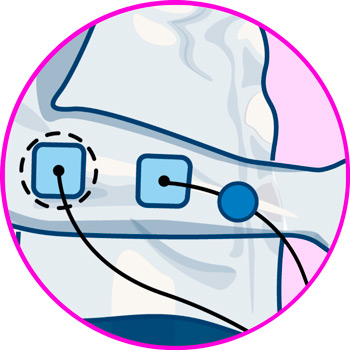
Electrodes for back
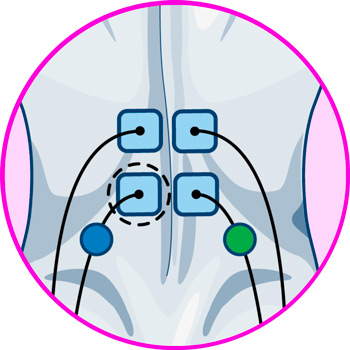
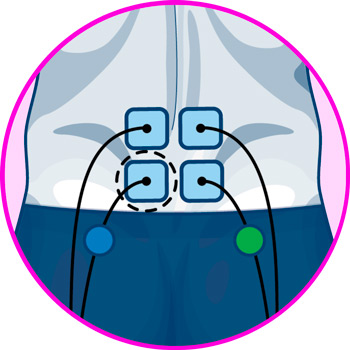
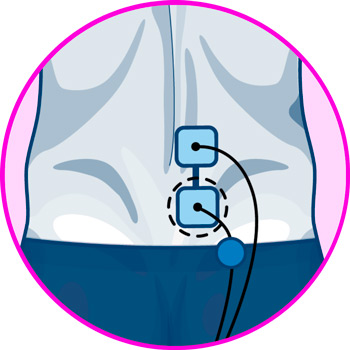
Electrodes for legs
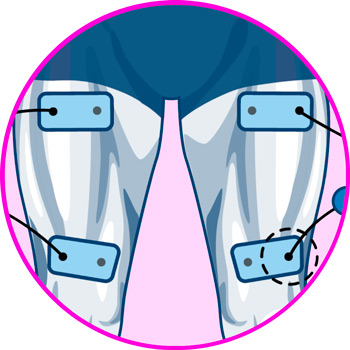
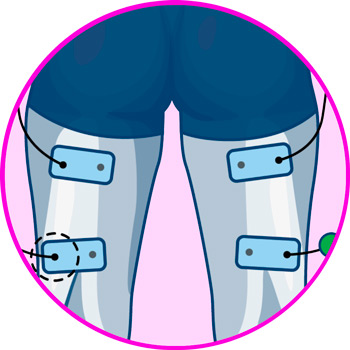
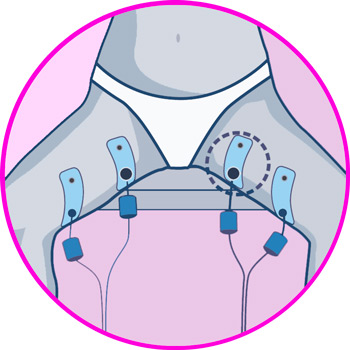
Electrodes for calf
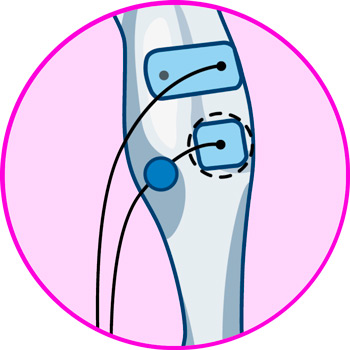
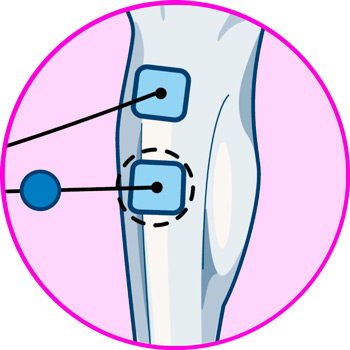
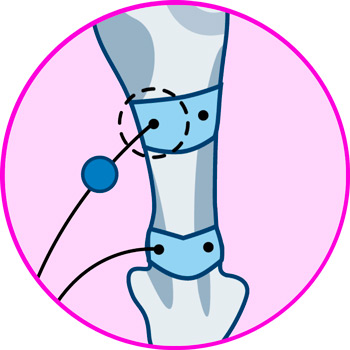
More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know about
What is nerve damage and what are the causes?
It refers to the damage that a nerve can receive because it has deteriorated over the years. Nerve damage can cause a nerve to atrophy, compressing or stretching in such a way that the electrical signals sent to the brain do not flow normally. But it can also generate a wear that makes these currents are not supported by the tissue, as when the insulation of a cable wears out and lets the voltage escape.
Among the main causes of nerve damage we can highlight the following:
- Hypertension: an increase in the amount of blood flowing through the arteries can cause damage to the arteries, nerves and various vital organs. High blood pressure is one of the five most common causes of nerve damage in the world.
- Recurrent injuries: these can be muscular, articular or even bone. The truth is that when we are injured, the nerve tissue that runs through the injured area becomes inflamed as well as the other tissues, which is why the characteristic pain of any injury is generated, since muscles and joints are covered by thousands of nerve branches that if constantly damaged can cause chronic and irreparable neuropathies.
- Cardiac conditions: as with hypertension, a failure in blood pumping due to cardiac diseases such as arrhythmia, is potentially harmful both for the nerves and for the other tissues and organs of the body.
- Diabetes: excess glucose in the blood changes its density and fluid composition, which gradually causes damage to all body tissues, including nerves.
- Brain damage: whether due to a tumor, a stroke or a car accident, any damage to the brain will directly affect the entire nervous system.
- Lifestyle: sedentary lifestyle, night life and addictions, especially to chemical drugs, have a negative impact on the nervous system that will wear it down over the years, until it generates some chronic and irreparable pathology.
What are the most common types of nerve damage?
The human body has between 31 and 33 pairs of nerves that originate in the spinal cord and extend throughout the body, joining bones, muscles and ligaments thanks to the fascia. This means that the number of diseases caused by damage to these nerves is quite large.
Below you will learn about the most common ones affecting society:
- Nerve impingement: occurs when a nerve shortens or contracts in a section of it, generating a tension that will cause intense pain.
- Nerve strain: occurs when a nerve is stretched too much, and maintains a longer than normal size for a considerable period of time, which generates weakness in this and the surrounding muscles. A common cause of this type of injury is pregnancy or muscle tears.
- Nerve percussion: occurs when a sharp object pierces the nerve, which is common in total fractures of large bones such as the femur, humerus or tibia.
- Nerve laceration: occurs when a nerve is cut with a sharp object, as may happen when receiving a stab wound, or by domestic accidents with a knife or some other lethal object of this style.
There are other classifications such as nerve freezing or damage from drug or heavy metal poisoning found in junk food and processed foods. Now, within each of these classifications there are a large number of injuries such as the following:
- Neuromas.
- Diabetic neuralgia.
- Peripheral neuropathy.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating damaged nerves?
To alleviate some of the ailments and symptoms generated by nerve damage, we can count on electrotherapy. This has two modalities known as TENS and EMS, which use currents to achieve a physiological response of the organism.
The TENS current or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation uses more intense currents, but these have a much lower frequency, which makes it enter through the skin and reach the nerve endings. It can be used to stimulate the nerves, which is very useful to rehabilitate them after a muscle or nerve injury, although its main function is to increase the pain threshold that a nerve can tolerate.
On the other hand, EMS or electrical muscle stimulation uses currents of lower intensity but with a higher frequency, which go through the skin and reach the muscle directly to achieve muscle contraction. At first glance it seems that it does not have much to do for people with nerve damage, but the reality is much broader.
The main difference between both therapies is mainly focused on the user experience; while TENS generates a tingling and tingling in the skin, EMS is more "aggressive" by generating a direct muscle contraction. In addition, there is also the range of work of each; TENS focuses on the nerves, while EMS focuses on the muscles.
Although it may not seem like it, both can help you both relieve and prevent nerve damage. While you may think that only TENS has this quality, EMS can also do this because by working on the muscle tissue, it can be of great help in releasing tension on the nerves and preventing future neuropathies.