- How to use TENS machines to relieve low back pain?
- Best TENS units to treat low back pain
- How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent low back damage?
- Best EMS machines to prevent sciatica and low back pain
- Video: How to place electrodes pads on the back?
- More types of EMS stimulators and TENS machines you should know about
- What is sciatica or lumbago and what are the causes?
- What are the most common types of back injuries?
- Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating sciatica and low back pain?
- Contraindications in the use of electrodes and electrotherapy
Regardless of the type of activity you do, the back is a vitally important structure for the support and stability of the body's center of gravity, and for protecting the spinal cord through the vertebrae. However, a variety of factors such as lifestyle, poorly executed exercises or bad posture can alter its integrity.
For this reason, it is necessary to have available methods to treat the ailments caused by the various injuries that can be suffered in the back, especially in the lumbar region. This is where TENS and EMS electrotherapy units come in, which are very useful for treating the symptoms of lumbar injuries.
How to use TENS machines to relieve low back pain?
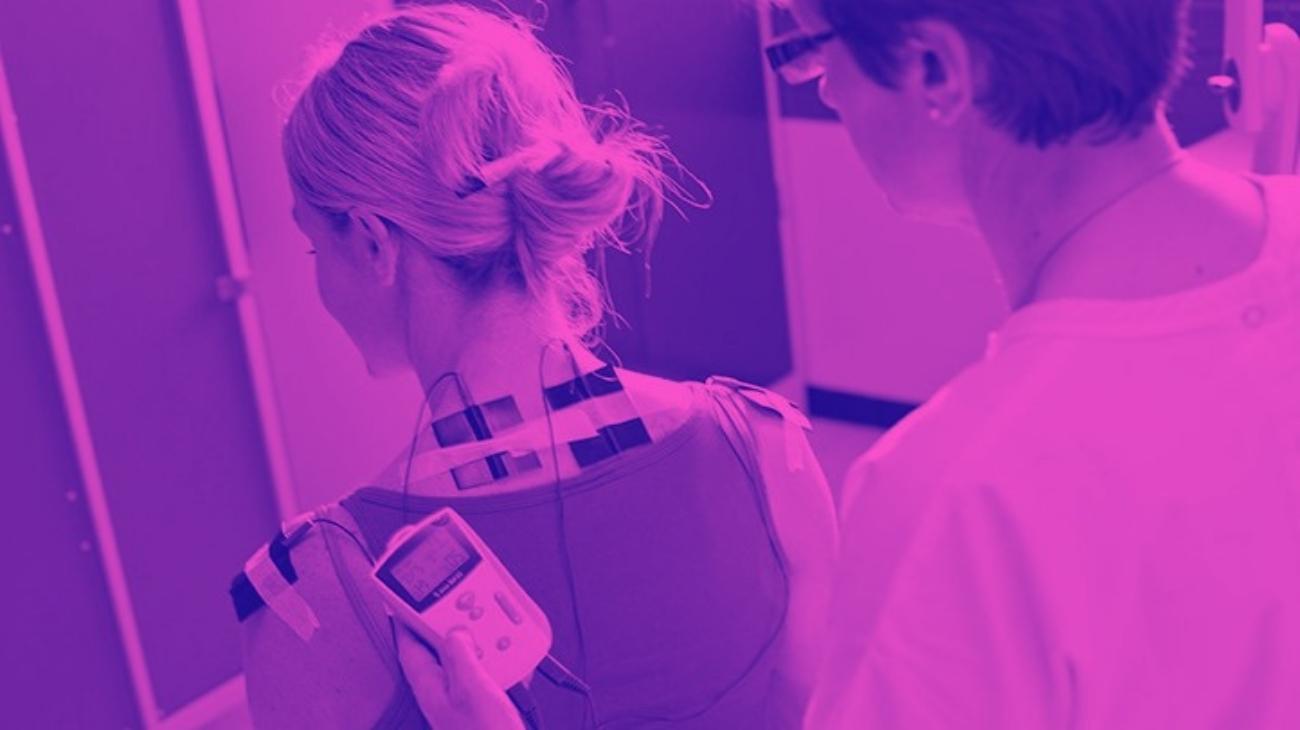
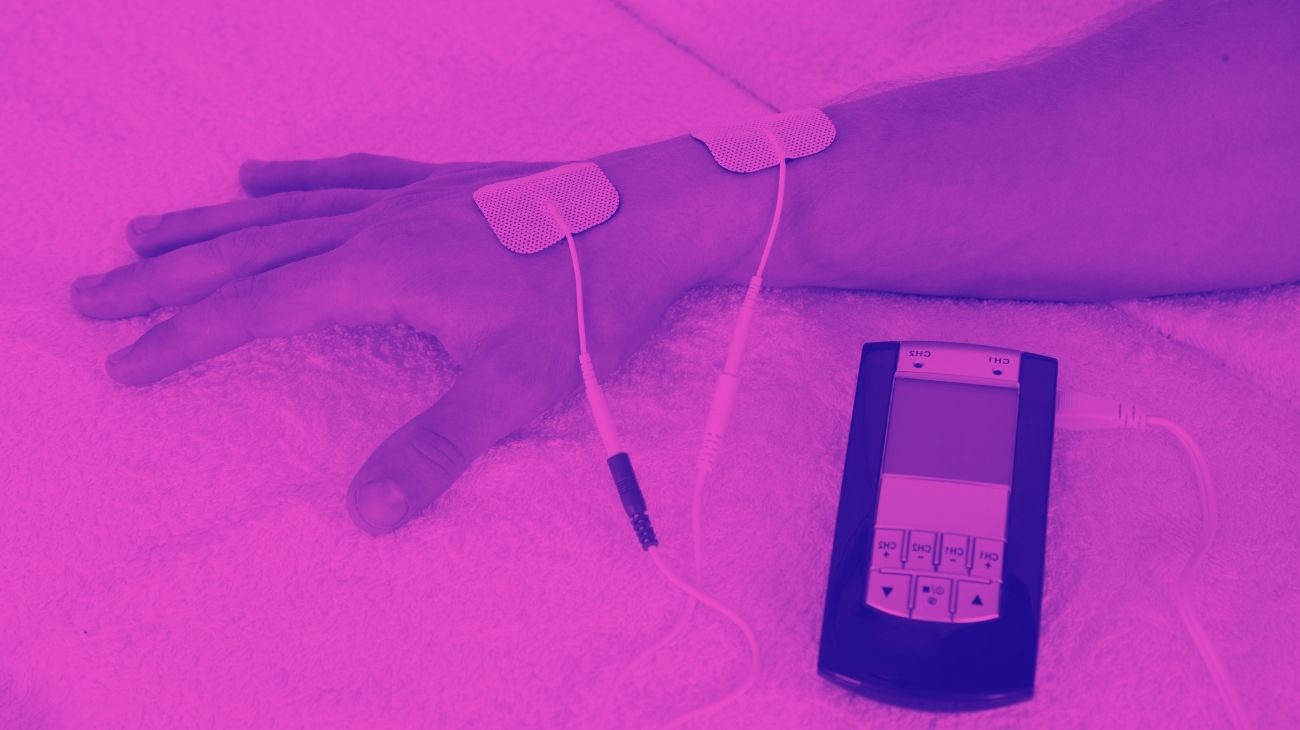
TENS units are relatively easy to use if you have the proper guidance. However, certain factors need to be taken into account in order to get the most out of each session. These are the location of the electrodes, and the current to be applied to the area.
Where to place the electrodes?
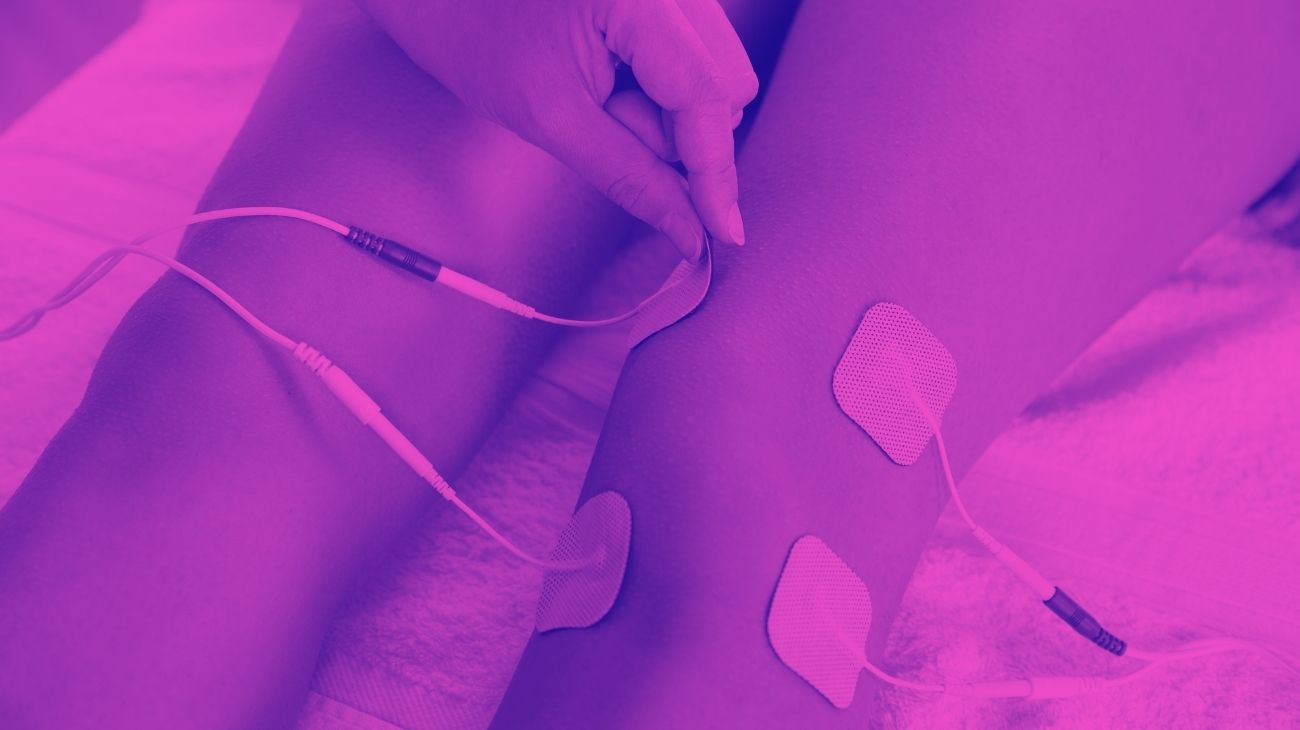
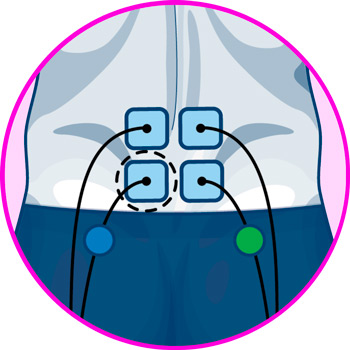
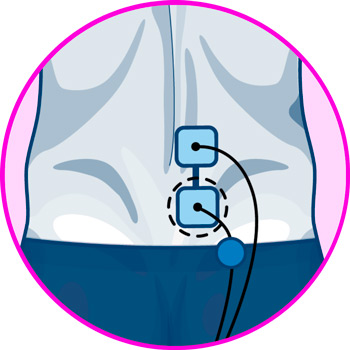
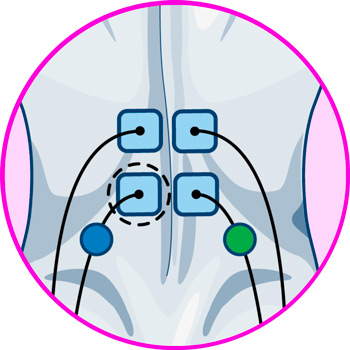
The location of the electrodes of the TENS machine will depend on the type of pain you are suffering from. In case of pain caused by overload of the lumbar muscles and nerves, the ideal position will be with the four electrodes on the lumbar frame, on each side of the spine, at the height of the L4 and L5 vertebrae, on the iliac crests.
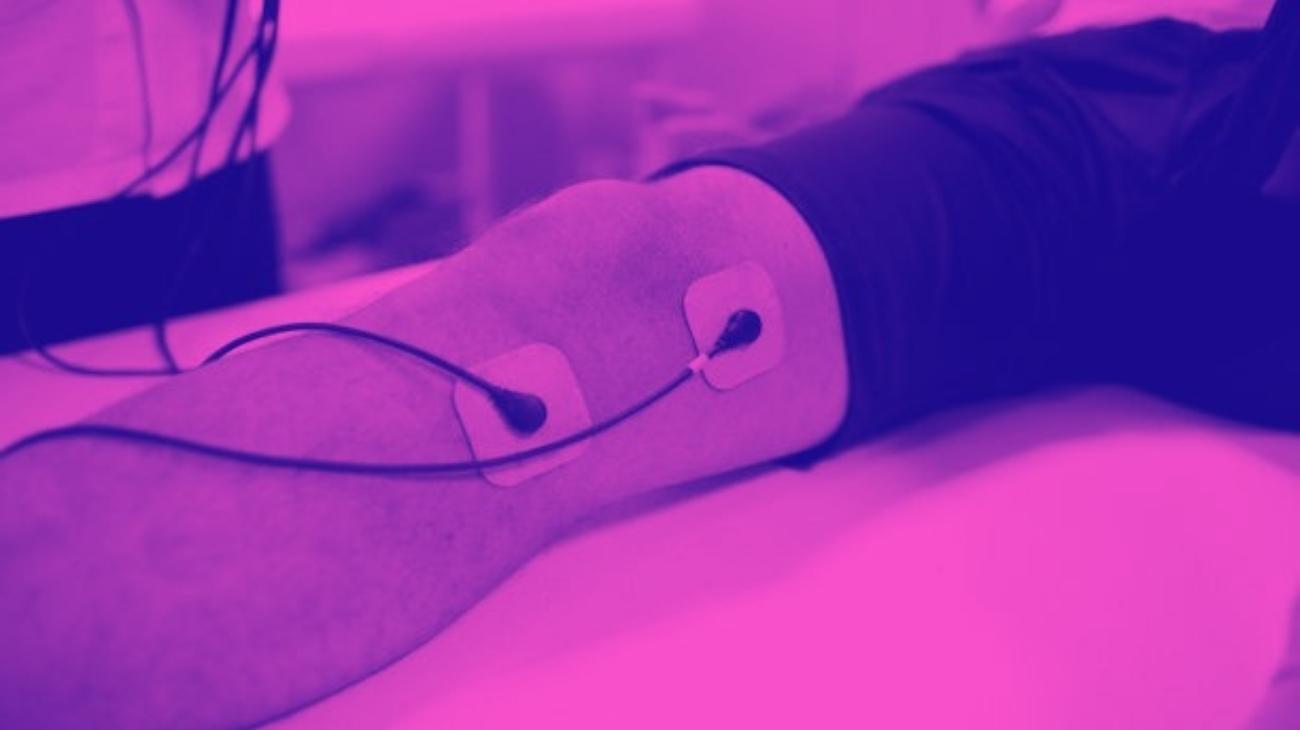
Now, the positioning for pain caused by the sciatic nerve is more complex, since this can extend to the sole of the foot and generally only affects one side of the body, which is also a factor to consider for positioning.
The first two electrodes should be placed in the lumbar region at the level of the iliac crests, where the sciatic nerve branches into the legs, while the last two electrodes should be placed in a vertical orientation on the back of the affected leg, along the extension of the sciatic nerve, on the biceps femoris muscle, just below the buttock.
Which current to use?
The intensity to be applied for the treatment of low back sciatic pain will depend to a great extent on the time that has elapsed since the onset of the pain, since the optimum intensity is different for acute and chronic pain.
Acute pains are those with a lapse of less than three months, during which the optimal intensity to be applied may vary between 90 and 120 Hz, depending on the cause of the pain and the level of pain. Conditions such as herniated discs pressing on the sciatic nerve require an intensity of approximately 100 Hz, while nerve degeneration caused by other diseases may require a higher intensity in order to reduce the sensation of pain.
If the condition has lasted more than three months, it is considered chronic pain, which requires more frequent treatments at a much lower intensity, between 2 and 10 Hz, with this range varying if the patient has disabling pain. This frequency favors a slower but longer lasting release of endorphins that act as the body's natural painkillers, mitigating the sensation of pain for a longer period of time.
Best TENS units to treat low back pain
The use of TENS therapy for the treatment of low back pain and sciatica is well established due to its effectiveness in relieving the sensation of pain. This relief effect can be increased by using the right devices, which are listed below:
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 20 Modes
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 10 hours)
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Improves blood circulation
- Rechargeable battery
- Portable and small size
- Includes user manual
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
- No heat therapy
It has an independent dual-channel control mode, which allows you to treat different parts of the body with different settings and intensities as required. You can select from 20 preset massage modes, each designed to relieve certain types of pain and produce an overall sense of relief.
Med-Fit - Dual channel TENS machine for fast, effective and accurate pain relief ideal for home use
- Type: TENS
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 5 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Batteries
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Improves joint mobility
- Improves blood circulation
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Includes user manual
- Does not specify intensity levels
- Does not specify which type of batteries to use
- Does not specify measurements and weight
Its transcutaneous electrical stimulation function offers an infallible form of acute and chronic pain relief through electrical impulses that block pain signals and promote the production of endorphins, making it ideal for treating the symptoms of arthritis, sciatica, muscle pain, joint pain and much more.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 4 Programmes
- Intensity: 15 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: 2 AAA Batteries
- Electrodes: 6 Pads
- Display: No display
- Size: 22cm x 13cm x 5cm - 417 gr
- Control from mobile app
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Includes user manual
- Improves joint mobility
- Portable and small size
- No display included
- Few types of programmes
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
With a size of 19 cm wide and 9 cm high, the WiTouch has the widest area of action on the market, with a current output strength of 0 - 110 mA for maximum effectiveness. It has a 2-button function that allows you to quickly change the device settings, and includes 3 reusable gel pads in the package you receive.
- Type: TENS
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 6 Modes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 4 gel electrodes
- Display: Touch
- Size: Not specified
- Improves joint mobility
- Improves blood circulation
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Wireless electrodes
- No intensity levels specified
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Not suitable for muscle hypertrophy
Its low intensity electric impulses offer a complete recovery of muscular and nervous pains, and its reusable electrodes have a superior quality adhesive gel, long lasting and easy to apply, so that each session can be carried out in a very simple way.
- Type: Combo (TENS+EMS)
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 15 Programmes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: 4 AAA
- Electrodes: 8 Pads
- Display: LCD
- Size: Not specified
- Improves blood circulation
- Includes 15 modes
- Independent control mode
- Reduces pain symptoms
- No rechargeable battery
- Does not specify intensity and size
It also has a session timer that allows you to control the duration of the therapies. You will be able to set the time of each session in an interval between 10 and 80 minutes. The package includes 1 electro stimulator, 4 sets of guide wires, 4 pairs of electrodes, 1 electrode case, 3 AAA batteries, 1 pad positioning guide and 1 user manual.
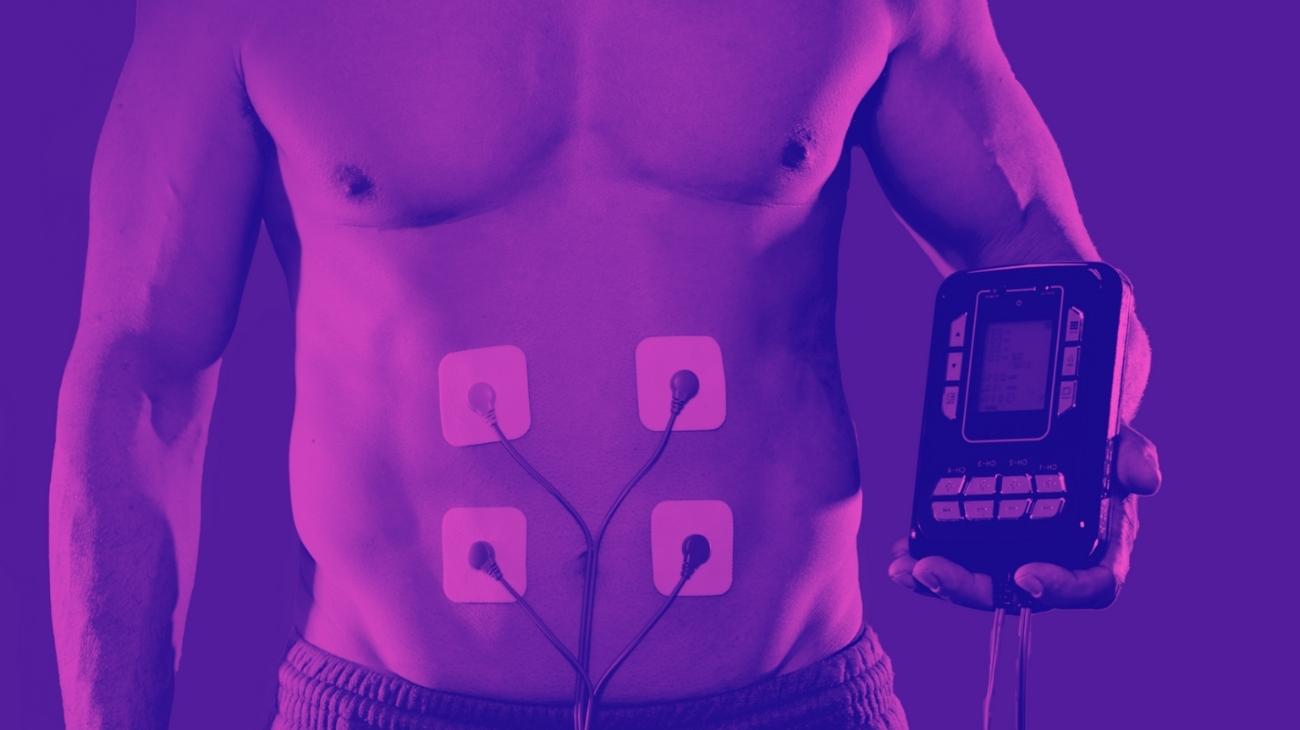
How to use EMS to strengthen muscles and prevent low back damage?
Although EMS is not intended for the treatment of symptoms of sciatic nerve injuries, it is possible to take advantage of its use on the muscles of the lower back to improve back stability and prevent future injuries
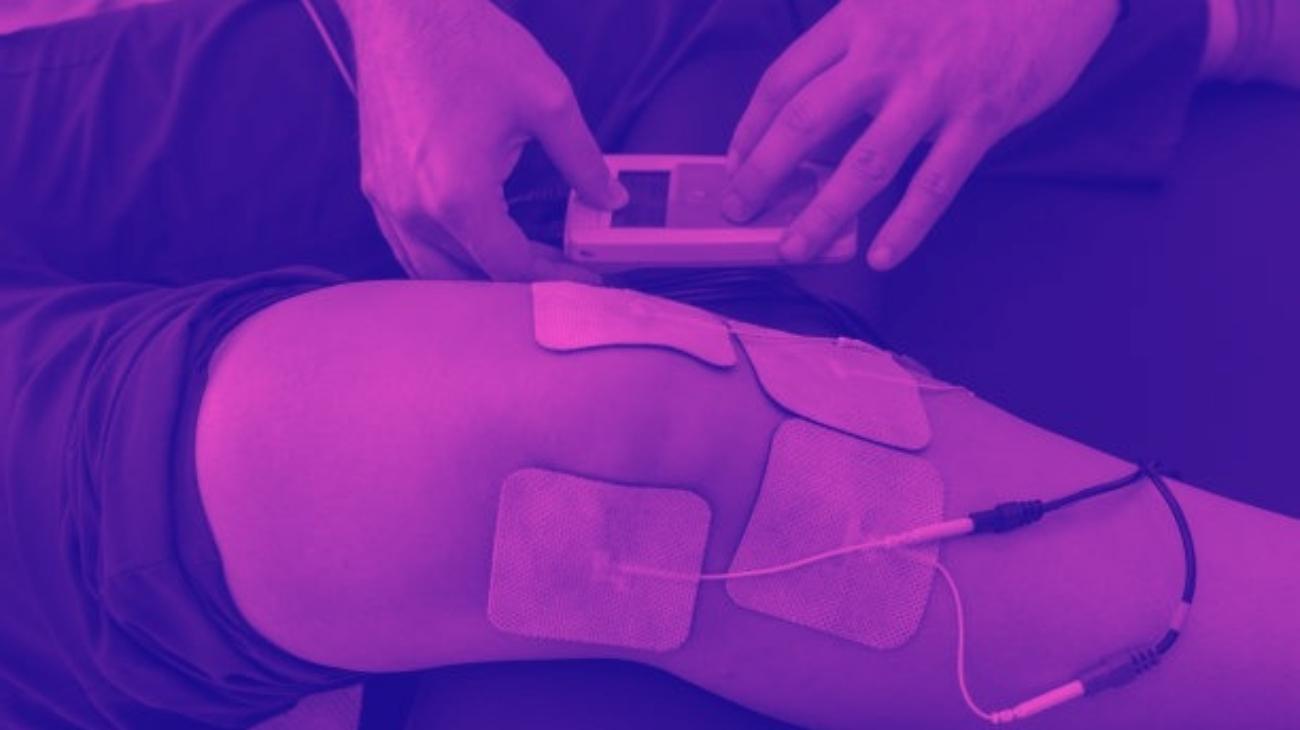
Where to place the electrodes?
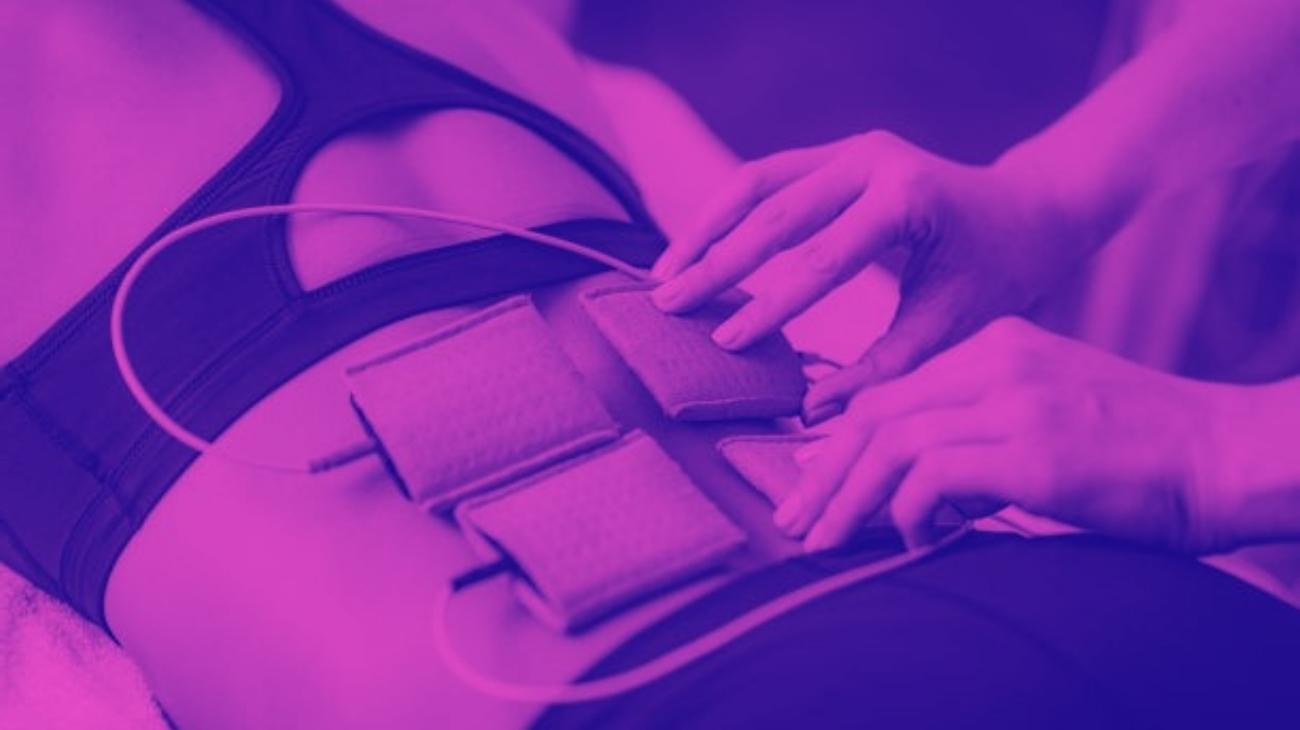
Unlike other areas of the body, the positioning of electrodes for lower back training is relatively simple, since the main location of the pads is the lumbar frame.
In this region, the electrodes should be positioned in pairs on each side of the spine, at the boundary between the thoracolumbar fascia and the erector spinae muscle, in order for the electrical impulses to cover both muscle groups.
What intensity to use?
The lower back muscles require a relatively low level of current compared to other muscles, since their strengthening does not require too intense a stimulus.
In the specific case of the erector spinae, oblique muscles and thoracolumbar fascia, the recommended intensity ranges from 60 to 85 Hz, depending on the individual's level of conditioning. Lower frequencies are usually applied in 60-second bursts to begin muscle adaptation to the contractions.
Subsequently, the intensity and frequency of the pulses can be increased as the user adapts.
Best EMS machines to prevent sciatica and low back pain
Conditioning the muscles of the lower back is especially important to protect the area from overuse injuries. To do this, it is necessary to make use of the appropriate machines. Among these we can highlight the following:
- Type: EMS
- Channels: 4
- Modes/Programs: 40 Programmes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable
- Electrodes: 4 electrodes
- Display: Digital
- Size: 15 x 34 x 30 cm; 200gr
- Wireless electrodes
- Includes user manual
- Prevents muscle atrophy
- Portable and small size
- Includes carrying bag
- No heat therapy
- No battery life specified
- No intensity levels specified
It features MI tracking technology, which allows the SP 8.0 to perform a quick automatic muscle scan, and set the appropriate program according to the goal you want to achieve. This professional-grade training device will revolutionize the way you exercise, as it is designed for athletes who practice their discipline on a daily basis.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Not specified
- Modes/Programs: Not specified
- Intensity: 20 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium (up to 8 hours)
- Electrodes: 2 Pads
- Display: -
- Size: Not specified
- Improves blood circulation
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Wireless Device
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- Reduces pain symptoms
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- No display included
- Modes/programs not specified
It has a rechargeable battery that provides an autonomy of up to 8 hours, and more than 1000 charges. You can charge it through its USB port, by means of the cable included in the package. In addition, you will find the mini electrostimulation unit, 1 butterfly electrode, 2 self-adhesive electrodes of 2x5 cm, 1 user manual and several guides for positioning the unit.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: -
- Modes/Programs: 15 Programs
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable Lithium
- Electrodes: 4 Pads
- Display: No display
- Size: Not specified
- TENS+EMS combo
- Control from mobile app
- Rechargeable battery
- Includes user manual
- Reduces pain symptoms
- No battery life specified
- No intensity levels specified
- Does not specify dimensions and weight
The simple interface of the PowerDot app will guide you through everything you need to know to operate the electrodes efficiently. The purchase package includes 2 pre-loaded pods, 2 sets of electrodes with corresponding pads, 2 sets of cables and 2 micro USB charging cables, along with a carrying case so you can take your electrodes with you wherever you go.
- Type: Combo (TENS+EMS)
- Channels: 4
- Modes: 30 Programmes
- Intensity: Not specified
- Wireless: No
- Heat therapy: No
- Battery: Rechargeable (10 hours of use)
- Electrodes: 16 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- 16 electrodes
- Rechargeable battery
- Portable device
- 30 different programmes
- No indication of size and weight
- No intensity specified
Its 4-channel function gives you the ability to apply 4 different therapies through 8 electrodes pads to different areas of the body, allowing you to treat them simultaneously with a specific mode of use for each area. Additionally, its long-lasting rechargeable battery will give you an autonomy of up to 10 continuous hours of use, and can be recharged a minimum of 1,000 times.
- Type: Combo
- Channels: Dual
- Modes/Programs: 5 Programs
- Intensity: 99 Levels
- Wireless: Yes
- Heat Therapy: No
- Battery: 2 AA Batteries
- Electrodes: 2 Pads
- Display: Digital
- Size: Not specified
- Improves blood circulation
- Accelerates recovery from sports injuries
- TENS+EMS Combo
- Portable and small size
- Good quality
- Does not specify measurements and weight
- Few types of programmes
- No heat therapy
The Alivia brand also has a specialized toning program for the pelvic floor that will allow you to strengthen this area with only 20 minutes of daily use, and has an innovative open circuit detection system that will calibrate the intensity of the electrical impulses to 0 if one of the electrodes becomes detached from the skin, protecting you against electric shocks.
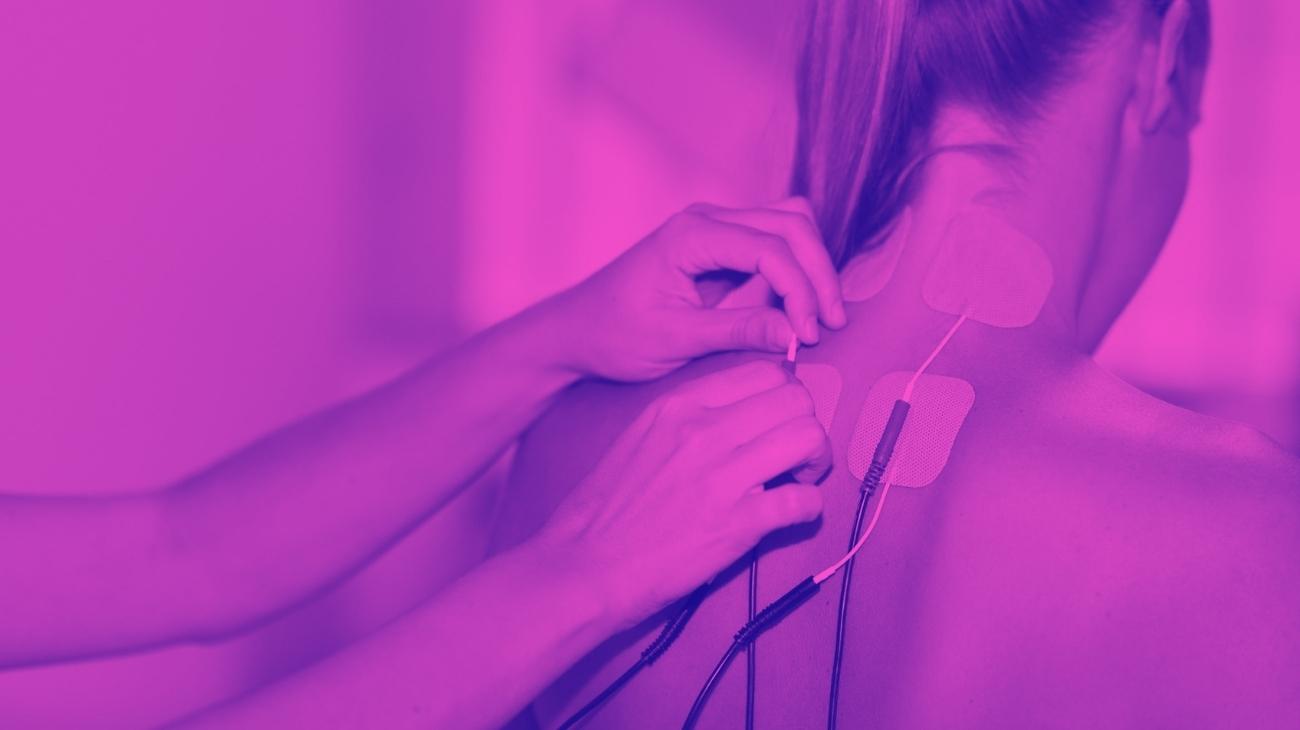
Video: How to place electrodes pads on the back?
Electrodes for back
More types of EMS stimulators and TENS machines you should know about
What is sciatica or lumbago and what are the causes?
Sciatica is a term that refers to a pain that covers the area that runs along the sciatic nerve, from the lower back, through the buttocks and ending in the legs. Usually, it is an ailment that affects only one side of the body.
The main cause of sciatica occurs due to the pinching of the sciatic nerve, which can be caused by factors such as those described below:
- Herniated disc: a herniated disc in the lower back can put pressure on the sciatic nerve, causing pain and numbness.
- Bone overgrowth: Bone spurs are very common in the spine, and can cause low back pain when they come in contact with the sciatic nerve.
- Tumors: on rare occasions, a tumor may appear in the lumbar area and produce a pinching of the sciatic nerve, causing pain.
- Nerve damage: certain diseases such as diabetes can cause damage to the sciatic nerve and generate a sensation of pain that can last for a long time.
What are the most common types of back injuries?
Throughout our lives, there are an enormous number of factors that can alter the condition of the back in its entirety. However, one of the most vulnerable areas is the lumbar area, which can be affected in the long term by poor standing position or heavy lifting, among many other factors.
These situations can cause a wide variety of diseases and ailments, among which the following stand out:
- Low back pain: is a pain located in the lower back that is highly related to the muscle and bone structure of the spine, can cause stiffness, difficulty of movement and pain of varying intensity. Its main causes are muscular overload, degeneration of the intervertebral disc and alterations of the vertebral structure, among others.
- Scoliosis: consists of a lateral deviation of the spine that can cause disparity of the hip, scapula or shoulders, muscle contractures and generalized pain in the back. It may present as a congenital condition or as a neuromuscular disorder.
- Herniated lumbar disc: A herniated disc is caused by wear and tear of the intervertebral discs that cushion the collision of the vertebrae during movement causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, tingling and weakness. Factors such as age, weight and genetics can increase the possibility of suffering from herniated discs.
- Impingement: Impingement low back pain occurs when there is acute compression of the sciatic nerve by adjacent tissue. It can produce numbness, weakness, stiffness and severe pain. This condition is caused by overuse, accidents, sedentary lifestyle or osteoarthritis, among other causes.
- Arthrosis: it is produced by the degeneration of the cartilaginous tissue of the lumbar area of the spine. This degeneration produces limited mobility, stiffness and acute pain. It may be caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors, or by trauma, infection or congenital malformation.
- Sciatica: it is a generally unilateral pain that is produced by pressure, pinching or degeneration of the sciatic nerve, it can cause variable pain and extend from the lumbar area to the leg.
Differences between TENS and EMS: Which is better for treating sciatica and low back pain?
TENS and EMS electrostimulation therapies are widely used in the field of physiotherapy due to their effectiveness in their respective areas. Although both work with electrical impulses, these are programmed with different intensities and frequencies, giving both therapies unique characteristics and functions.
To begin with, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is a therapy oriented to the treatment of pain that is defined by the following characteristics:
- It uses low intensity electrical impulses, between 1 and 250 Hz.
- It numbs the nerve endings of the sciatic nerve and the terminal branches of the lumbar nerves, thus attenuating the sensation of pain and generating relief in the patient.
- It is used only for the treatment of symptoms of injuries and diseases. It is not a method to cure injuries.
EMS or Electro Muscular Stimulation, on the other hand, is a physical conditioning and rehabilitation method used in physiotherapy and high competition sports, which has the following characteristics:
- The intensity of its discharges varies between 70 and 150 Hz.
- It is used in muscle training and conditioning.
- It increases the strength, resistance and elasticity of the muscles by means of contractions caused by electrical impulses.
- It is not recommended for the treatment of painful injuries.
The best therapy to treat pain caused by alterations in the sciatic nerve is TENS stimulation therapy, since its frequency exerts an effect on the sciatic nerve endings and the ramifications of the lumbar spinal nerve that innervates part of the quadratus lumborum muscle, the iliopsoas muscle and the obturator externus. This effect is the release of endorphins and the suppression of the cells that produce pain, causing a feeling of relief in the patient.
On the other hand, EMS therapy is contraindicated for the treatment of sciatic nerve pain, since the muscle contractions caused by its electrical discharges can increase pain in the affected area and produce other adverse results.