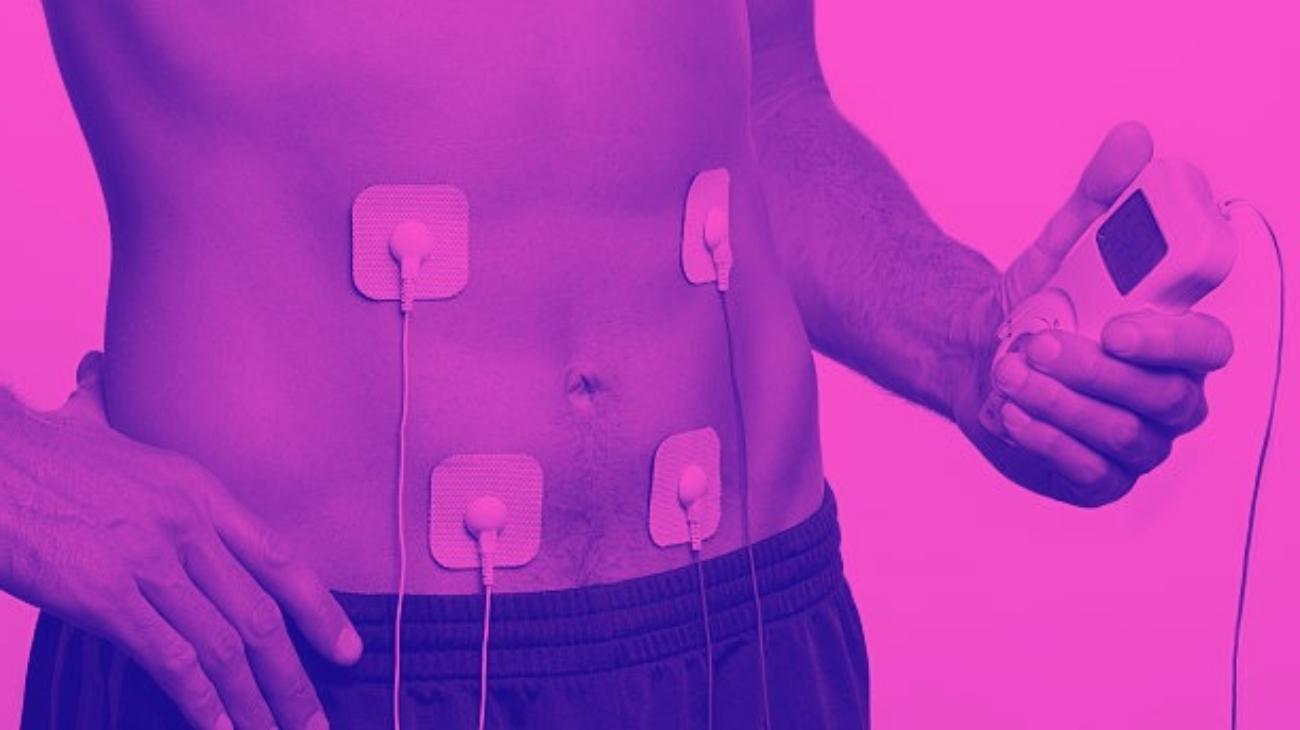
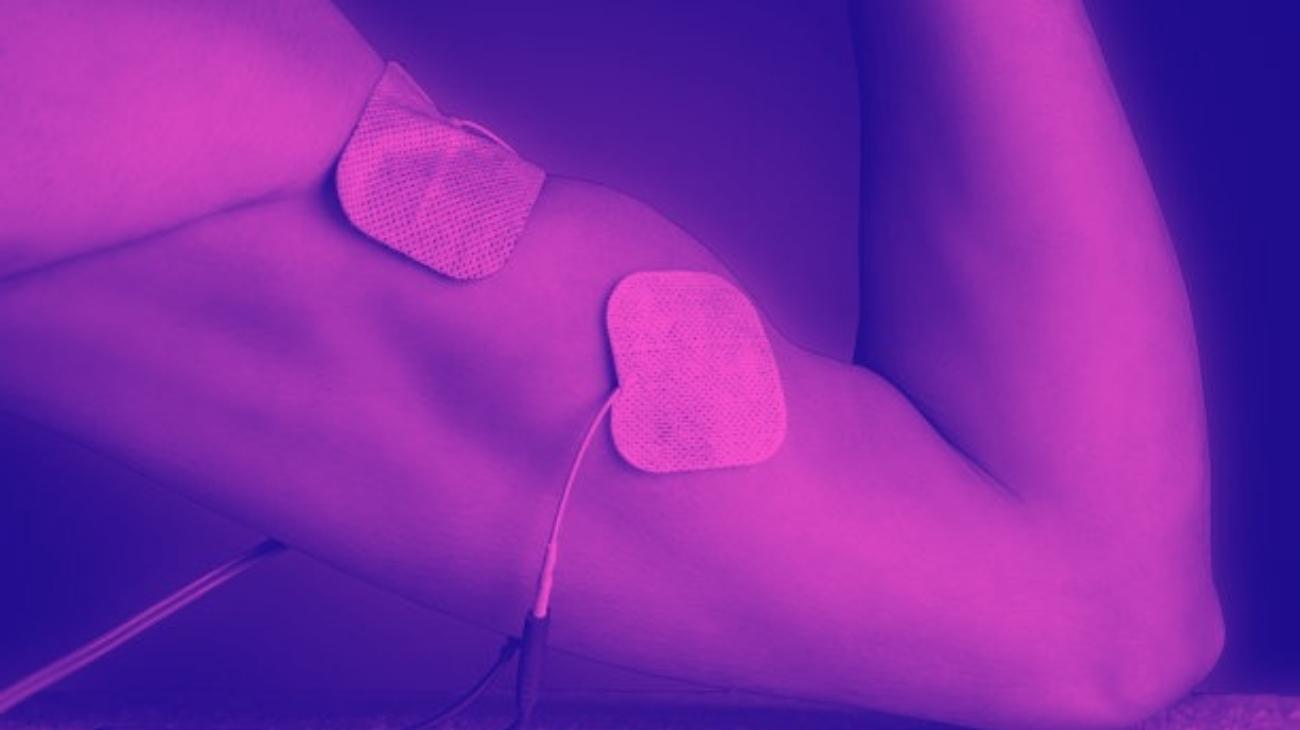
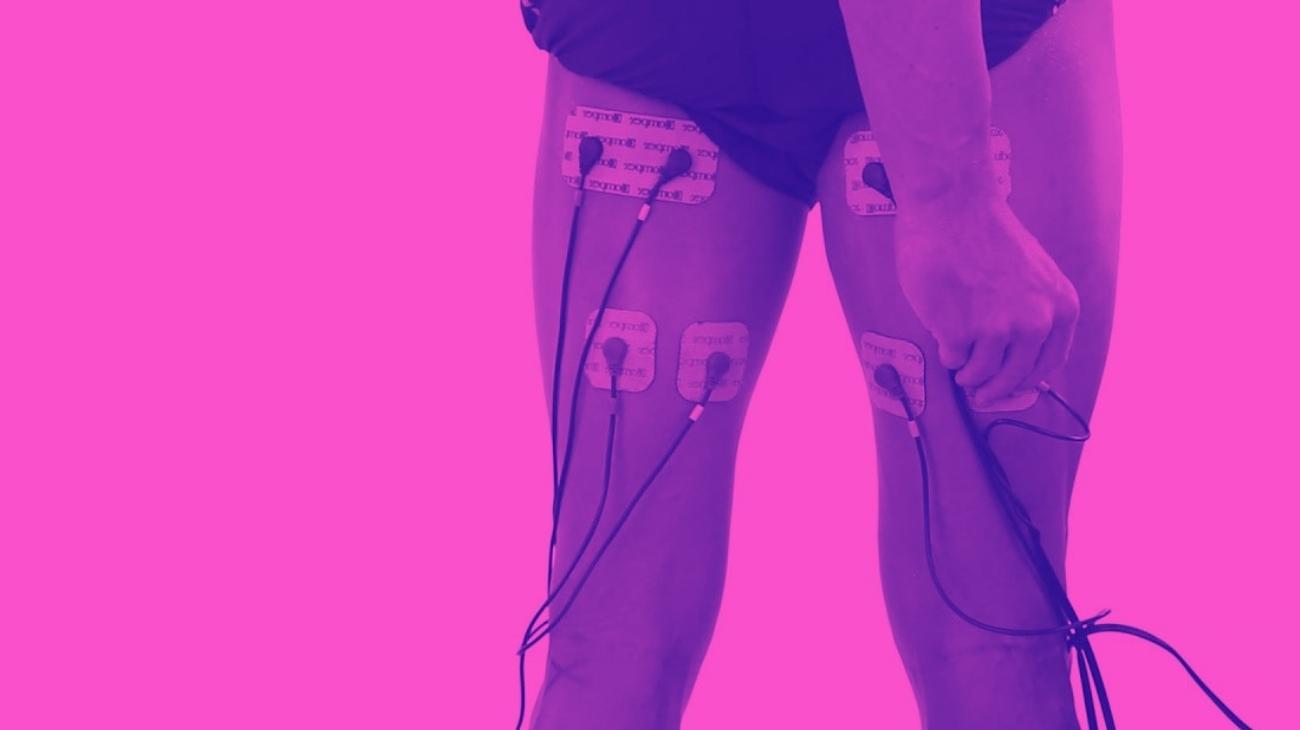
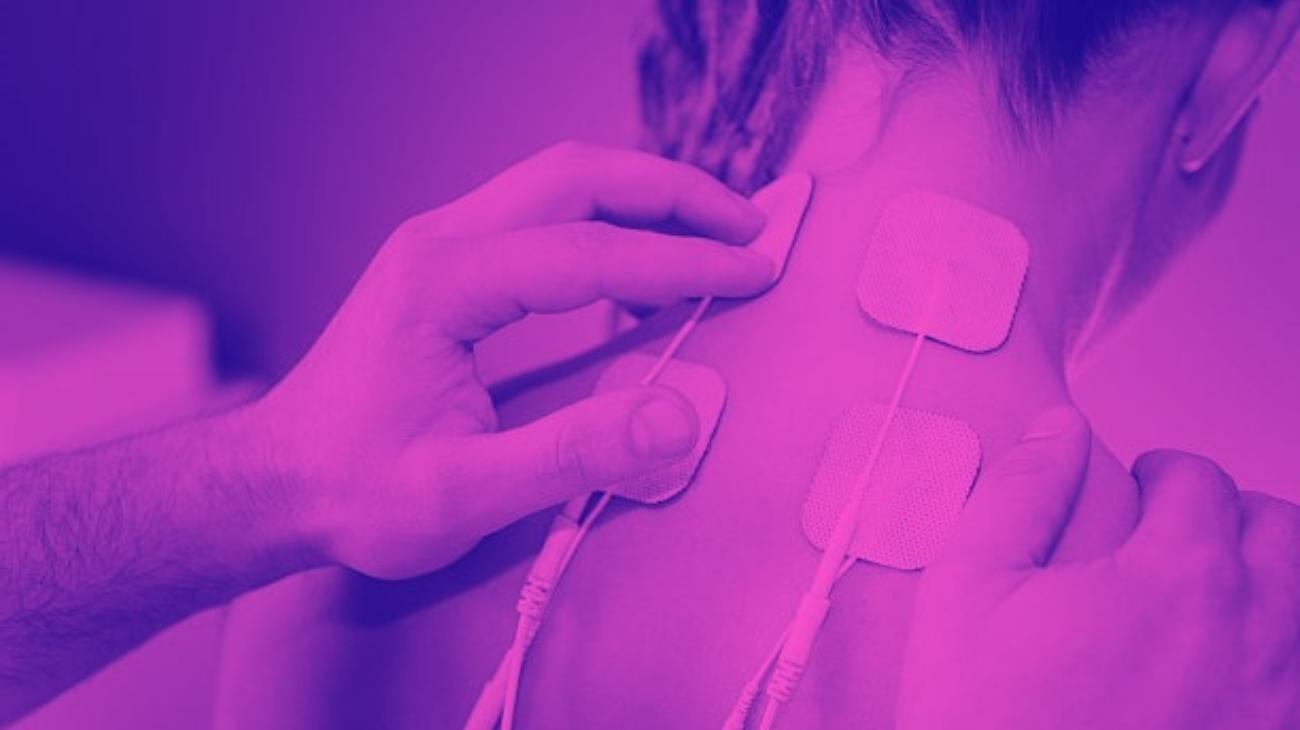
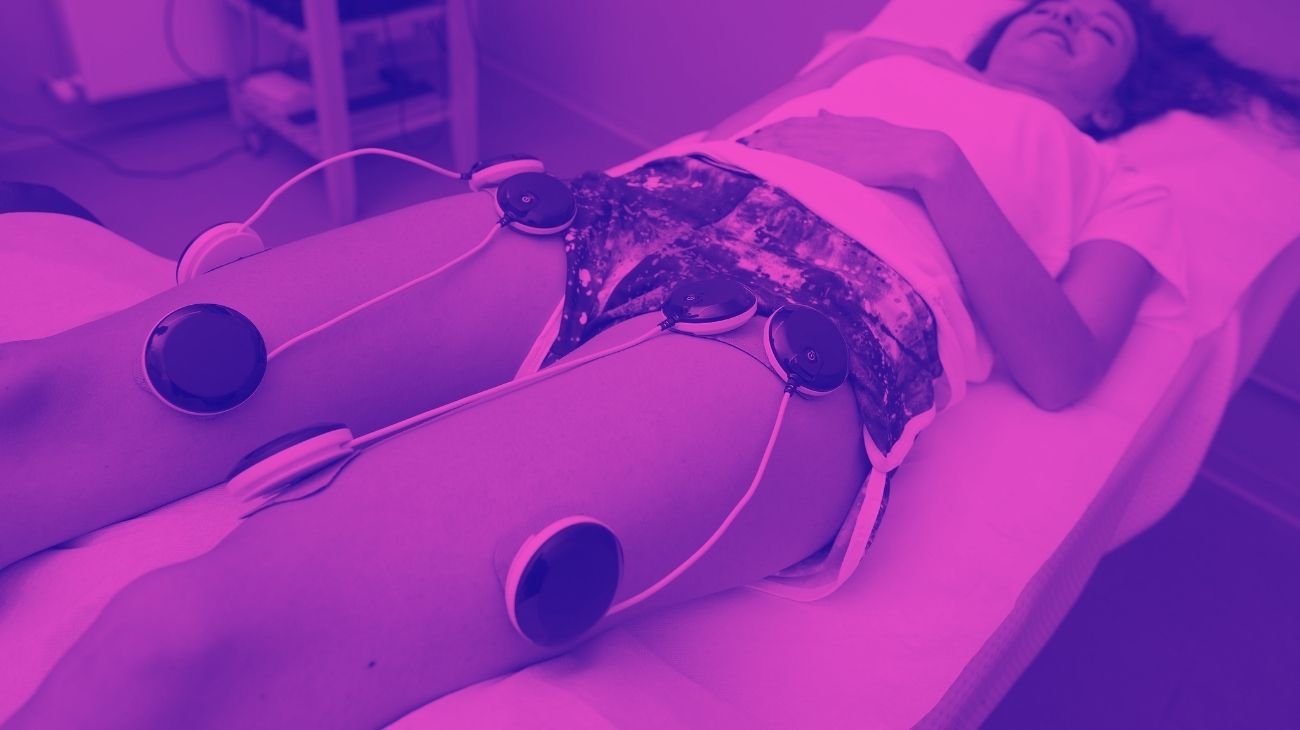
- How to use a TENS machine to relieve arm pain?
- Best TENS Machines for Forearm Injury Recovery
- How to use an EMS muscle stimulator for biceps and triceps?
- Best EMS electrostimulators to strengthen arm muscles
- Video: How to place electrodes pads on arms and forearms?
- More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
- Most common types of arm and forearm injuries
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which one to use for arm pain?
- Contraindications in the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
The arms and forearms occupy most of the upper extremities, being indispensable in most of the daily tasks we perform, and even more so in the practice of high impact sports such as baseball, soccer or tennis. This exposes them to many injuries that cause acute pain that sometimes becomes even unbearable, affecting people's quality of life.
To treat these pains, electrotherapy makes available to people the TENS and EMS currents, which together can achieve a perfect balance between pain relief during recovery from injuries, and muscle strengthening to minimize the chances of suffering them in the future. Here are all the ways they can help you improve the health of your arms and forearms.
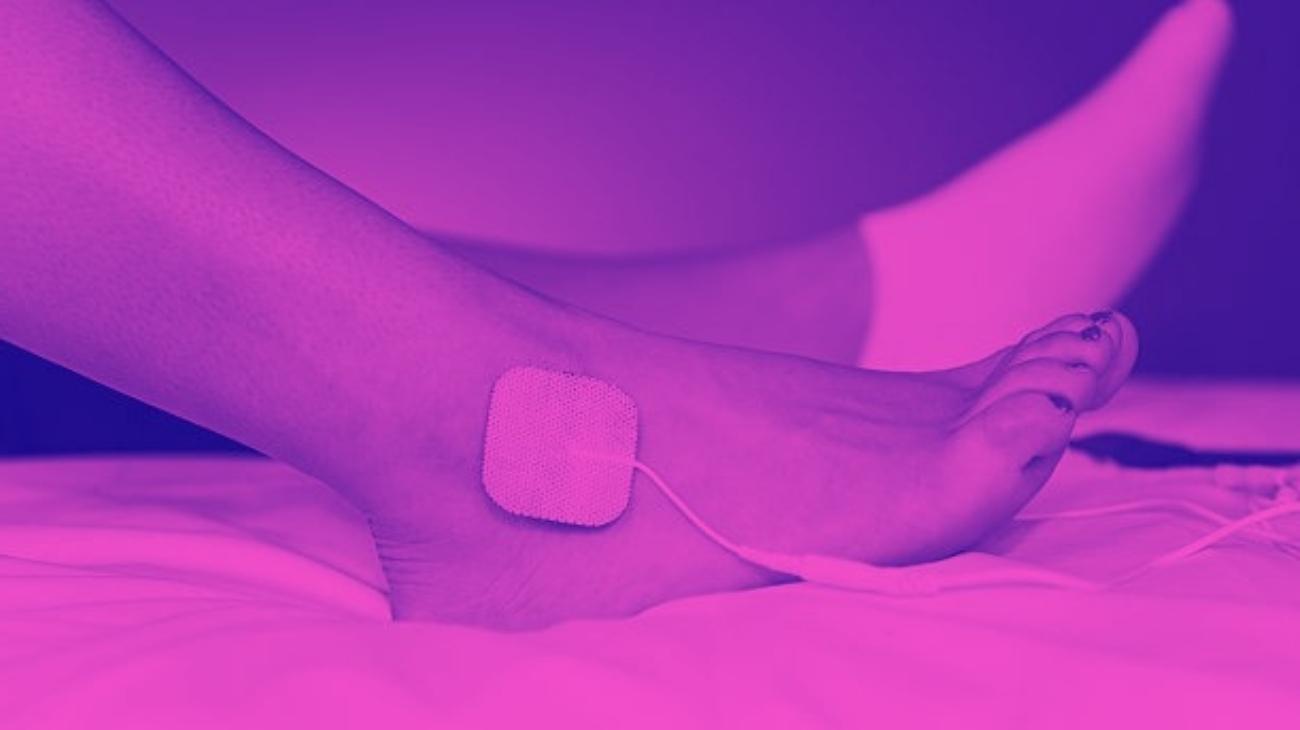
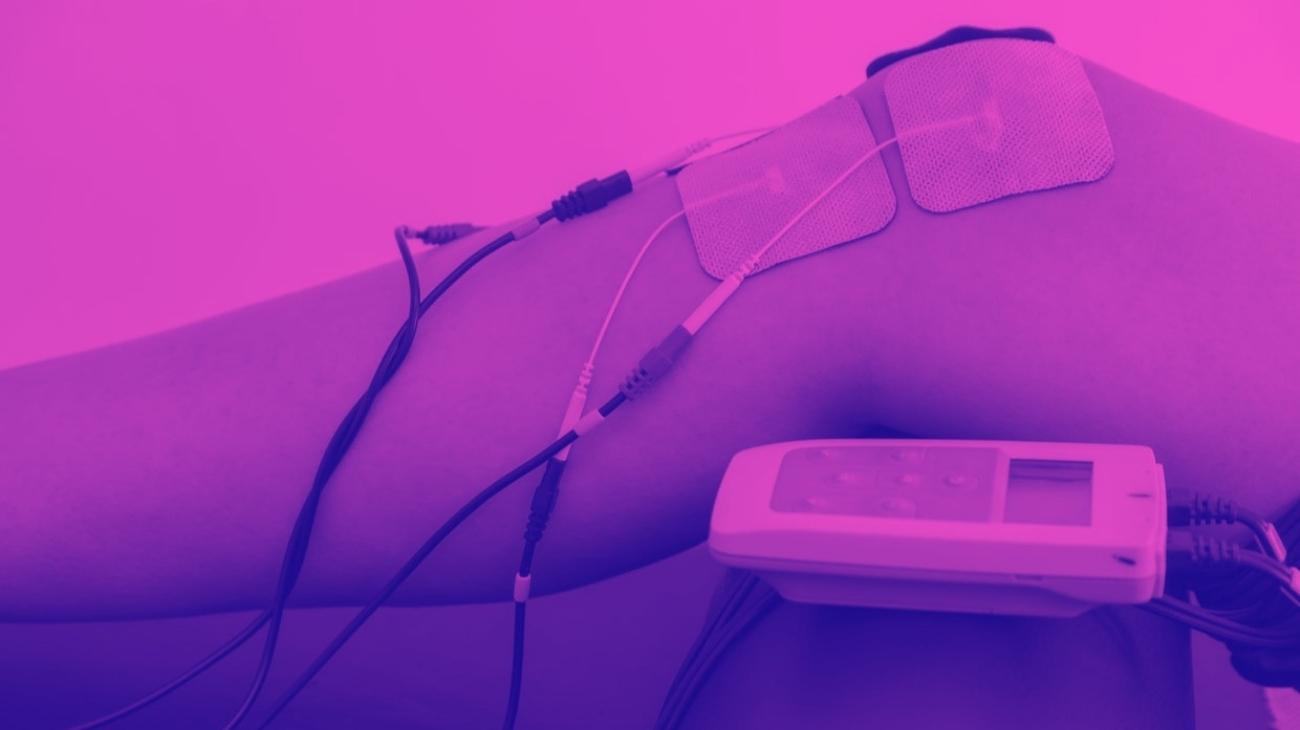
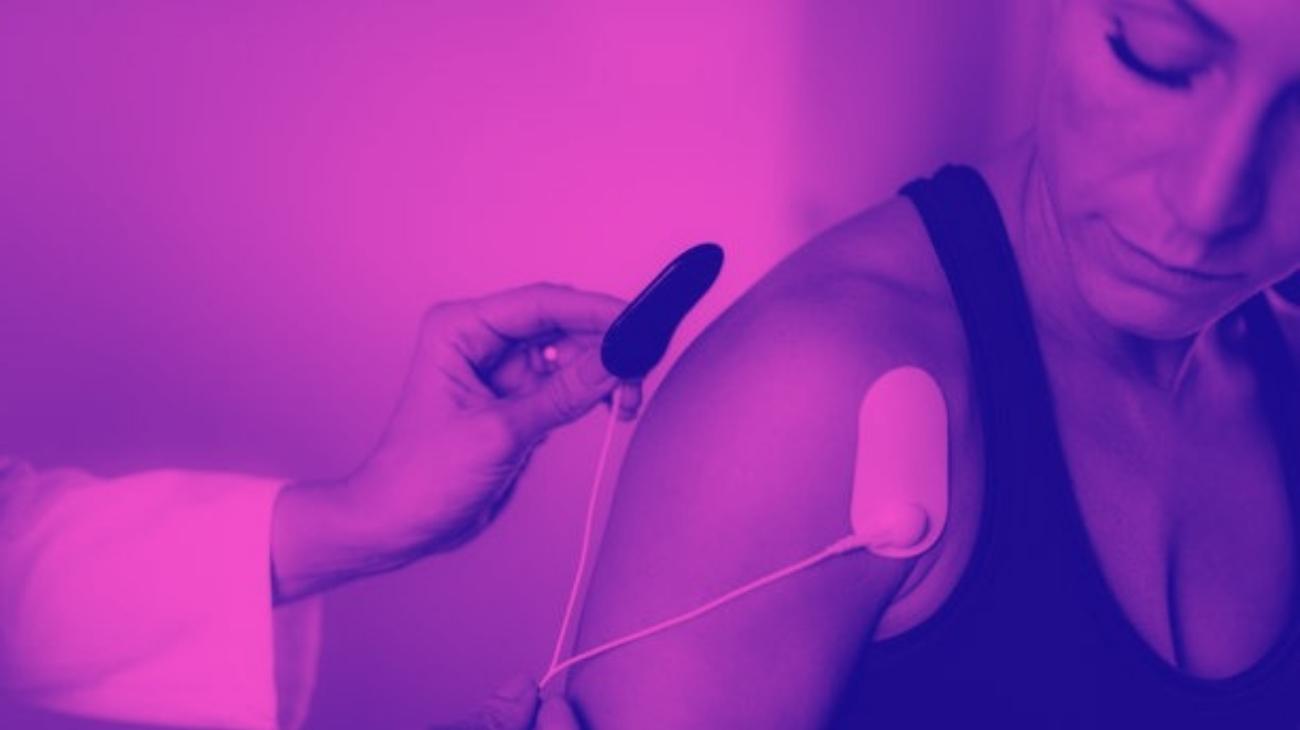
How to use a TENS machine to relieve arm pain?
TENS therapy is one of the most widely supported therapies worldwide for relieving joint and muscle pain, with hundreds of nerve studies affirming its effectiveness and even considering it a useful tool for speeding up recovery processes by making them more pleasant for its users.
Among the main uses and benefits we can highlight the following:
- Raises the pain threshold: the transcutaneous current intercepts the pain receptors located in the ulnar, median and radial nerves, altering their natural charge so that they need more information to send a signal to alert the brain of pain, increasing the threshold and the patient's resistance to it.
- Limits pain-producing cells: once an impact or movement that generates pain occurs, the body creates nociceptors, spinal cells that flow through the nerves until they reach the spinal cord, which then sends the pain signal to the brain. Transcutaneous current alters the functioning of these cells to prevent them from easily reaching the receptors of the median, ulnar or radial nerve, as well as minimizing their production, causing the pain to gradually stop.
- Alterations in the reciprocal innervation: when we feel pain in the forearm or arm, the body automatically generates an involuntary muscle contraction in the biceps, triceps or flexor muscles of the forearm, which can increase the severity of the pain. TENS therapy prevents these responses by making it easier for the muscle to come to rest and the sensation of relief is achieved more quickly.
- Vasodilation: when using TENS, we will have a warm sensation on the skin of the arms and forearms, which will dilate blood vessels allowing greater oxygenation of the sore tissue, which in turn has an analgesic effect that will help relieve pain faster.
These characteristics make TENS therapy extremely useful for relieving pain in arms and forearms caused by injuries such as:
- Tendonitis
- Median nerve impingement
- Radial nerve impingement
- Ulnar nerve impingement
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Elbow or wrist osteoarthritis
- Myofascial pain syndrome
It should be noted that although TENS will work to relieve pain momentarily, it cannot replace the treatment indicated by the specialist, since electrotherapy is not a curative method. That is, it will work to relieve pain in the arms and forearm, but it will not recover from the injury that causes the pain, so as long as you do not treat the cause, the pain will continue to appear.
Best TENS Machines for Forearm Injury Recovery
Here are some of the best transcutaneous nerve stimulation devices that will help relieve most arm and forearm pain to ease the injury recovery process.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 14 Modes
- Intensity: 25 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 6 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- Rechargeable battery
- Includes user manual
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Battery life not specified
- Does not include touch screen
The compact size of the device makes it incredibly practical and easy to carry, so you can use it anywhere you like quickly and discreetly. It is FDA approved, so it is completely safe to use, and its LCD screen gives you a full display of all settings so you can easily adjust your requirements.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 24 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 24 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- TENS+EMS combo
- Includes carrying bag
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Rechargeable battery
- Battery life not specified
- No intensity levels specified
- No heat therapy
It has 4 channels of operation, 5 modes of TENS currents, 3 modes of EMS stimulation; and 24 predefined programs that generate low intensity electrical impulses to stimulate the nerve endings in the treated area, effectively blocking pain signals.
Hi-Dow - Dual channel TENS/EMS unit for physical therapy with 8 modes & 20 intensity levels & 4 pads
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 8 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: 6" x 4" x 5" - 0.63 lbs
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Portable and small size
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Includes user manual
- Rechargeable battery
- Battery life not specified
- No carrying bag included
- No heat therapy
It has 8 preset programs and 20 intensity levels, along with a session timer function that you can set between 10 and 60 minutes. Its built-in rechargeable lithium battery provides excellent durability, and the package contains 1 XP Micro 8 electrostimulator, 1 set of large pads, 1 set of small pads, 2 cables, 1 power adapter, 1 user manual and 1 carrying case to take it wherever you need it.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: 1
- Modes/Programs: Not specified
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Not specified
- Electrodes: 1 Pad
- Display: No display
- Size: 6.22" x 1.42" x 3.27"
- Improves joint mobility
- Improves blood circulation
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Wireless electrodes
- No intensity levels specified
- Does not specify weight
- Not for muscle hypertrophy
Its efficient use of TENS technology allows it to block pain signals before they reach the brain, making it a safe method of treating ailments. It also has a long-lasting lithium battery and an energy-efficient function, which turns the device off every 20 minutes. One of the best devices on the market in terms of portability, discretion and functionality.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 10 Programs
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: 3.3 x 0.2 x 2.5 inches
- Reduces pain symptoms
- With adjustable timer
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves blood circulation
- No battery life specified
- No weight specified
- No heat therapy
It has 10 pre-programmed massage modes and 20 intensity levels that focus on treating various types of pain, and a session timer function that allows you to set the duration of these between 10 and 60 minutes. Additionally, it has a lithium battery that allows you to apply therapy for more than 20 hours at a time.
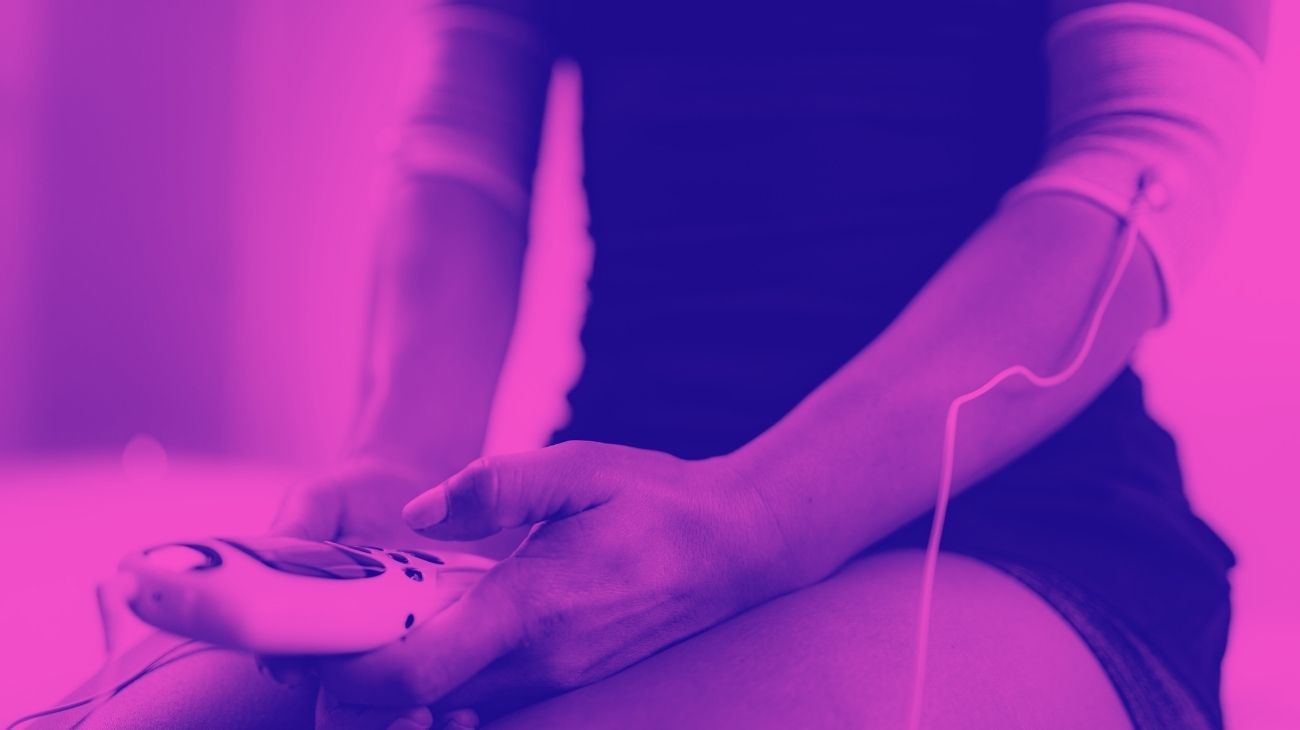
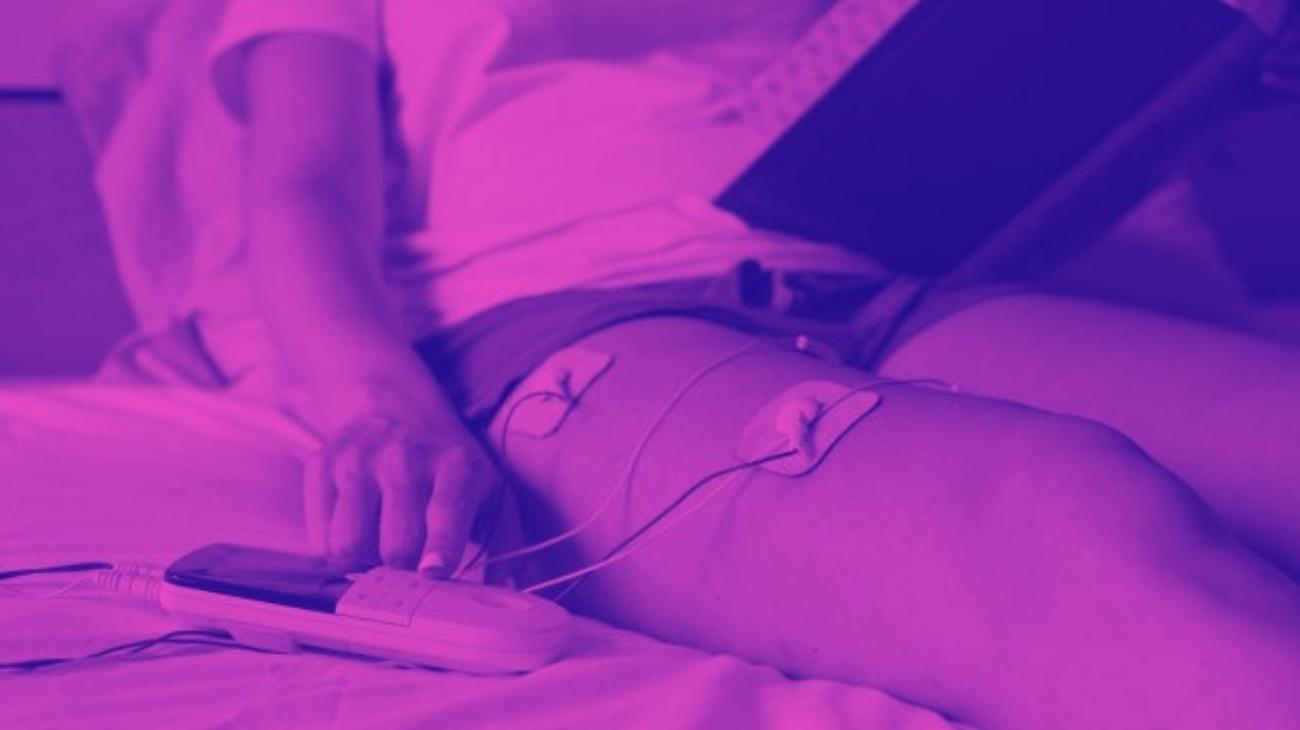
How to use an EMS muscle stimulator for biceps and triceps?
EMS therapy uses currents of different frequencies that act at a muscular level, stimulating the nerve in a different way since it does not interfere with its sensory functions, but stimulates it to achieve a natural contraction of the muscle.
This simple action has multiple benefits such as the following:
- Strengthening and muscle toning of biceps, triceps and muscles that make up the forearm, which although it does not completely replace traditional training, can help maintain fitness in people who do not have much time to go to training centers.
- Reduction of fatigue, by getting the muscle fibers of the biceps, triceps and forearm extensors to reduce their oxygen consumption, which will make their resistance to fatigue much higher. This is one of the main advantages of EMS therapy that make it a favorite of athletes around the world.
- It improves the power of the muscles since less oxygen is needed in the muscle fibers so that they can be activated faster when they are needed for an explosive movement or intense weight lifting at the maximum of their capabilities.
- Stops the loss of tissue due to a sedentary life or little use of the upper limbs, which eventually weakens the muscle fibers of the biceps, triceps and other muscles that compose it.
- Improved blood flow due to the dilation of blood vessels during the session. This will increase the assimilation of nutrients and oxygen for healthier and more resistant muscles in the arms and forearms.
Best EMS electrostimulators to strengthen arm muscles
Below we share with you a list of the best EMS muscle electro stimulators that you can use to strengthen your biceps, triceps and forearm extensors, thus reducing the chances of suffering from injuries in your upper extremities.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Normally 2 (Dual)
- Modes/Programs: 6 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (7 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 2 Pods and 6 electrodes
- Display: Smartphone
- Size: Not specified
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Portable and small size
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Wireless electrodes
- Rechargeable battery
- Size and weight not specified
- No intensity levels specified
- No heat therapy
It has a rechargeable battery that can provide an autonomy of up to 7 hours per charge, 6 unique training programs focused on different branches of fitness to help you achieve your goals, and compatibility with your mobile for easy use. It is recommended for those physically active people looking for a compact, portable and natural way to deal with workout-related ailments.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 15 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: No display
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Control from mobile app
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes user manual
- Rechargeable battery
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
- Battery life not specified
- Does not specify intensity levels
With more than 400 modes of use and a variety of intensity levels, the PowerDot 2.0 is one of the most complete electro stimulators available, as its functions focus on muscle recovery, improved physical performance, and pain relief. All these features make it the leading choice for the immediate treatment of any pain, whether caused by injury or illness.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 24 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 20 hours)
- Electrodes: 6 electrodes
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- Includes user manual
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Long battery life (up to 20 hours)
- Portable and small size
- Good quality
- Few intensity levels
- Does not specify size and weight
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
It has multiple modes of use and its A-B output channel allows you to apply two types of massage simultaneously, making it one of the most versatile devices available on the market. The package includes 1 control, 1 protective case for the TENS unit, 3 pairs of electrodes, 4 power output cables, 1 USB cable, 1 user manual, 1 plastic case and 1 belt clip.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: 2
- Modes/Programs: 35 Programs
- Intensity: 50 Levels
- Wireless: No
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 3 AAA batteries included
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Portable and small size
- Improves blood circulation
- Includes user manual
- Does not specify size and weight
- No heat therapy
- Powered by AAA batteries
This device is powered by 3 AAA batteries that are included in the package. It does not require frequent changes or recharging, due to its efficient power consumption. Additionally, it has a dual channel function, so you can work different parts of the body simultaneously as required.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 12 Modes
- Intensity: 30 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Batteries
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Includes carrying bag
- Improves blood circulation
- Portable and small size
- Improves joint mobility
- TENS+EMS Combo
- No battery type specified
- No heat therapy
- Does not specify size and weight
It offers a professional solution through its 12 massage modalities with 30 intensity levels, which you can easily adjust to adapt the therapy to your needs. Additionally, its dual channel function allows you to apply different modalities on the A and B channels of the stimulator, allowing you to treat two different areas of the body, or even two different people, simultaneously.
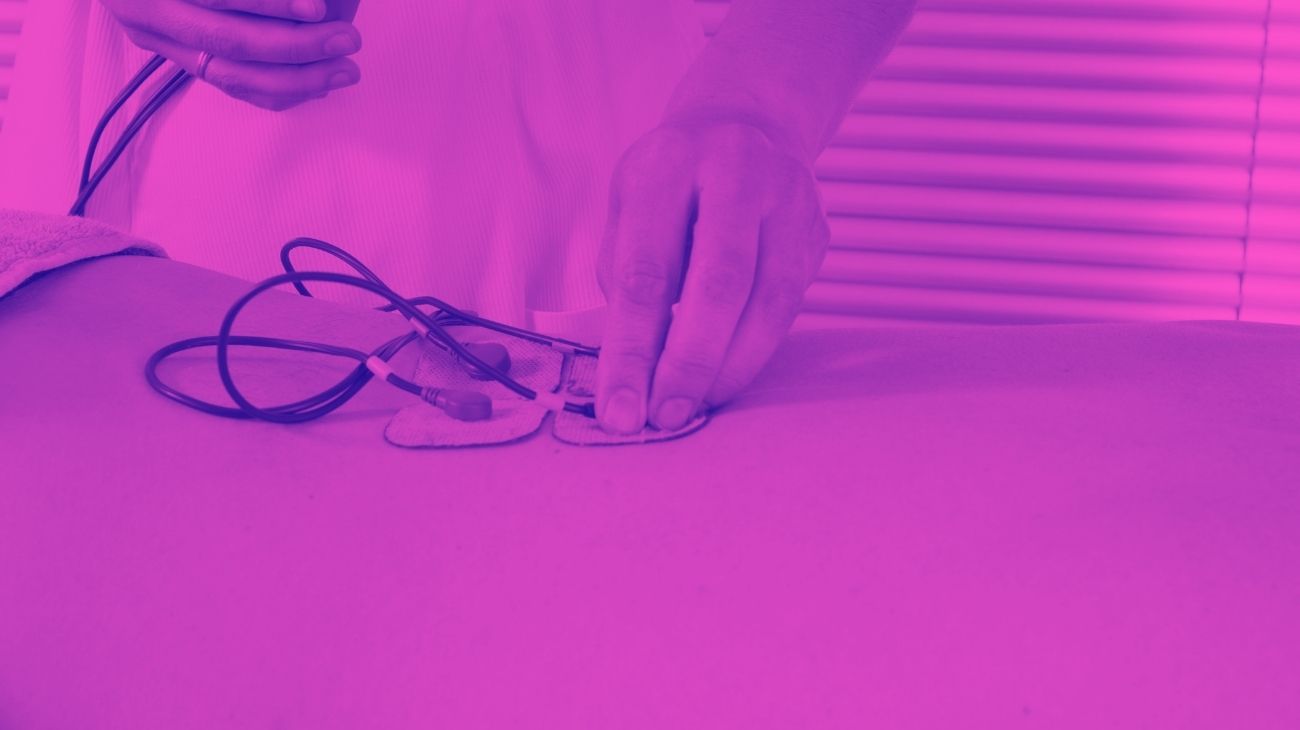
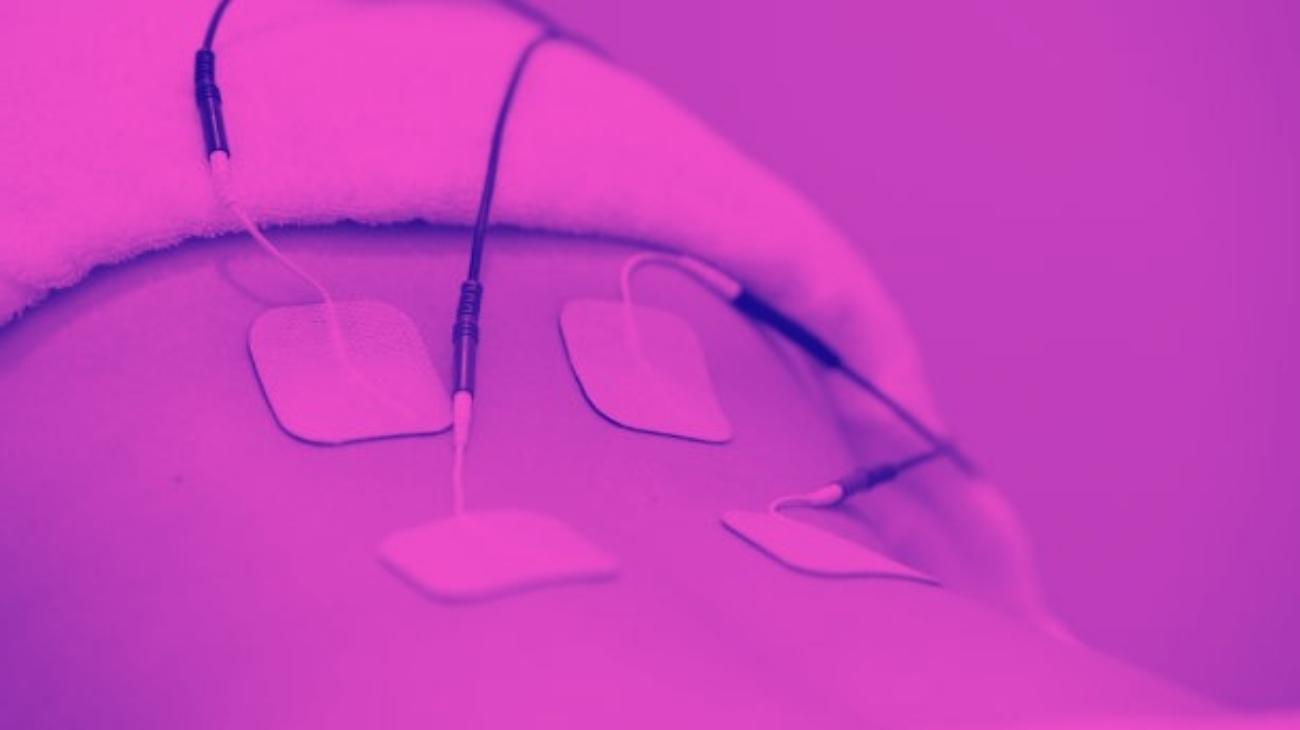
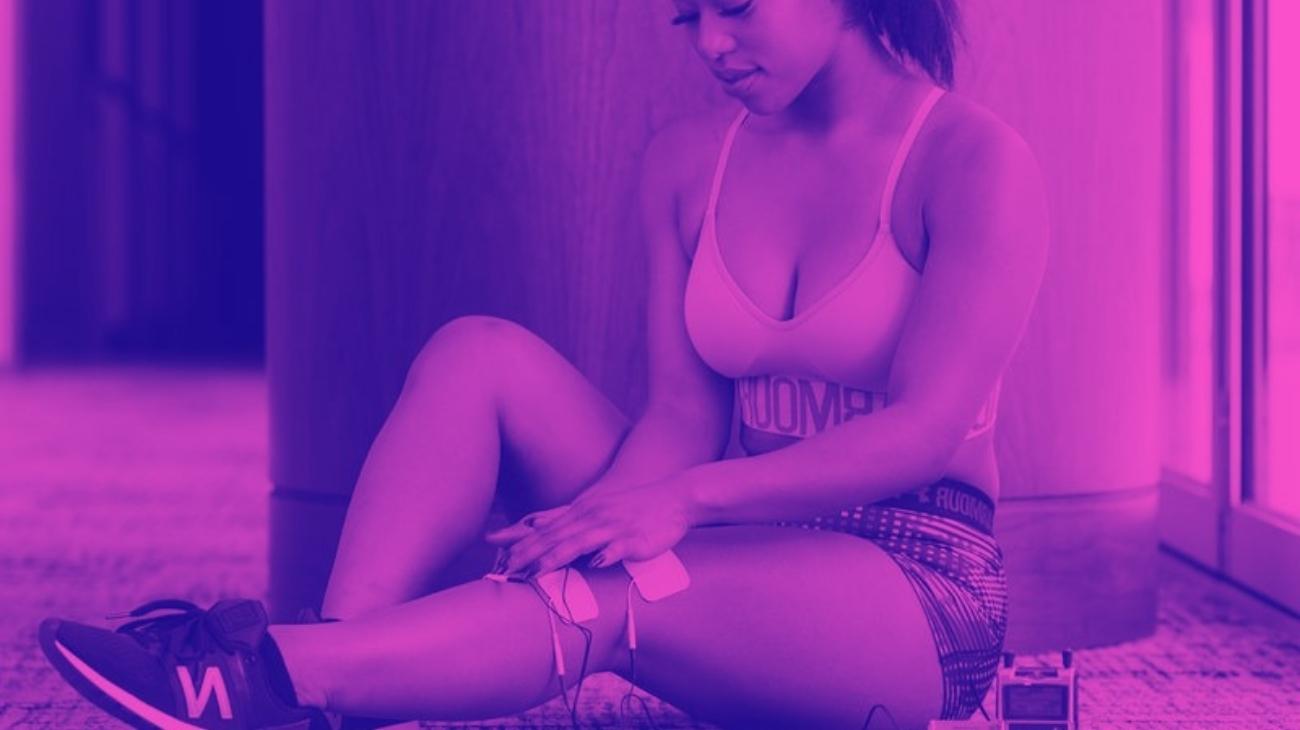
Video: How to place electrodes pads on arms and forearms?
Electrodes for arms
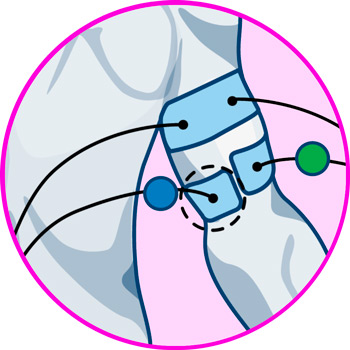

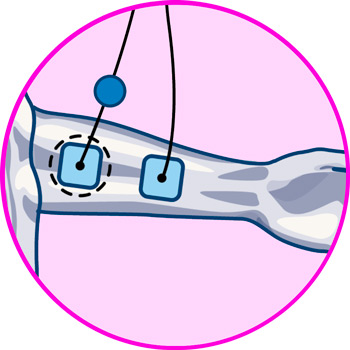
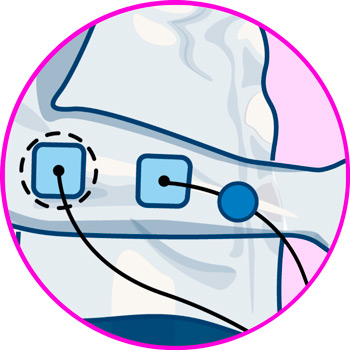
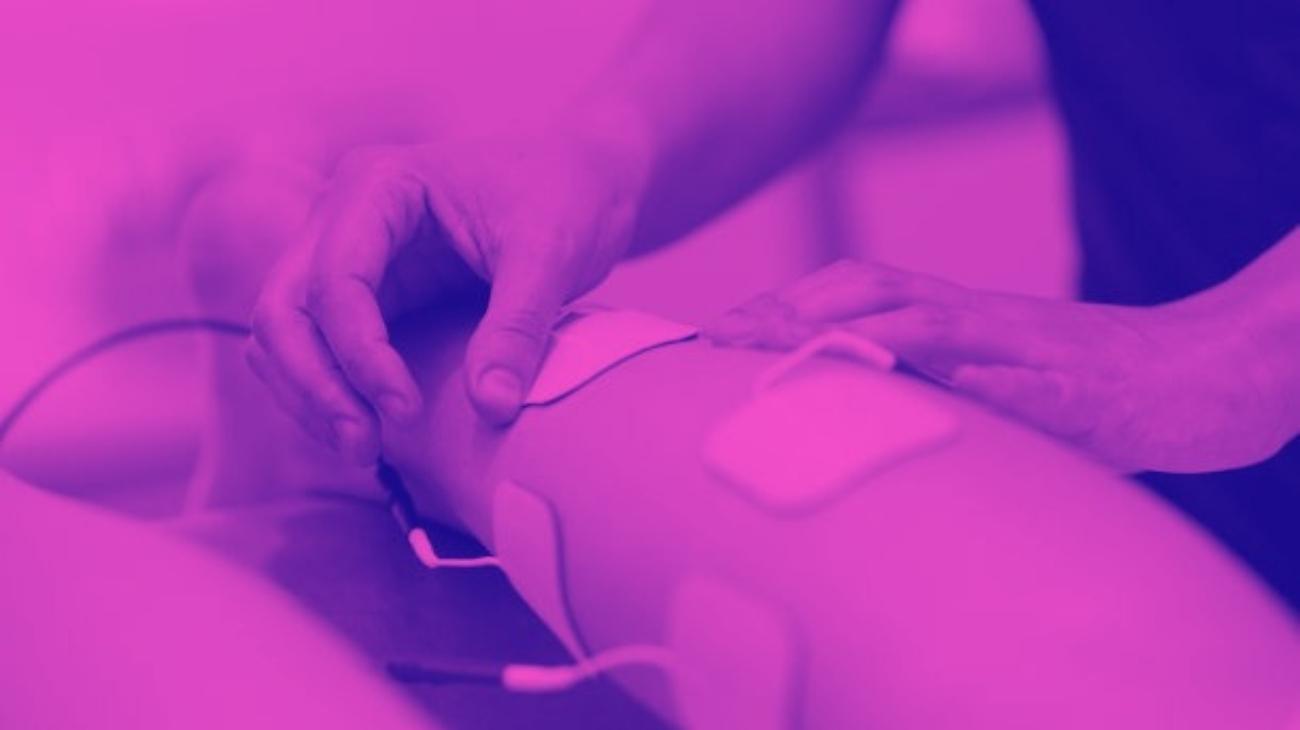
- For biceps pain: For biceps pain we proceed to place one pad on the upper part of the muscle, just at the limit where it joins with the deltoid, while the other goes on the lower part where it joins with the end of the biceps ligament that joins with the elbow.
- For triceps pain: For the triceps the procedure is similar, one electrode is placed on the upper head of the muscle where it joins the deltoids of the shoulder, while the other just on the upper part of the elbow without being over the joint.
- For tennis elbow: To treat injuries such as tennis elbow, one pad is placed on the brachioradialis muscle located on the outer side of the elbow, while the other is placed on the inner side of the elbow on the carpal flexor muscle.
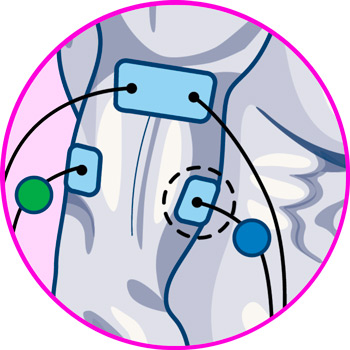
- Biceps training: To train the biceps, we proceed to flex the elbow so that the muscle is retracted, and position one just below the junction with the deltoids of the shoulder, and the other at the junction with the biceps ligament, without touching the joint.
- Triceps training: For the triceps the position of the first electrode goes on the upper part of the lateral head of the muscle, and another one on the lower part of it. While for training the other zones of the muscle, one electrode is positioned on the medial head of the triceps, and another in the middle part of the long head of the muscle.
- Forearms training: For the forearms, a pad is placed on the external side of the elbow just on the brachioradialis muscle, and another one lower down on the medial part of the same. After finishing the session, the electrodes are placed on the carpal flexor following the same principle; one just below the internal lateral side of the joint, and the other in the middle area of the muscle.
More types of EMS electrostimulators and TENS machines you should know
Most common types of arm and forearm injuries
Tennis players, boxers and basketball players all have in common that for 100% of the time during which they compete, they are using their arms, and in fact, even those of us who are not athletes are constantly using them, which exposes us to suffer from ailments such as the following:
- Lateral epicondylitis: known as tennis elbow, this condition occurs when the ulnar collateral ligament, which joins the forearm muscle with the epicondyle to flex the elbow, is irritated to the point of becoming inflamed, which generates a sharp pain when moving the joint. It is caused by the constant performance of repetitive movements such as a racket backhand or the constant flexion of the elbow when bouncing the basketball against the floor.
- Bursitis of the elbow: it is the inflammation of the synovial fluid bag that is in the union between the humerus with the radius and the ulna, forming the elbow joint. This may occur due to wear and tear caused by repetitive movements, or by a blow when trying to break a fall with the hand.
- Nerve impingement: the radial, ulnar and median nerves are found along the arm. This injury occurs when one of them is compressed or irritated, generating a constant pain that can be felt throughout the arm from under the armpit or over the shoulder to the fingertips.
- Elbow sprain: occurs when the joint is forced to perform an unnatural movement, causing the ulnar and radial collateral ligaments, as well as others that stabilize the mobility of the elbow, to overextend and suffer a partial or total tear, which will manifest itself with joint inflammation and acute pain for several weeks, limiting the functionality of the joint.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which one to use for arm pain?
Electrotherapy is a treatment that uses low and high intensity currents to achieve a nervous response that benefits the patient's health at a nervous and muscular level. From this principle, both TENS transcutaneous nerve stimulation and EMS muscle electrostimulation are born.
The former uses currents on the skin to reach the nerves and have a direct effect on the sensation of pain, slowing down the nerve functions that manifest it to provide a sensation of localized relief.
EMS uses currents that reach the muscle directly in order to achieve a muscle contraction that simulates that which is naturally achieved when using a muscle group in the gym. In this way, muscle strengthening can be achieved without the need to go to a training center.
This makes this therapy a viable alternative for people who want to be in shape but do not have time to go to the gym, or athletes who want to extend their training time without sacrificing hours of the day.
In other words, the ideal therapy for pain relief is TENS, which will intercept the nerve signals that travel through the median, ulnar and radial nerves to inform the brain of the sensation of pain. This is achieved by acting on the medullary cells responsible for communicating the cause of pain in the muscle or joint, and slowing down their production to increase the threshold of pain endured by the user.