- How to use TENS machines to relieve elbow pain?
- Best TENS units to treat elbow injuries
- How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent epicondylitis and epitrochleitis?
- Best EMS machines to avoid elbow joint injuries
- Video: How to place electrodes pads on the elbow?
- More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
- What types of elbow injury are there and what are the causes?
- Differences between epicondylitis and epitrochleitis?
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating tennis or golfer's elbow?
- Contraindications in the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
The elbows are among the most important joints of the human body, since they are responsible for much of the mobility of the arm, in addition to carrying a large amount of stress, which can vary depending on the lifestyle of each person. Among the most common elbow joint injuries are lateral epicondylitis, popularly known as tennis elbow, and medial epicondylitis or golfer's elbow.
These almost exclusively sports injuries can be particularly painful, so an effective method of treating their symptoms is necessary. This is where TENS and EMS electrostimulation therapies come in. Below, we will teach you everything you need to know about this ailment, and how to use electrotherapy to treat its symptoms effectively.
How to use TENS machines to relieve elbow pain?
The electric shocks applied by TENS devices have the characteristics of being able to interact on the innervation of the treated area, so they are very effective when applied on a nerve-covered area such as the elbow.
Next, you will learn how to place the electrodes and the optimal intensity to apply to achieve an optimal TENS session:
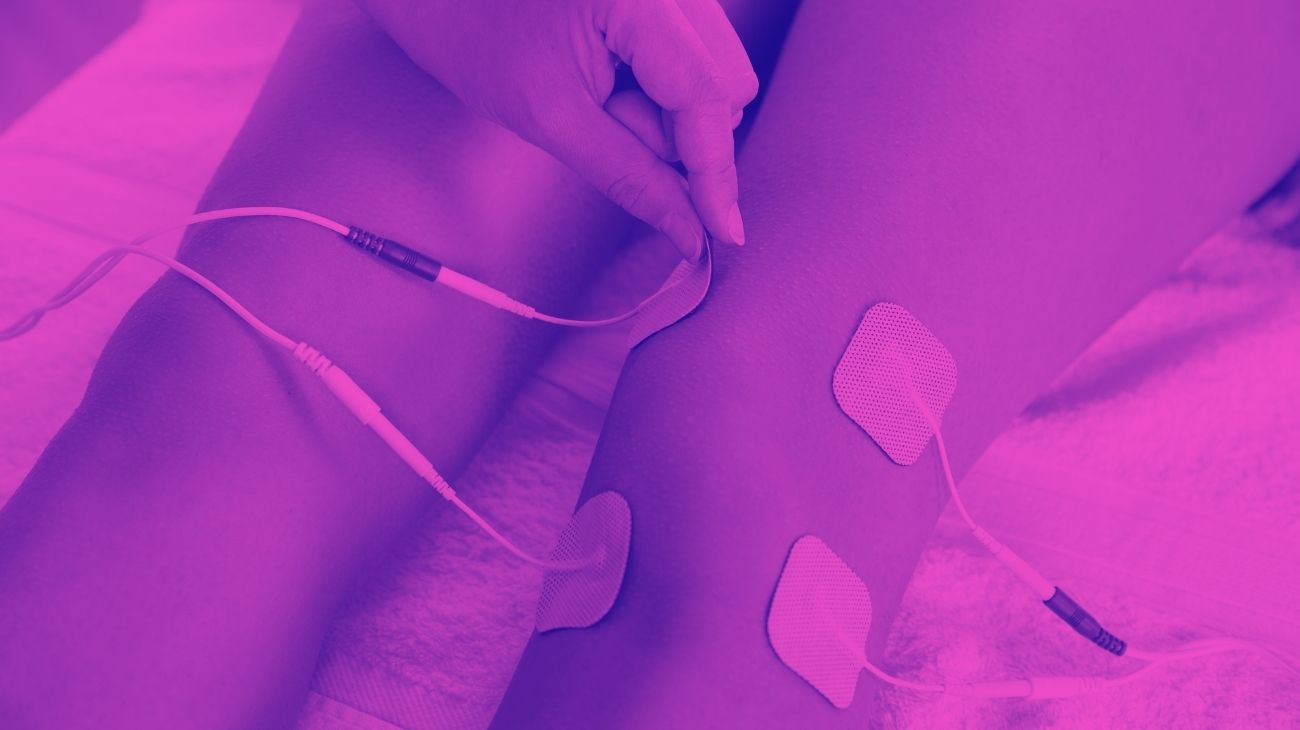
How to place the electrodes?
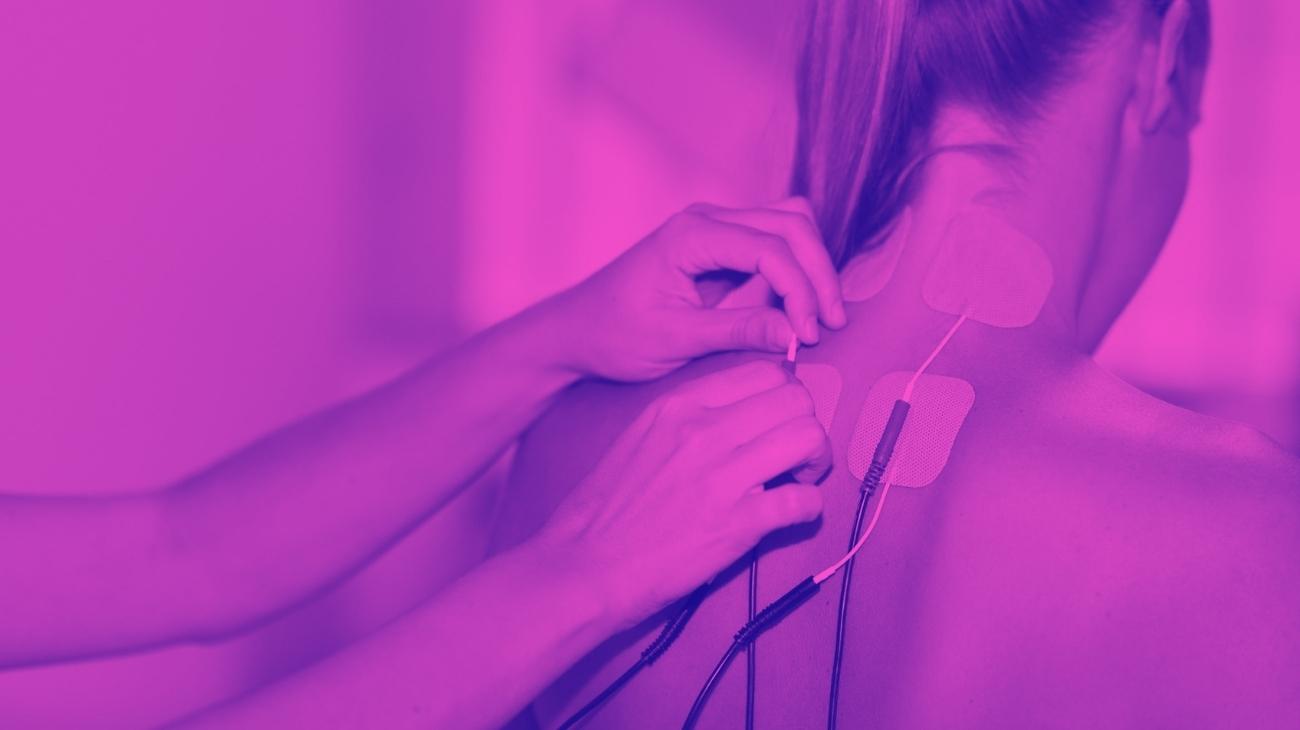
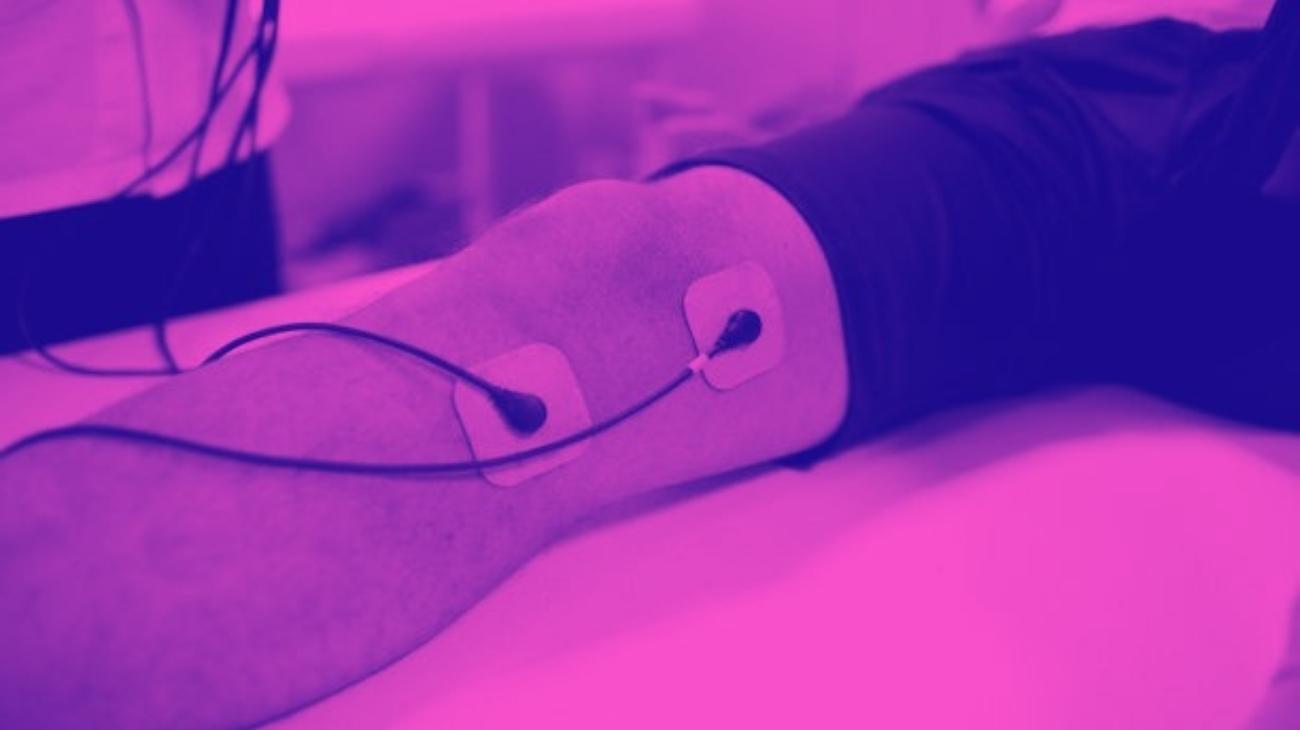
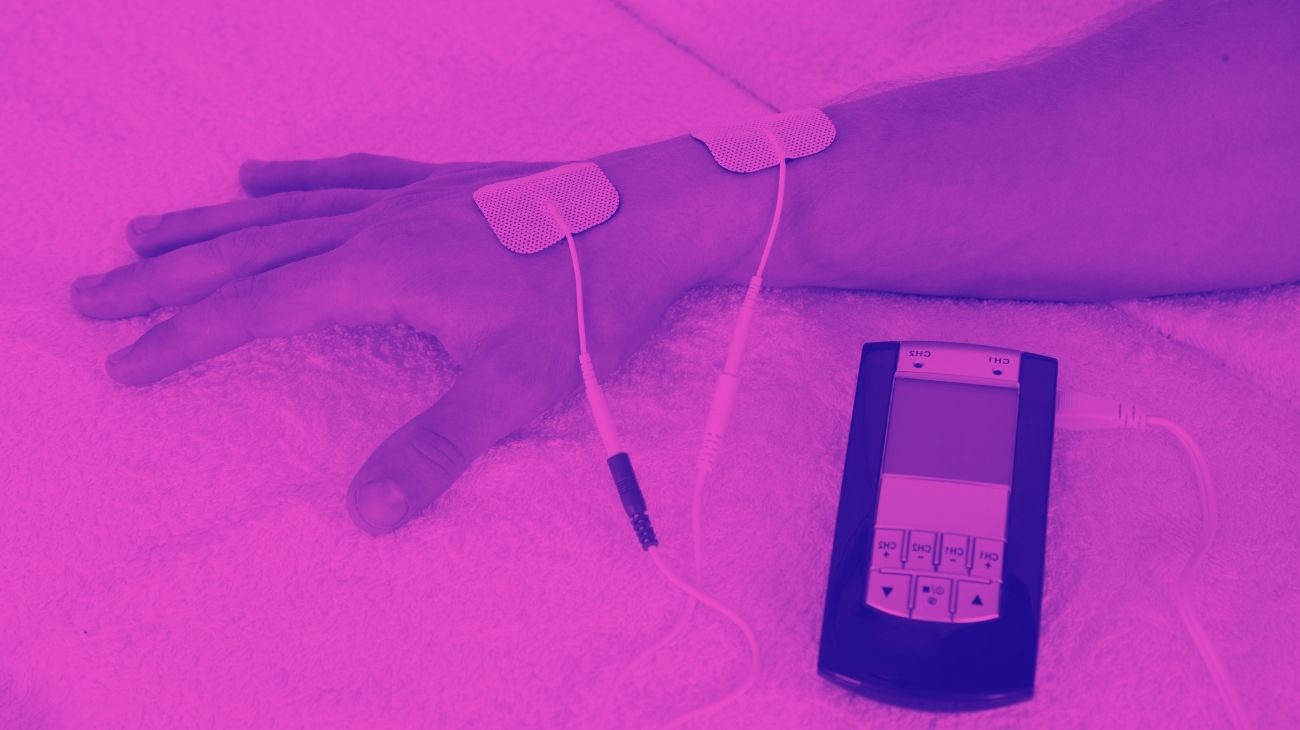
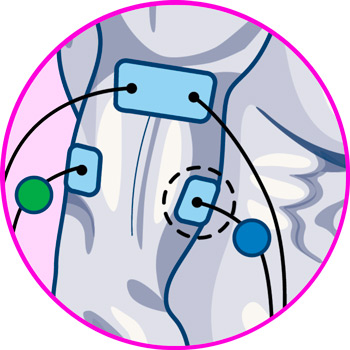
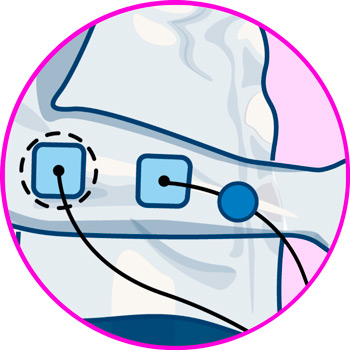
For TENS therapy to be effective in treating elbow pain, it is necessary to take into account the positioning of the electrodes. It is important to emphasize that the point of pain should be located in the middle of both pads, so that the current passes through it correctly.
For pain in the external aspect of the elbow, a common symptom of tennis elbow, two electrodes should be placed, one in each of the following positions:
- Triceps brachii vastus externus
- Pronator teres muscle
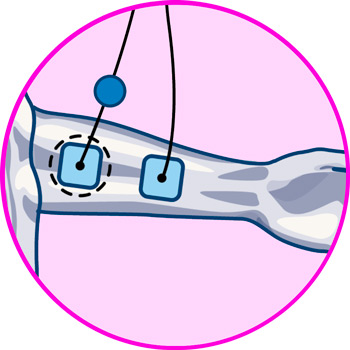
For golfer's elbow, the positioning differs slightly, with the ideal locations being as follows:
- Medial head of triceps brachii
- Brachioradialis muscle, at the border with the pronator teres muscle.
What current intensity to use?
The optimal current for the treatment of symptoms caused by injuries such as tendonitis and epicondylitis will depend largely on two factors: the intensity of the pain and the duration of the pain.
For conditions lasting less than three months, known as acute pain, the ideal is to apply moderately high frequencies, between 90 and 120 Hz, to ensure maximum interaction with the radial, median and ulnar nerves, and to achieve a rapid and prolonged effect
In the case of chronic pain, the situation is different, since they are persistent ailments that afflict the patient for periods longer than three months. For these ailments, the ideal current is between 2 and 10 Hz for prolonged periods, in order to stimulate the release of endorphins and generate a feeling of relief in the patient.
Best TENS units to treat elbow injuries
The variety of TENS devices that have emerged thanks to their effectiveness and popularity for pain treatment gives us a wide selection of machines with their own programs for treating the symptoms of epicondylitis and other elbow ailments. Among the best devices you can use, we can highlight the following:
Hi-Dow - Dual channel TENS/EMS unit for physical therapy with 8 modes & 20 intensity levels & 4 pads
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 8 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 6" x 4" x 5" - 0.63 lbs
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Portable and small size
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Includes user manual
- Rechargeable battery
- Battery life not specified
- No carrying bag included
- No heat therapy
It has 8 preset programs and 20 intensity levels, along with a session timer function that you can set between 10 and 60 minutes. Its built-in rechargeable lithium battery provides excellent durability, and the package contains 1 XP Micro 8 electrostimulator, 1 set of large pads, 1 set of small pads, 2 cables, 1 power adapter, 1 user manual and 1 carrying case to take it wherever you need it.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 14 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 3 AAA Batteries
- Electrodes: 12 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Improves joint mobility
- Improves blood circulation
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Transport bag not included
- Without heat therapy
It has a total of 14 massage modes, of which 7 are TENS-type currents for pain relief, 1 mode for arthritis pain treatment, and 6 modes for muscle recovery and therapy. In addition, you can adjust the intensity to any of its 25 levels, and define the duration of each session from 5 to 60 minutes thanks to its timer function.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 16 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 30 hours)
- Electrodes: 12 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Good quality
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Long battery life (up to 30 hours)
- Includes carrying bag
- No heat therapy
- No touch screen included
- Does not specify measurements and weight
What distinguishes this electrostimulator from others on the market is its lightweight design with black and gold finishes, its high quality materials and the inclusion of a dust-proof leather bag with which you can take it wherever you want safely. The compact size in which you can find this device will allow you to take it with you and use it wherever you like very easily, as it is incredibly discreet.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 15 Programs
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- Independent control mode
- Instant pain relief
- 20 intensity levels
- 15 different working modes
- Portable device
- Battery life not specified
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
- No heat therapy
All its modes of use are FSA and HSA approved, making it completely safe for anyone to use. It can be operated and set up very easily. The package includes reusable electrodes coated with adhesive gel in 3 sizes: 2 units of 2x4 inches, 4 units of 2x2 inches and 2 units of 1.5x1.5 inches.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 6 electrodes
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Portable and small size
- Good quality
- Few intensity levels
- Does not specify size and weight
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
It has multiple modes of use and its A-B output channel allows you to apply two types of massage simultaneously, making it one of the most versatile devices available on the market. The package includes 1 control, 1 protective case for the TENS unit, 3 pairs of electrodes, 4 power output cables, 1 USB cable, 1 user manual, 1 plastic case and 1 belt clip.
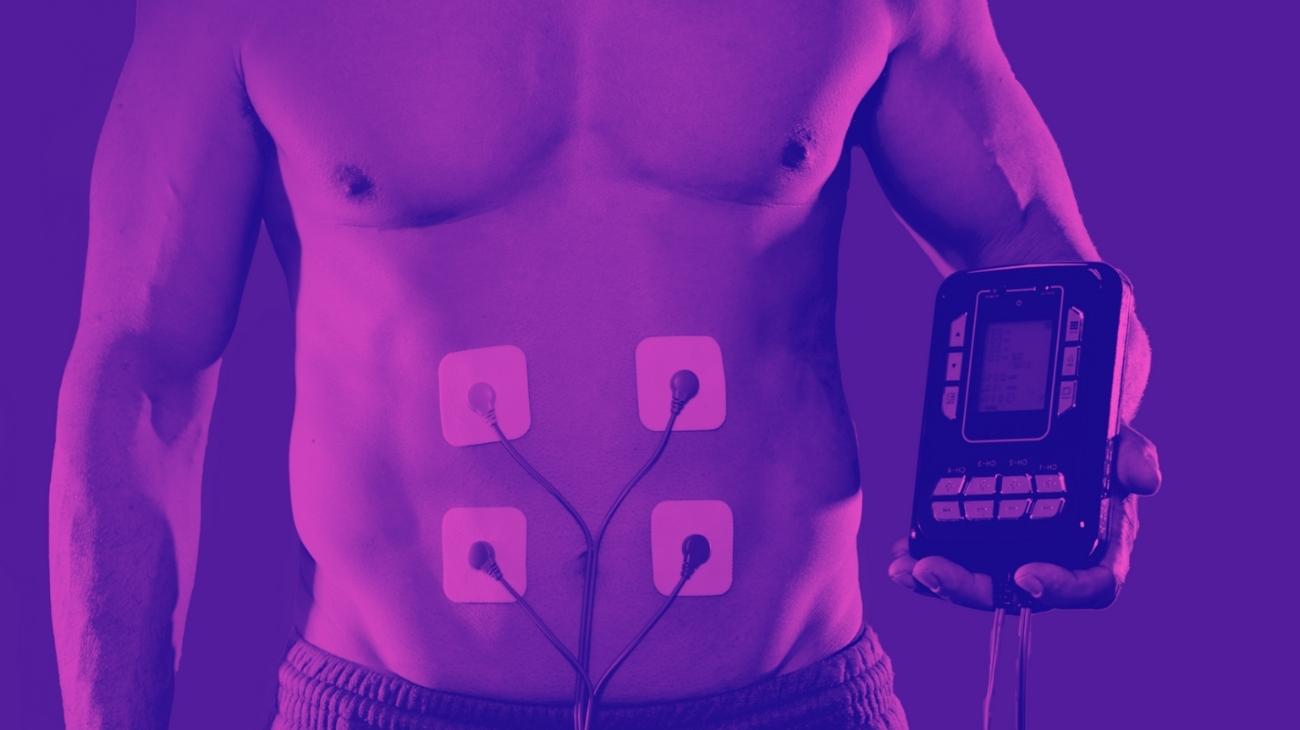
How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent epicondylitis and epitrochleitis?
While EMS therapy is contraindicated for elbow injuries, it has great potential to condition the musculature surrounding and moving the elbow in order to reduce the chances of suffering any of these.
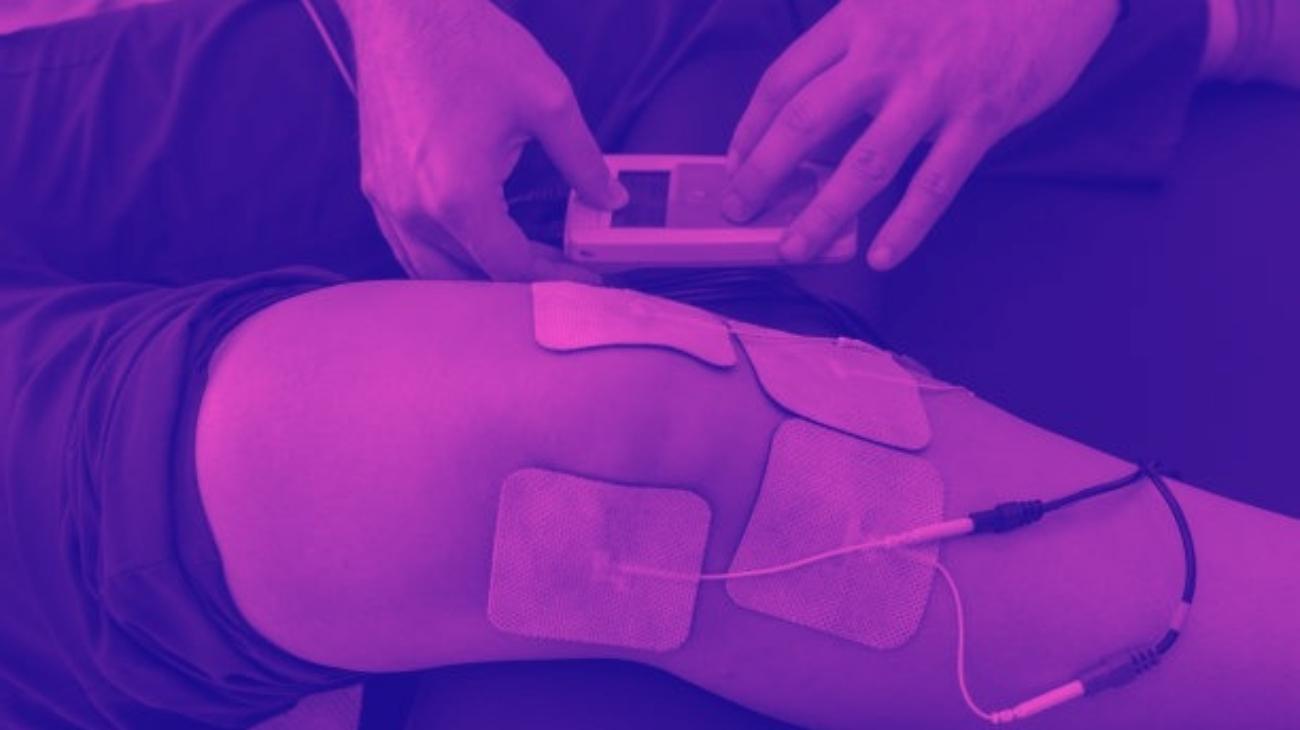
Where to place the electrodes?
Below, we will show you how to position the electrodes and what intensity of current to apply to the arm musculature to increase the stability of the elbow joint and prevent epicondylitis, epitrochleitis and other injuries.
To strengthen the muscles that surround and stabilize the elbow, it is necessary to position an electrode on the muscle belly of each muscle you want to work, so that the electrical impulse generates a complete contraction in the muscle or muscle group.
The ideal areas to position the EMS machine's electrodes are as follows:
- Long portion and short portion of biceps brachii
- Anterior brachioradialis muscle
- Triceps brachii
- Anterior and posterior part of the forearm
What intensity of current to use?
The use of electrical impulses on the muscles adjacent to the elbow is very useful when it comes to improving the stability and resistance of the joint, helping to prevent injuries and improve its capabilities, for which it is necessary to choose the frequency indicated for the muscles in question.
In the case of the triceps brachii, anterior brachialis and biceps brachii, the ideal frequency for training purposes ranges from 65 to 85 Hz, with variations in the duration of each session and the time of each shock, which depend on the user's objectives.
Best EMS machines to avoid elbow joint injuries
In the sports arena, muscle training and conditioning is vitally important, both to thrive in the competitive environment and to keep the body in optimal condition and avoid wear and tear, which is particularly important when it comes to maintaining joint stability.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 10 Programs
- Intensity: 5 levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 16 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: 4.25" x 2.75" x 0.75", 1 Lb
- Wireless electrodes
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Improves joint mobility
- Reduces pain symptoms
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Touch screen not included
- No battery life specified
- No heat therapy
It is the perfect tool to maximize the results of your workout thanks to its electrical impulses that stimulate the growth of muscle fibers, while reducing and even preventing pain caused by exercise and promoting a quick recovery.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 14 Programs
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 5 hours)
- Electrodes: 2 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Rechargeable battery
- Improves blood circulation
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves joint mobility
- Portable and small size
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- No heat therapy
- Non-universal electrode replacements
It has 14 operating programmes dedicated to particular functions. 7 are designed for pain relief, 1 is designed to treat arthritis, and the remaining 6 are different muscle conditioning modalities. In addition to the controller, the box includes 2 wireless pods, 2 reusable 3x5 inch adhesive electrodes, a rechargeable lithium battery, a USB charging cable, a carrying case and an instruction manual.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 6 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Lithium Rechargeable (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 13 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS combo
- Long battery life (up to 10 hours)
- Portable and small size
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Improves joint mobility
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify size and weight
- Some electrodes dry quickly
It has a rechargeable lithium battery that allows you to use your device for up to 20 uninterrupted hours. It can be plugged into wall outlets, or charged via USB connection. It is a perfect alternative for the treatment of ailments without side effects and avoiding the use of drugs.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 24 Programs
- Intensity: 30 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (20 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 10 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes carrying bag
- With 30 intensity levels
- 24 modes
- With 10 pads
- Timer option
- No heat therapy
- No size specified
It has 24 modes of use and 30 intensity levels that you can program individually on each of its 4 channels, so you can apply them to different parts of the body, or even different people, simultaneously. Its high-powered battery will allow you to apply electrostimulation for 20 continuous hours, and is fully rechargeable through the current or from a USB charger.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes carrying bag
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- No heat therapy
- No touch screen included
The use of TENS and EMS that this device provides will allow you to use them to apply relaxing massages that relieve any ailment in a natural way, stimulating the production of endorphins and blocking the body's pain signals, as well as electrical discharges that stimulate muscle movement, creating contractions that encourage the growth of muscle fibers, increasing the tone and strength of the muscles.
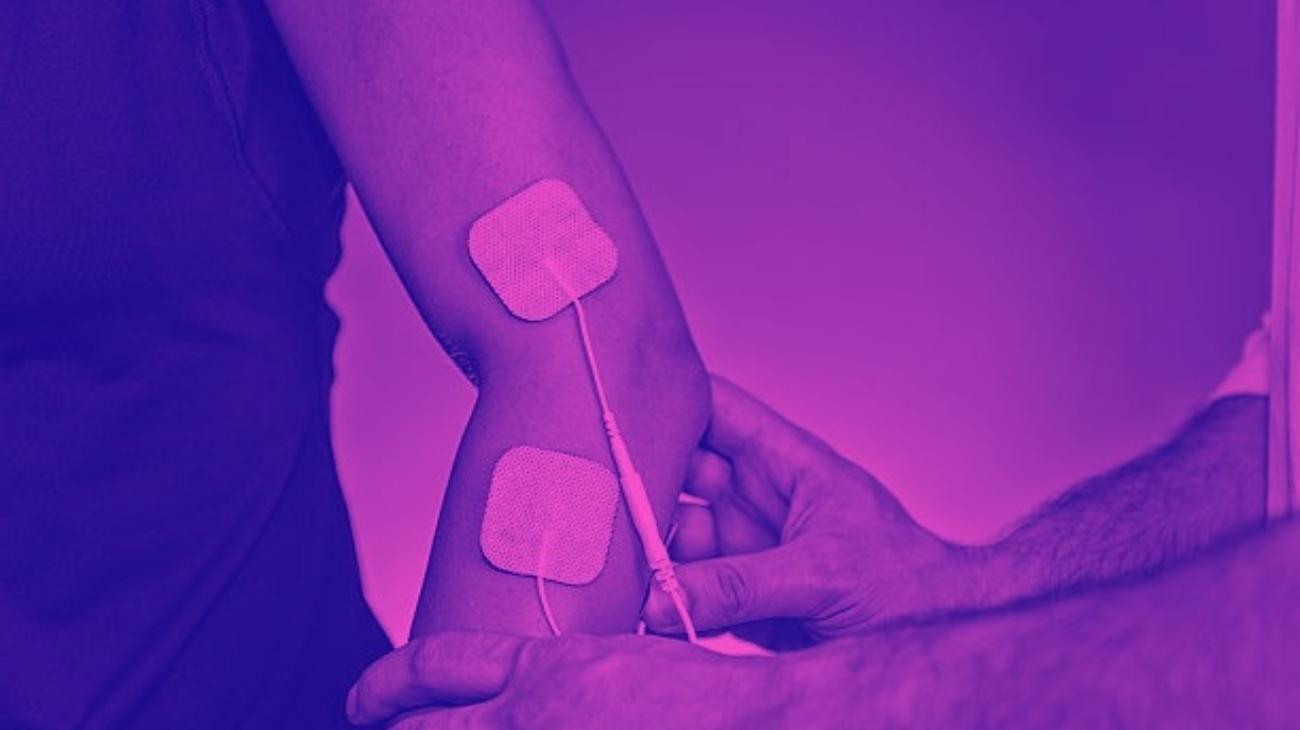
Video: How to place electrodes pads on the elbow?
Electrodes for elbow
More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
What types of elbow injury are there and what are the causes?
While it is a fairly resilient joint, the elbow is made up of soft tissues that can be injured if used excessively, with improper technique and without medical precautions, making the joint vulnerable to a variety of injuries from different causes.
Among the most common elbow injuries we can find the following:
Epicondylitis
It is an almost exclusively sports injury that causes pain in the external part of the elbow, and although it is not serious, it can have a significant impact on the patient's life if the appropriate treatment and rehabilitation methods are not applied.
Epicondylitis does not have a list of probable causes. It is caused by repetitive extension and supination of the arm, which causes micro-injuries to the tendons and muscles in the elbow joint, leading to tendonitis. These injuries accumulate until the initial tendonitis evolves into epicondylitis
Fracture
A fracture is a very painful injury caused by the breakage of one or more bones due to trauma. In the particular case of the elbow, the fracture can be of varying complexity and require different treatment depending on the severity of the injury and the bones involved.
Elbow fractures have the following causes:
- Falls
- Direct impacts
- Excessive twisting
- Osteoporosis
- Loss of bone mass
Olecranon bursitis
It is a very frequent disorder in the elbow that affects the synovial bags, or bursae, which are responsible for cushioning the movement of bones, tendons and muscles. This disorder causes inflammation of the olecranon bursa and is popularly known as "Popeye's elbow".
The main causes of this ailment are the following:
- Repetitive movements of the joint
- Exerting pressure on the elbow for prolonged periods of time
- Injuries, falls and trauma to the elbow
- Inflammatory arthritis
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is an injury caused by inflammation of the tendons that attach the muscles to the bone. While primarily a sports injury, tendonitis can occur when constant stress is placed on the joint through extension and supination movements.
Other common causes of tendonitis are described below:
- Sudden elbow injury
- Tendon overload
- Poor exercise technique
Differences between epicondylitis and epitrochleitis?
Both epicondylitis and epitrochleitis are diseases that affect the fibrous tissues of the elbow and generate pain sensation in the patient. However, they have crucial differences that cause them to be categorized as distinct diseases.
Epicondylitis has the following characteristics:
- Inflammation of the tendons responsible for wrist extension and arm supination
- Pain on the inside of the elbow
- Difficulty lifting the arm
- Pain when holding light objects
- Common among racquet sports athletes
Epicondylitis has similar origins, although it affects slightly different areas, in addition to being identified by means of other characteristics, among which we can highlight:
- Inflammation of the tendons that attach to the epitrochlea
- Weakness in the wrist joint
- Pain on the outside of the elbow
- Numbness, tingling and stiffness
- Pain when making a fist
Basically, the main difference between epicondylitis and epitrocleitis is the area in which the pain occurs. Since while the first one originates in the internal part of the elbow, the second one affects the external side.
In addition to this, both ailments share many similarities, as they both originate from microtrauma to the fibrous tissues of the elbow caused by repetitive, high-intensity activities involving use of the joint.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating tennis or golfer's elbow?
When it comes to electrotherapy treatment, sometimes there is confusion between transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) therapies, because in both cases electrical impulses are used for treatment. However, it is necessary to emphasize that each therapy is oriented to a different objective and works in a unique way.
In the case of TENS therapy, it is a means of physiotherapy focused on the treatment of pain produced by injuries, disorders and chronic diseases, which is distinguished by its own unique characteristics, among which we can mention:
- Its main focus is the treatment of symptoms of injuries and diseases that cause pain at specific points of the body.
- Its electrical impulses interact directly on the median, radial and ulnar nerve endings, numbing the nociceptors and mitigating the sensation of pain.
- It uses electric shocks of variable intensity (between 1 and 250 Hz) applied through electrodes placed on the skin at specific points of the body.
- It is used in the field of physiotherapy and treatment of chronic injuries to generate a sensation of relief in the patient.
On the other hand, EMS therapy is a method of training, rehabilitation and physical conditioning that focuses on the stimulation of muscle tissue. The most outstanding characteristics of this therapy are the following:
- The base intensity of its electrical impulses is higher, since it varies between 70 and 150 Hz.
- It interacts with the muscle tissue generating contractions that create physical activity in the muscle or muscle group being worked on.
- Applying the correct intensity, it can be used for the rehabilitation of low level pain injury, applying a gentle muscle massage.
- It is focused on physical conditioning and is widely used by medical teams in highly competitive sports.
With this in mind, we conclude that the optimal method for treating ailments caused by any of the forms of epicondylitis is transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, since its impulses interact with nociceptors in the median, radial and ulnar nerves, decreasing pain and generating a sensation of relief in the patient that can last up to several minutes after the session.
In contrast, EMS therapy is contraindicated for cases of epicondylitis, or any type of painful injury in the elbow, because the joint itself is composed of hard tissue and fibrous tissue (bones, ligaments, tendons and bursae), so its lack of muscle tissue, at best, will make ineffective the use of EMS impulses, and at worst, generate an adverse effect due to muscle contractions that their electrical impulses cause.